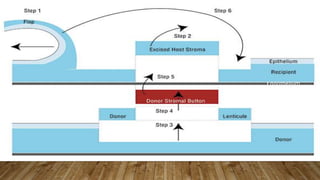
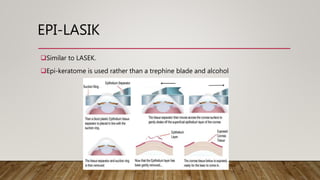
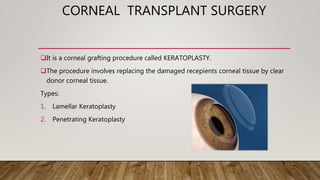
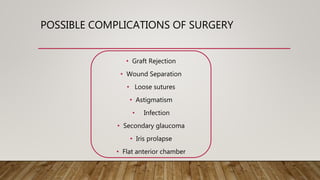
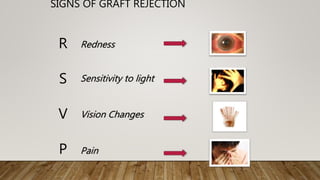
This document discusses corneal surgery, including corneal refractive surgery and corneal transplant surgery. It describes the different types of corneal refractive surgery, which include flap surgery techniques like LASIK and surface procedures like PRK. Corneal transplant surgery, also called keratoplasty, is described as replacing damaged corneal tissue with healthy donor tissue. The common techniques used are penetrating keratoplasty and lamellar keratoplasty. The document outlines the donor corneal preparation and storage methods, as well as the surgical techniques and potential complications of corneal transplant surgery.