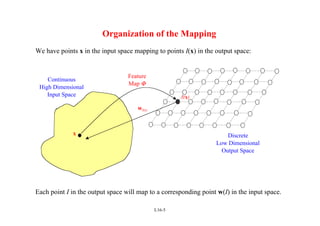
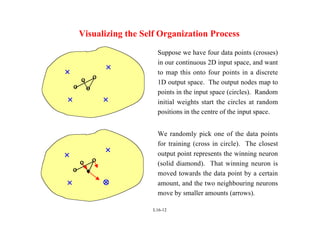
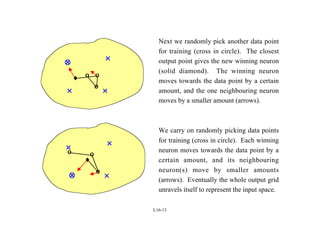
Self Organizing Maps (SOMs) are a type of neural network that uses unsupervised learning to map high-dimensional input data to a low-dimensional discrete map. SOMs learn the topological relationships in the training data and organize themselves through competition between neurons to become selectively tuned to different input patterns. The algorithm involves initializing weights, finding a winning neuron for each input, and updating the weights of the winning neuron and its neighbors to more closely match the input. Repeated iterations of this process cause the neurons to self-organize the input space onto the map in a topologically ordered fashion.