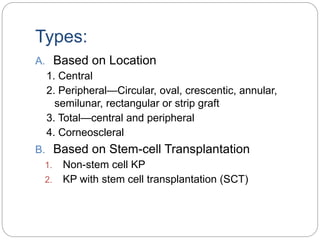
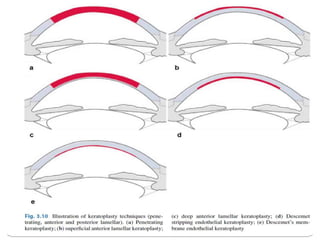
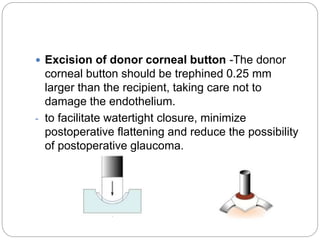
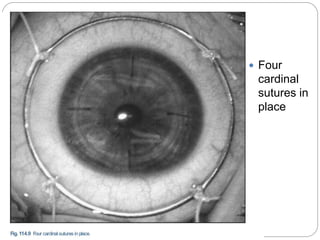
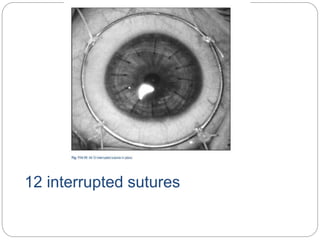
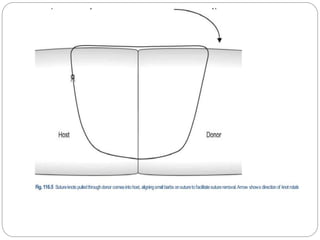
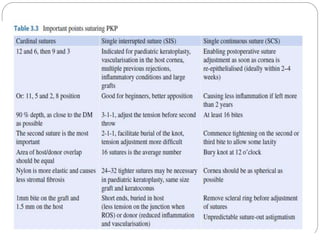
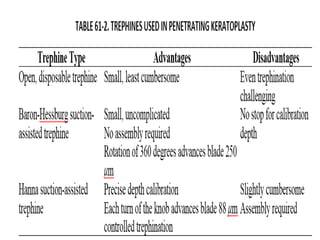
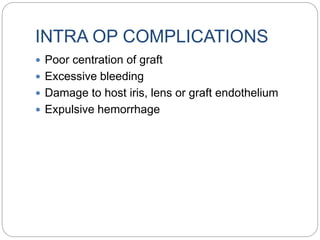
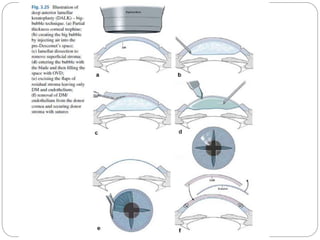
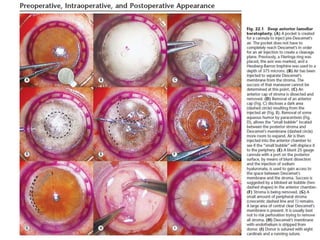
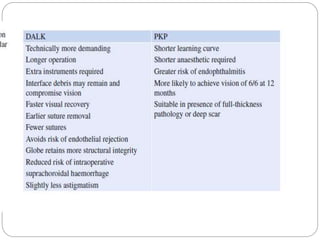
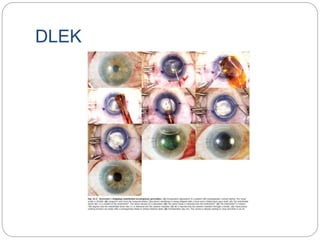
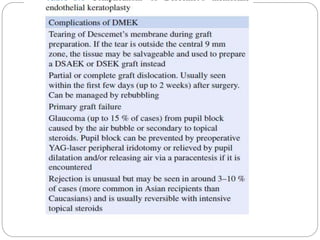
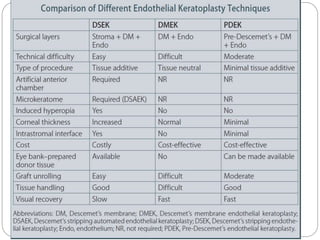
Keratoplasty involves replacing diseased cornea with donor tissue. The main types are penetrating keratoplasty (PK), which replaces the full corneal thickness, and lamellar keratoplasty, which replaces only diseased layers. PK indications include scarring, infections, dystrophies and injuries. It has risks of rejection, infection, and high astigmatism. Newer techniques like deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK) and Descemet's membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) replace only diseased layers, reducing risks. Careful donor screening, surgical technique and postoperative management including steroids can reduce complications of keratoplasty.