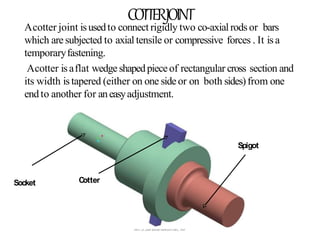
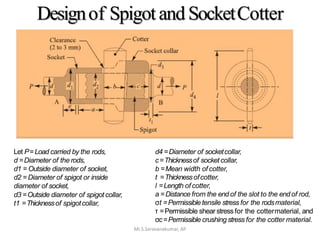
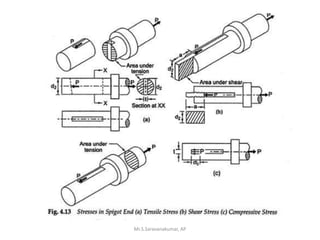
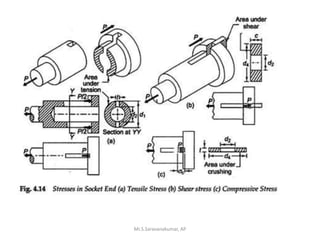
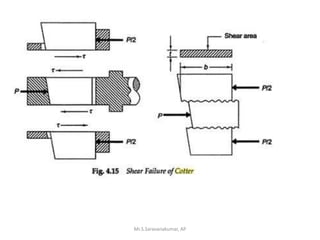
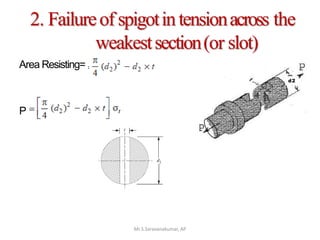
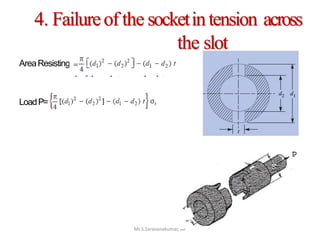
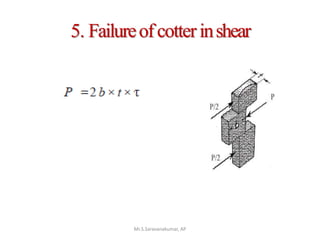
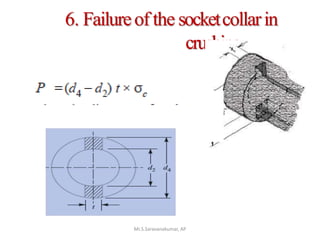
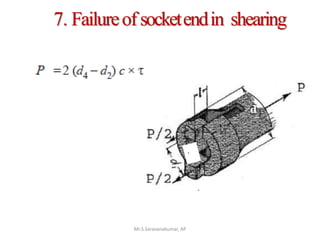
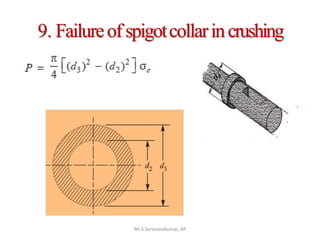
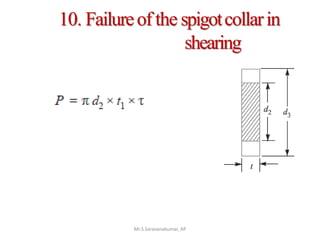
This document discusses the design of a socket and spigot cotter joint. A cotter joint is used to rigidly connect two coaxial rods subjected to axial tensile or compressive forces. It consists of a tapered wedge-shaped cotter that fits into slots in the spigot and socket. The document outlines various failure modes of the joint and provides examples of sizing a cotter joint to withstand specified loads.