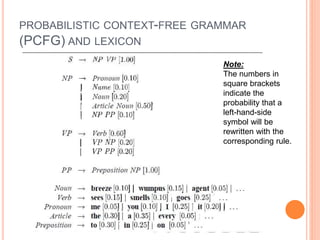
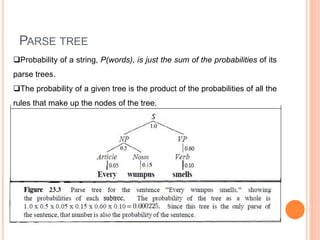
This document discusses various probabilistic language models used in natural language processing applications. It covers n-gram models like bigram and trigram models used for tasks like speech recognition. It describes how probabilistic language models assign probabilities to strings of text based on counting word occurrences. It also discusses techniques like additive smoothing and linear interpolation that are used to handle zero probability word pairs in n-gram models. Finally, it introduces probabilistic context-free grammars which use rewrite rules with associated probabilities to model language structure.









![VITERBI EQUATION
It takes as input a unigram word probability
distribution, P(word), and a string.
Then, for each position i in the string, it stores in
best[i] the probability of the most probable string
spanning from the start up to i.
It also stores in words[i] the word ending at
position i that yielded the best probability.
Once it has built up the best and words arrays in a
dynamic programming fashion, it then works
backwards through words to find the best path.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5aiapplications-210916100710/85/Artificial-Intelligence-10-320.jpg)