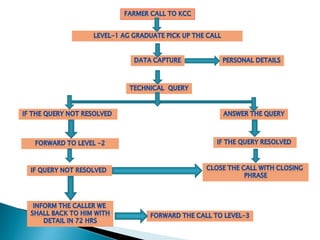
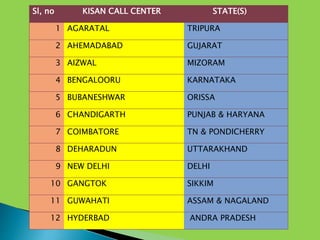
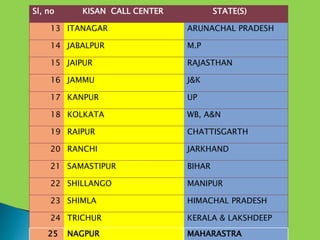
The document discusses individual contact methods used by extension workers to communicate directly with farmers. It describes methods like farm/home visits, phone calls, SMS, flags, letters, email and video calls. It then provides statistics on India's rural/urban population and growth of telecom access. A key program discussed is the Kisan Call Center, launched in 2004 to provide extension services to farmers via a toll-free phone line. The call center infrastructure and operations are explained, along with the role of different levels in responding to farmer questions.