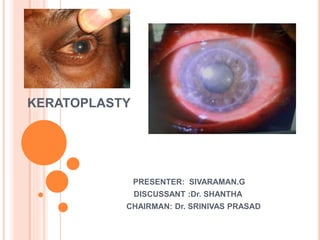
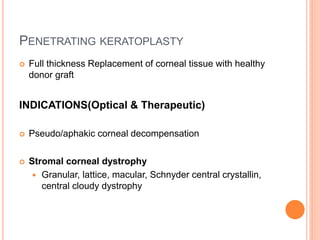
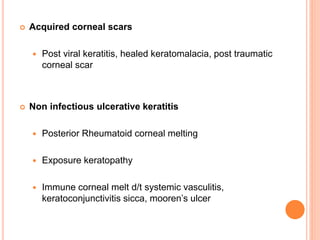
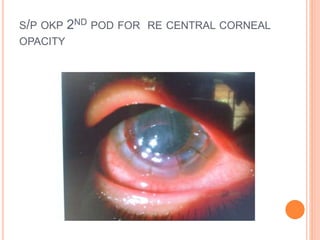
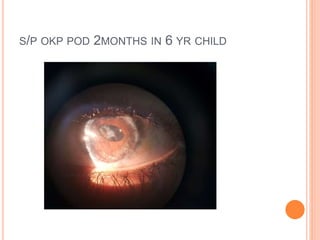
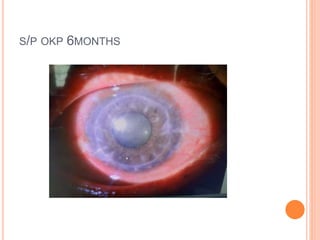
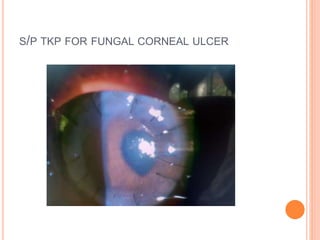
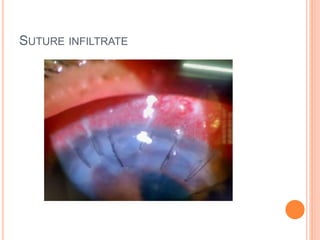
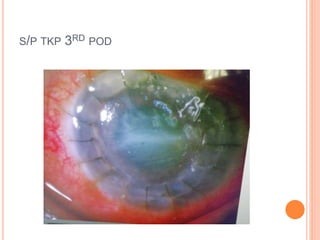
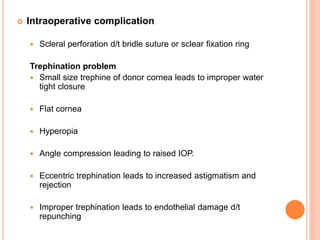
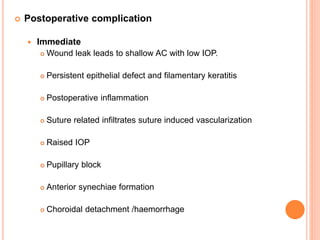
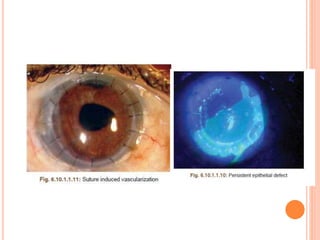
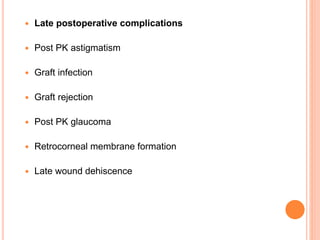
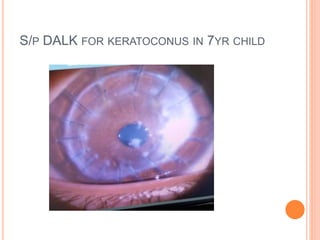
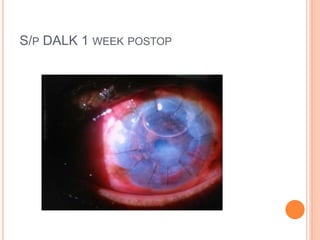
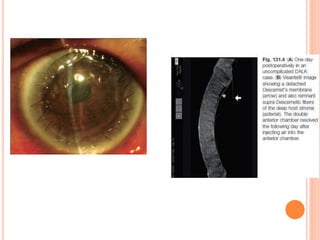
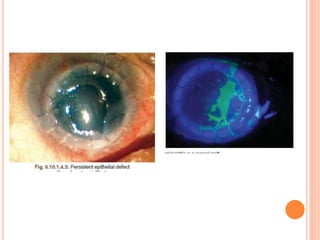
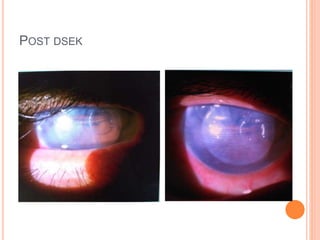
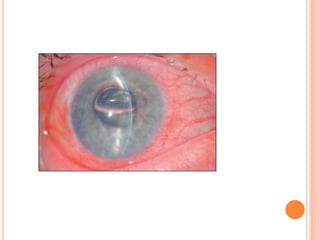
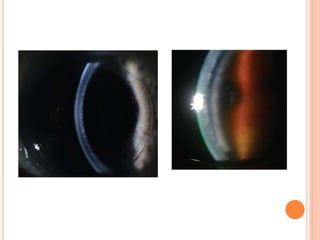
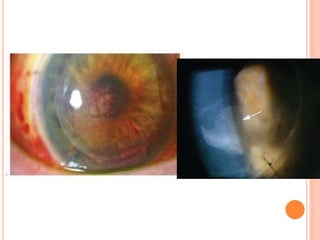
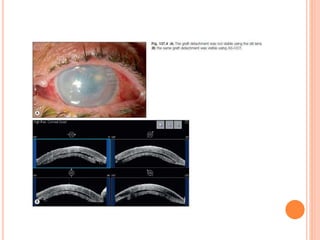
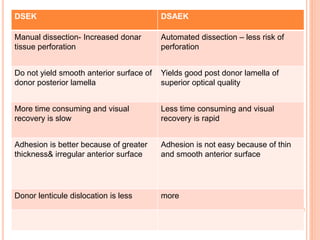
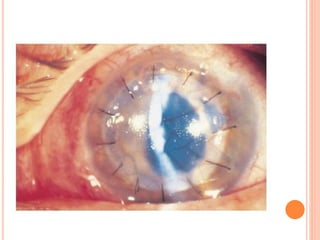
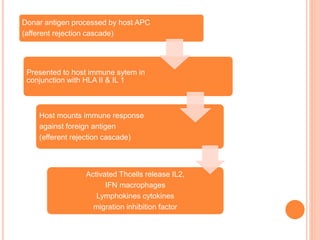
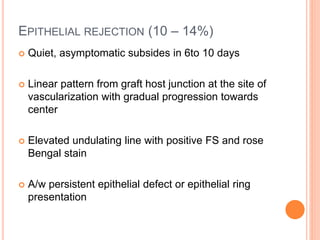
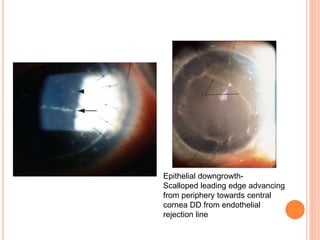
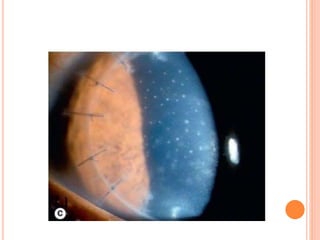
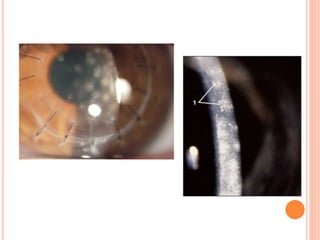
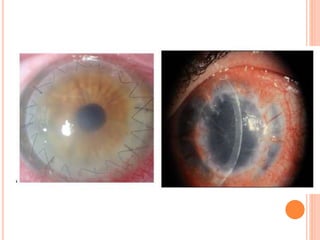
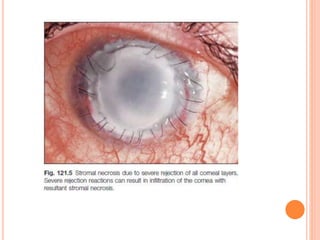
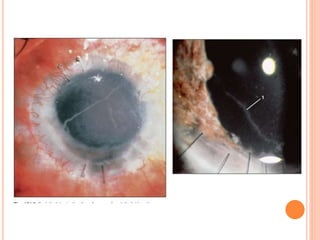
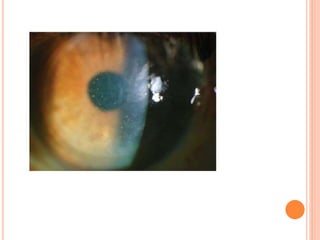
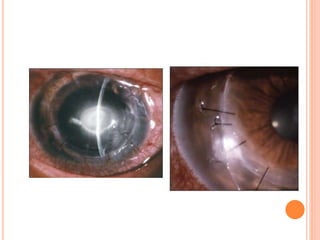
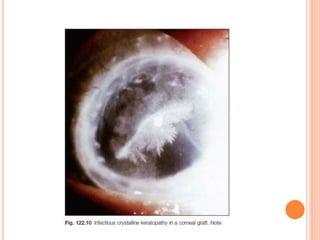
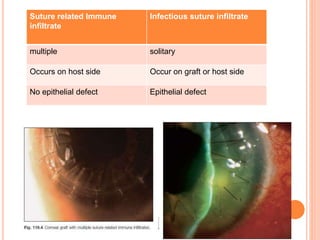
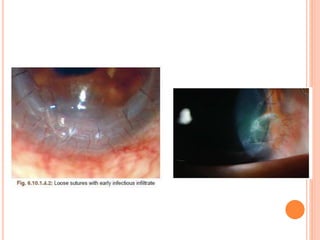
The document provides an extensive overview of keratoplasty, detailing its definitions, types, indications, preoperative evaluations, and potential complications involved. It discusses various keratoplasty techniques, including penetrating, anterior lamellar, and posterior lamellar surgeries, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it addresses the issues of corneal graft rejection, failure, and the management of postoperative complications.