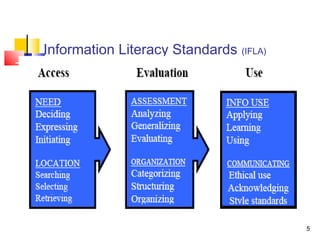
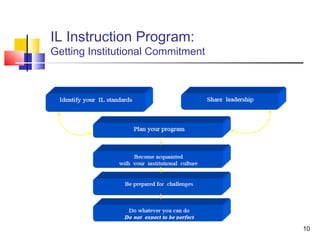
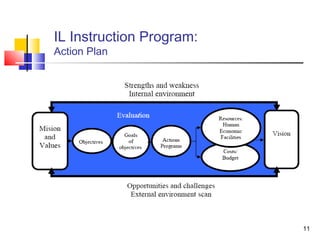
This document discusses information literacy and its importance as a 21st century survival literacy. It defines information literacy as the ability to recognize when information is needed and to locate, evaluate, and effectively use that information. The document outlines several standards and frameworks for information literacy from organizations like IFLA, ACRL, and Unesco. It also discusses developing an information literacy instruction program in higher education, including getting institutional commitment, creating an action plan, and instruction management. Finally, it provides resources for further information on information literacy.