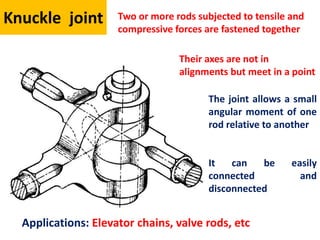
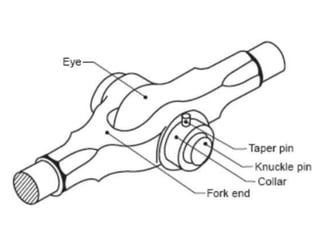
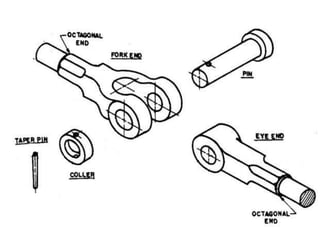
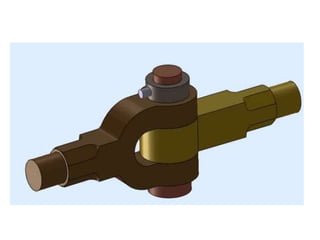
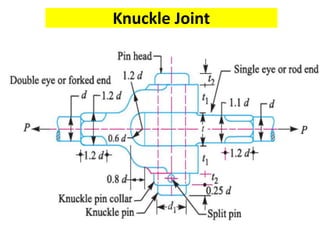
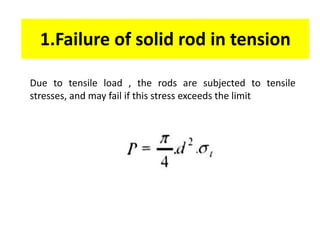
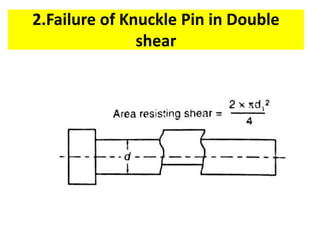
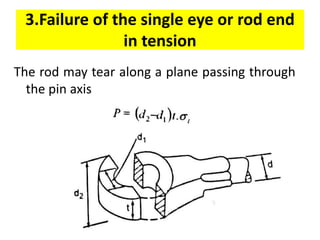
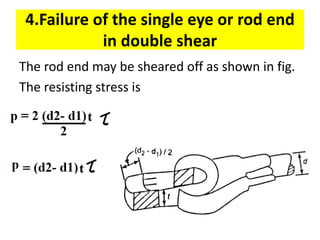
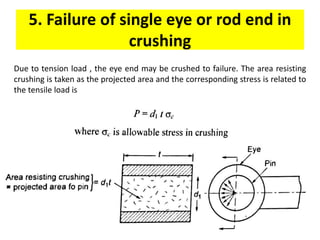
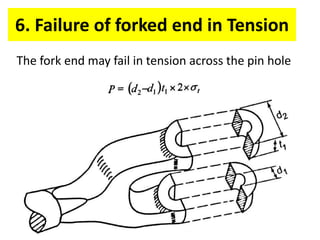
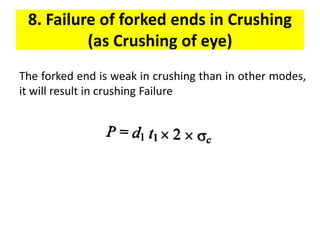
A knuckle joint connects two rods under tensile loads. It consists of a forked or double eye rod, a single eye rod, and a knuckle pin. The joint allows a small angular movement of one rod relative to the other. Applications include elevator chains and valve rods. It allows rods subjected to tensile and compressive forces to connect and disconnect while accommodating some angular movement.