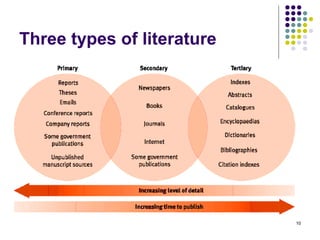
This document outlines an agenda for a literature review workshop led by Prof. Dr. Khalid Mahmood. The workshop covers topics such as searching for print and online sources, evaluating sources, reading critically, analyzing and synthesizing findings, writing and presenting literature reviews, and avoiding plagiarism. Training methods include lectures, question/answer sessions, sharing experiences, and discussing participants' research projects. The document defines a literature review and explains its purposes such as defining problems, placing studies in context, avoiding duplication, and suggesting hypotheses. It also distinguishes between narrative, systematic and meta-analysis types of literature reviews.