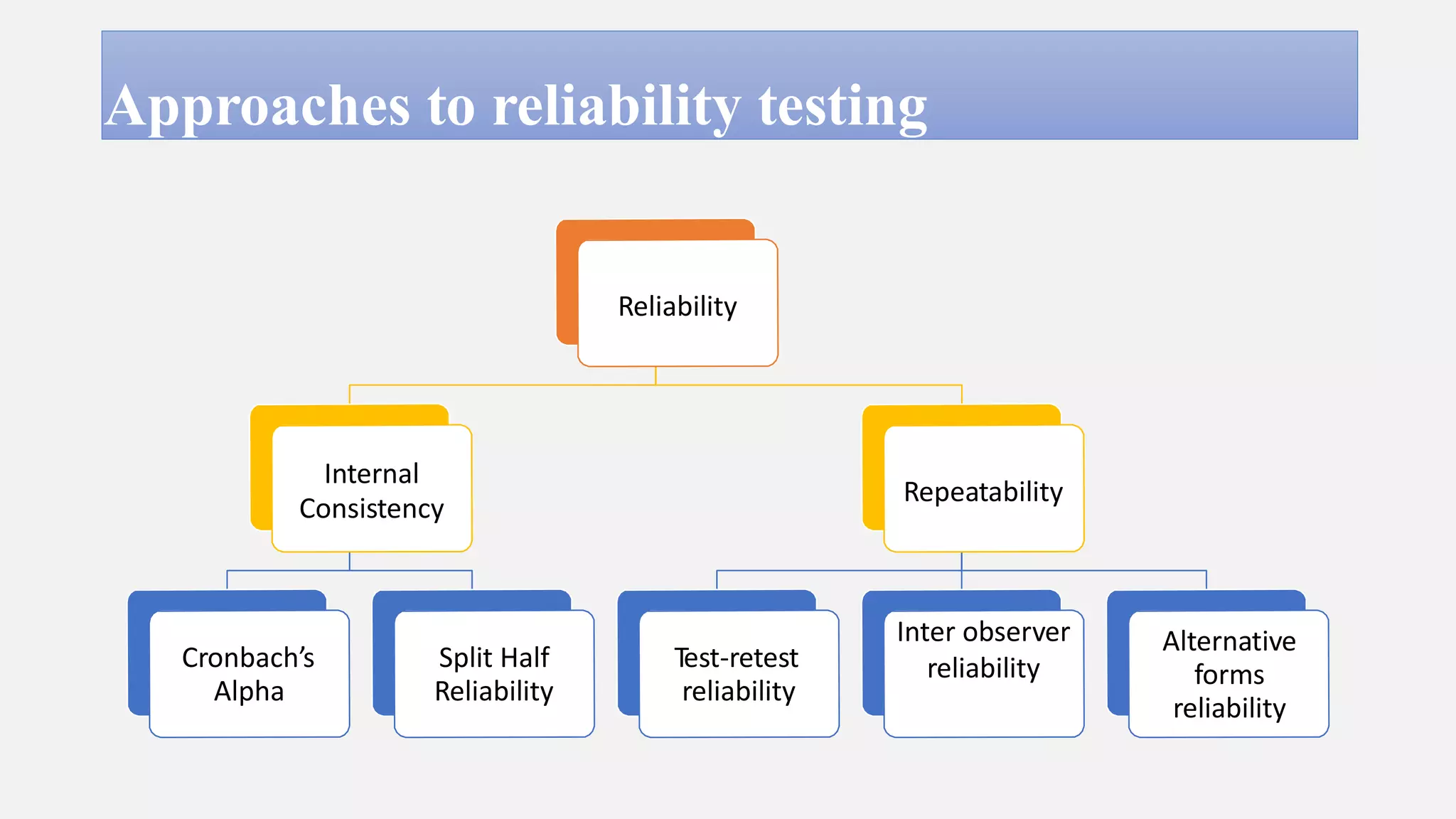
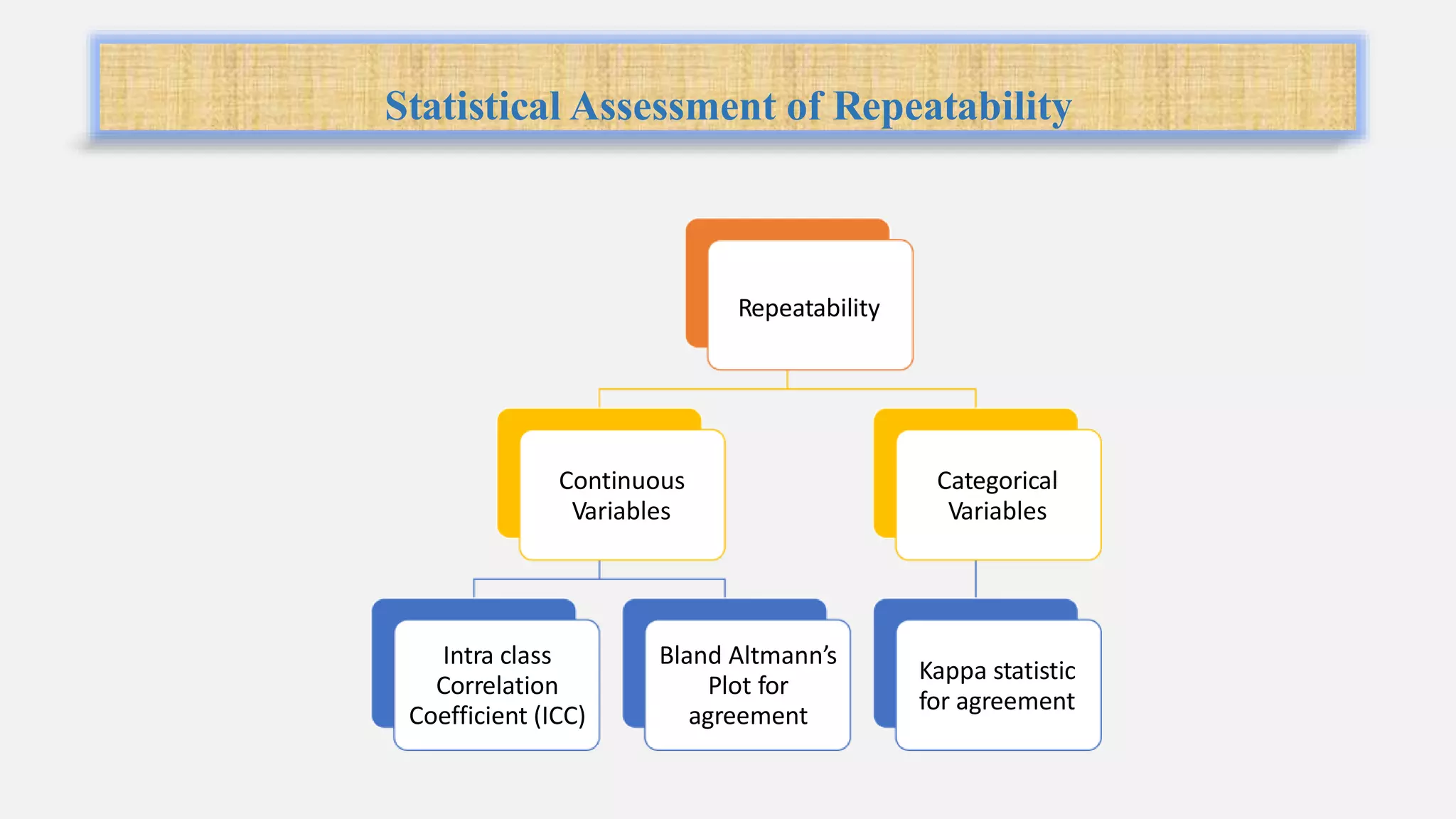
Reliability refers to the consistency of scores obtained from the same test administered under different conditions when no actual change has occurred. There are two broad approaches to assessing reliability: internal consistency and repeatability. Internal consistency is measured using Cronbach's alpha or split-half reliability and indicates how well test items measure the same construct. Repeatability, measured using test-retest reliability or inter-observer reliability, indicates the variation in measurements taken under the same conditions. For continuous variables, intraclass correlation and Bland-Altman plots are used, while kappa statistics assess agreement for categorical variables. Reliability coefficients above 0.7 indicate moderate to good reliability.









![Kappa Statistics
Kppa = observed agreement – chance agreement / 1- chance agreement
Observed agreement Pr(a) = a + d / a+b+c+d
Expected agreement Pr(e) = [(a+b) * (a+c) / a+b+c+d] + [(c+d) * (b+d) / a+b+c+d] / (a+b+c+d)
k = Pr(a) – Pr(e) / 1 – Pr(e)
Kappa < 0.4 – poor reliability
Kappa 0.41 – 0.74 – moderate to good reliability
Kappa >0.74 – Excellent reliability
Rater 1 – positive Rater 1 – negative
Rater 2 - positive a b
Rater 2 - negative c d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reliability-181112090049/75/Reliability-12-2048.jpg)
