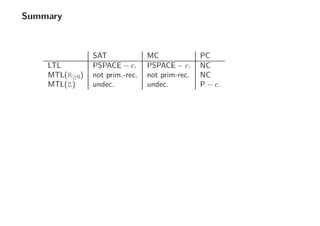
This document discusses temporal logics for verification including Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) and Metric Temporal Logic (MTL) and their applications to different models like words, timed words, and data words. It introduces the syntax and semantics of LTL, MTL, and extensions of MTL to these different models. It also discusses different decision problems like satisfiability, model checking, and path checking for these logics and complexity results for different classes of structures. Finally, it advertises an open call for a research training group on quantitative logics and automata.


![Verification Problems for LTL
The Satisfiability Problem
Given: An LTL formula
Question: Does there exist a word that satisfies the formula?
The Model Checking Problem
Given: An LTL formula, and an abstract model that generates/recognizes words
Question: Does every word generated/recognized by the model satisfy the formula?
The Path Checking Problem
Given: An LTL formula, a word
Question: Does the word satisfy the formula?
- Satisfiability and model checking of Kripke structures is PSPACE-complete
[Sistla & Clarke, 1985]
- Path checking for LTL is in NC [Kuhtz & Finkbeiner, 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesshort-150305091902-conversion-gate01/85/Karin-Quaas-4-320.jpg)
![Verification Problems for MTL over Timed Words
The Satisfiability Problem
Given: An MTL formula
Question: Does there exist a timed word that satisfies the formula?
The Model Checking Problem
Given: An MTL formula, and a timed automaton (recognizing timed words)
Question: Does every timed word recognized by the timed automaton
satisfy the formula?
The Path Checking Problem
Given: An MTL formula, a timed word
Question: Does the timed word satisfy the formula?
- Satisfiability is EXPSPACE-complete for timed words over N
[Alur & Henzinger, 1993]
- Satisfiability and model checking is decidable [Ouaknine & Worrell, 2005]
- Path checking for MTL is in NC [Bundala & Ouaknine, 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesshort-150305091902-conversion-gate01/85/Karin-Quaas-6-320.jpg)



![Verification Problems for MTL over Data Words
The Satisfiability Problem
Given: An MTL formula
Question: Does there exist a data word that satisfies the formula?
The Model Checking Problem
Given: An MTL formula, and a one-counter machine (simulating data words)
Question: Does every run of the one-counter machine satisfy the formula?
The Path Checking Problem
Given: An MTL formula, a data word
Question: Does the data word satisfy the formula?
- Model checking is undecidable, decidable for deterministic one-counter
machines [Q, 2013]
- Satisfiability is undecidable [Carapelle, Feng, Gil, & Q 2014]
- Path checking for MTL is in P-complete [Feng, Lohrey, & Q, 2015 (not pub.)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidesshort-150305091902-conversion-gate01/85/Karin-Quaas-11-320.jpg)