The document outlines the process of developing kernel modules using the Extensible SDK (esdk) within the Yocto Project framework. It covers the integration of these modules into the kernel, compares the advantages and disadvantages of placing modules inside or outside the kernel tree, and describes the steps required to build and deploy a kernel module. Additionally, it provides guidance on automatic loading of modules at system boot and includes code examples for practical application.













![18 Yocto Project | The Linux Foundation
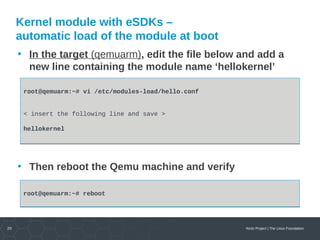
Kernel module with eSDKs – load the module
• In the target (qemuarm), load the module and observe
the results
root@qemuarm:~# depmod -a
root@qemuarm:~# modprobe hellokernel
[ 874.941880] hellokernel: loading out-of-tree module taints kernel.
[ 874.960165] When half way through the journey of our life
root@qemuarm:~# lsmod
Module Size Used by
hellokernel 929 0
nfsd 271348 11
root@qemuarm:~# depmod -a
root@qemuarm:~# modprobe hellokernel
[ 874.941880] hellokernel: loading out-of-tree module taints kernel.
[ 874.960165] When half way through the journey of our life
root@qemuarm:~# lsmod
Module Size Used by
hellokernel 929 0
nfsd 271348 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yoctodevdayadvancedclassprague9slideshare-171112092728/85/Yocto-Project-Dev-Day-Prague-2017-Advanced-class-Kernel-modules-with-eSDK-18-320.jpg)
![19 Yocto Project | The Linux Foundation
Kernel module with eSDKs – unload the module
• In the target (qemuarm), unload the module
root@qemuarm:~# modprobe -r hellokernel
[ 36.005902] I found that I was in a gloomy wood
root@qemuarm:~# lsmod
Module Size Used by
nfsd 271348 11
root@qemuarm:~# modprobe -r hellokernel
[ 36.005902] I found that I was in a gloomy wood
root@qemuarm:~# lsmod
Module Size Used by
nfsd 271348 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yoctodevdayadvancedclassprague9slideshare-171112092728/85/Yocto-Project-Dev-Day-Prague-2017-Advanced-class-Kernel-modules-with-eSDK-19-320.jpg)