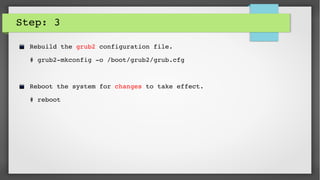
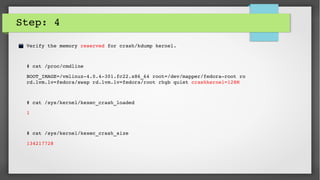
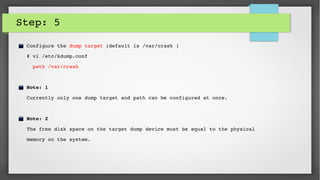
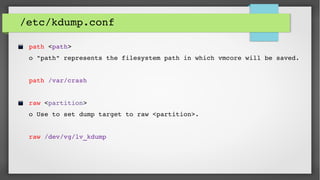
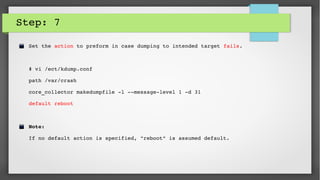
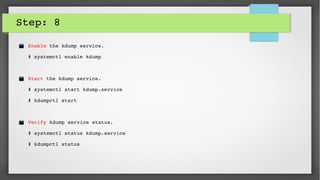
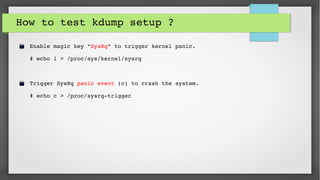
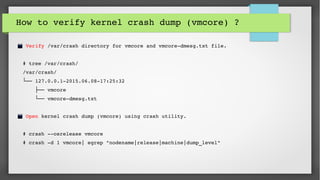
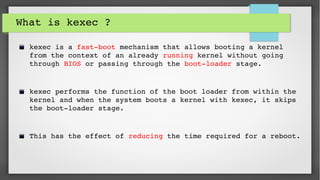
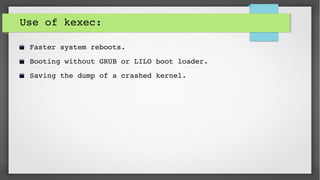
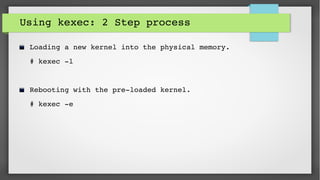
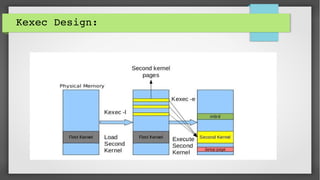
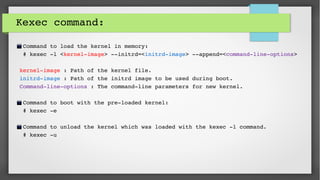
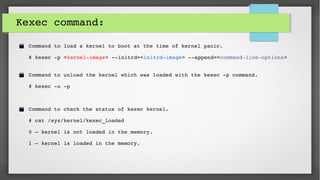
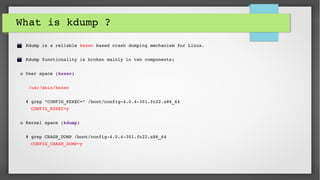
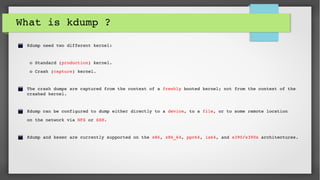
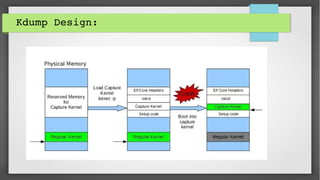
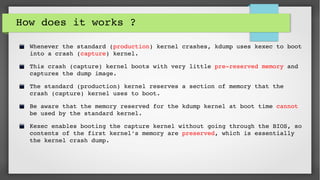
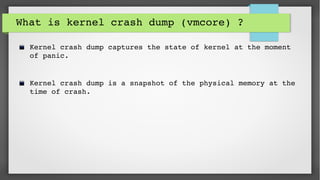
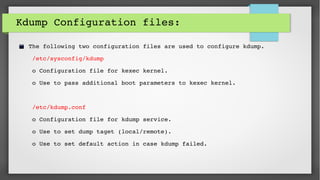
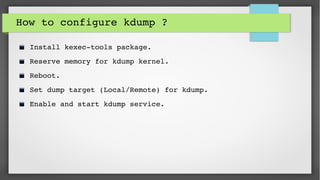
This document provides an introduction to kdump and kernel crash dump analysis. It discusses kexec, which allows fast rebooting by loading a new kernel from an already running kernel. Kdump uses kexec to boot a capture kernel to analyze the state of a crashed production kernel and capture a vmcore dump file. The document outlines how to configure kdump by reserving memory, setting the dump target, enabling the kdump service, and testing a crash. Kernel crash dumps can be analyzed using the crash utility to help debug issues.




![Step: 2
Set kernel boot parameter "crashkernel" to reserve memory for crash/kdump kernel.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=fedora/swap rd.lvm.lv=fedora/root rhgb quiet
crashkernel=128M"
The size of crashkernel depends on;
o Machine Architecture.
o Total amount of installed system memory.
o [128 MB + 4 bits for every 4KB page]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e4cfa623-7815-4ad3-a8af-89f887fb7067-150702140016-lva1-app6891/85/Kdump-FUDcon-2015-Session-22-320.jpg)