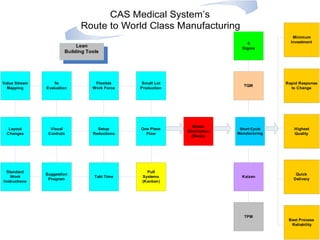
This document discusses Pull Systems and Kanban Cards. It provides an overview of Pull vs Push inventory systems, explaining that Pull Systems like Kanban only produce or replenish inventory based on actual customer demand, leading to less excess inventory compared to Push Systems. Kanban uses visual cards to signal when more inventory is needed to "pull" production or replenishment. The document outlines the basics of the Kanban system and card usage, including examples of different card types and ground rules for effective Kanban implementation. It concludes with the "Family Milk Story" to summarize the key points.