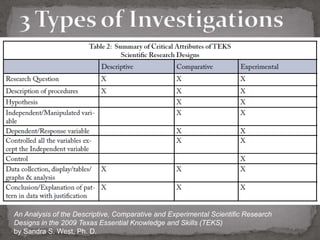
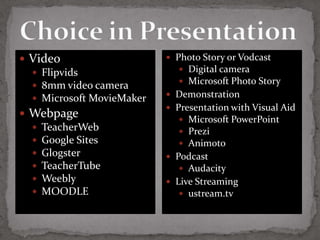
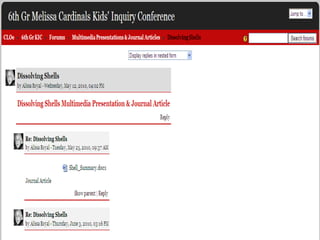
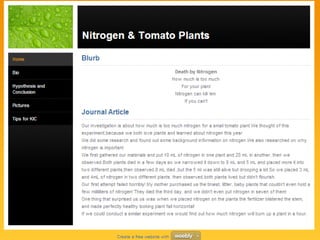
The document discusses the transformation of the science fair experience into a Kids' Inquiry Conference, emphasizing the development of scientific literacy among students through inquiry-based learning and various forms of presentation. It details the planning stages, types of investigations, and resources available to support students in presenting their scientific inquiries. The goal is to foster authentic experiences and collaboration while integrating technology for effective communication and presentation skills.