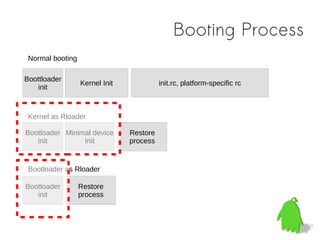
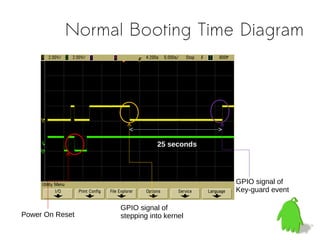
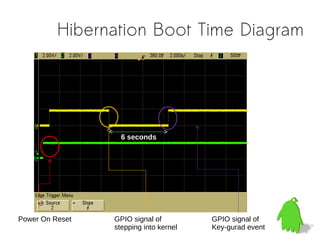
The document discusses approaches to reduce boot times for ARM Linux devices by implementing technologies like rloader and hibernation. It highlights key methods for measuring boot time, optimizing bootloader processes, and different software hibernation technologies. The content is aimed at improving user experiences in various devices including smartphones and tablets, illustrating challenges and potential solutions.