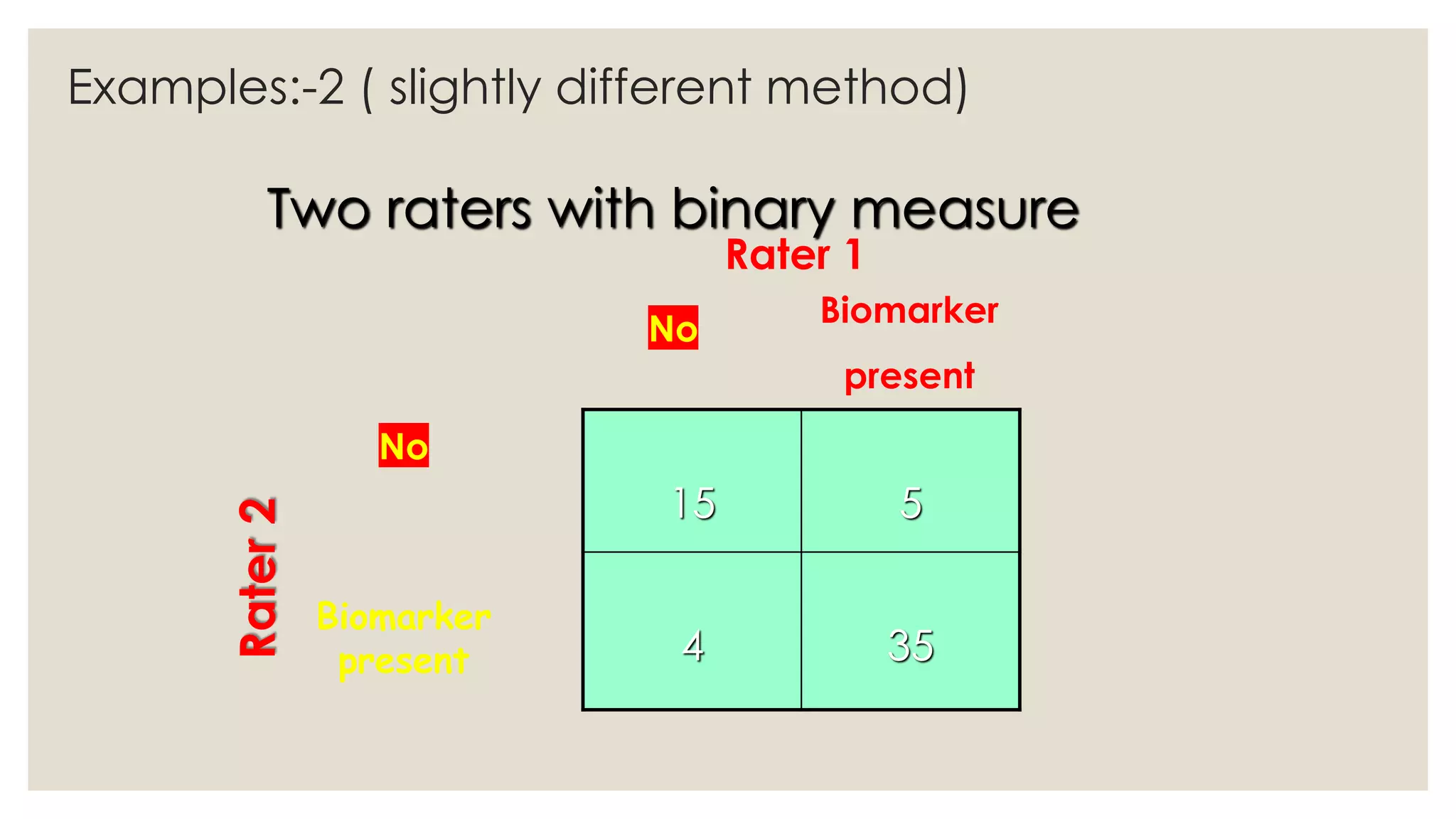
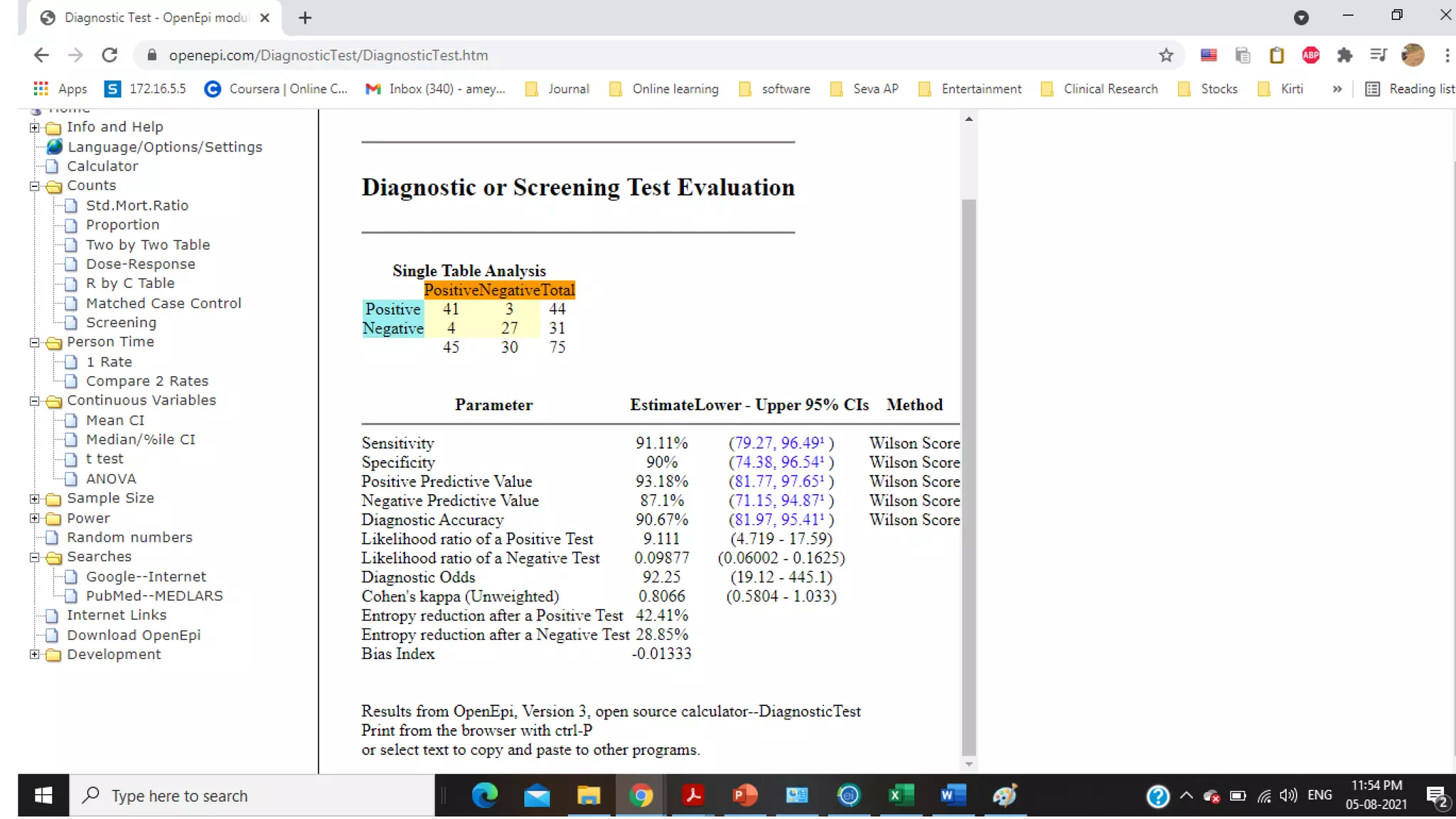
This document discusses kappa statistics, which measure interrater reliability beyond chance agreement. Kappa statistics are useful when multiple raters are interpreting subjective data, such as radiology images. The kappa statistic formula calculates observed agreement between raters compared to expected chance agreement. Examples show how to calculate kappa when two raters are assessing whether a biomarker is present or absent in samples. Confidence intervals for kappa are determined using 1.96 as a constant to generate a 95% confidence level.


![Kappa- agreement
◦ Without good agreement results are difficult to interpret
◦ Measurements are unreliable or inconsistent
◦ Need measures of agreement - kappa
◦ Remember-
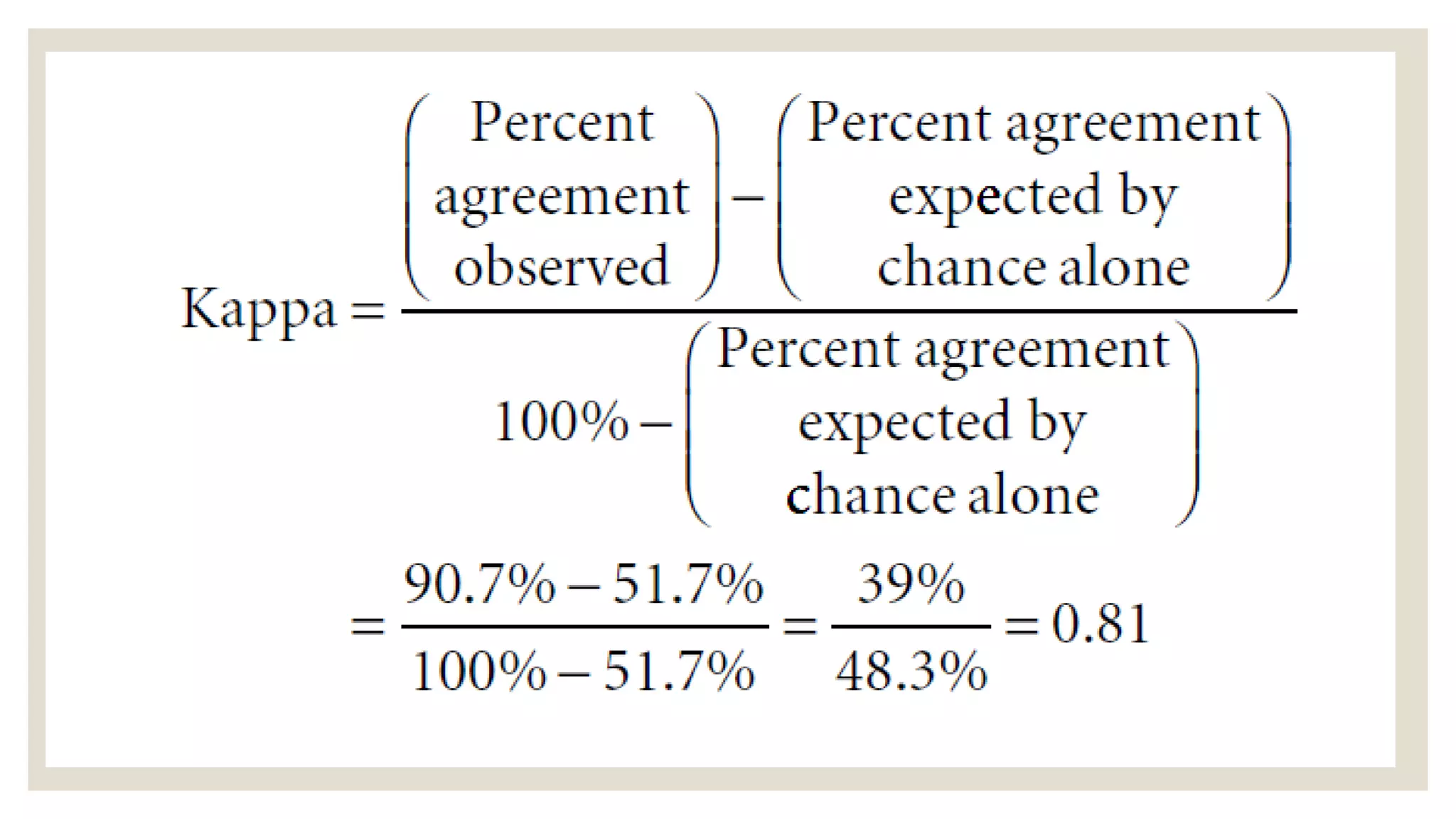
Extent to which the observed agreement exceeds that which would be expected by
chance alone (i.e., percent agreement observed − percent agreement expected by
chance alone) [numerator] relative to the maximum that the observers could hope to
improve their agreement (i.e., 100% − percent agreement expected by chance alone)
[denominator].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ameydhatrak-kappa-210813121008/75/Kappa-statistics-3-2048.jpg)