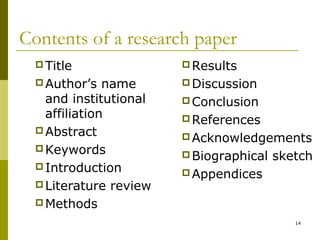
This document provides an overview of publishing research. It discusses writing for publishing, finding publishing avenues, the review process, publishing from theses, online publishing, self-publishing, promoting publications, and ethical and legal issues. The presenter, Prof. Dr. Khalid Mahmood, provides his own publishing case study as an example, having published over 100 journal articles and books in various countries.