The document provides an overview of Kanban and how it can be used to improve processes and outcomes. Some key points:
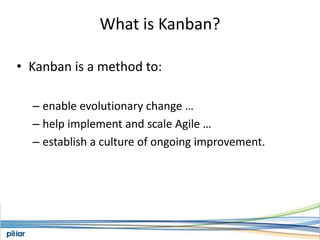
- Kanban is a method to enable evolutionary change, help implement Agile at scale, and establish a culture of ongoing improvement.
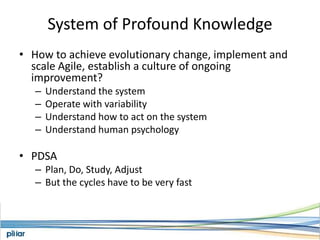
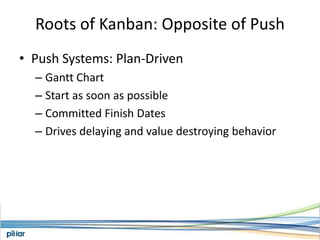
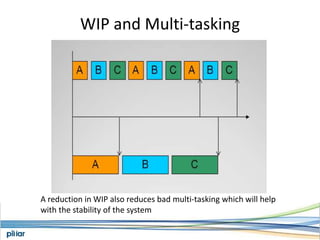
- It is based on Lean principles like limiting work-in-progress to improve flow and pull-based systems to pace work based on demand rather than estimates.
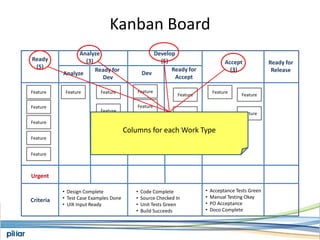
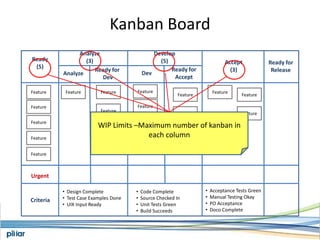
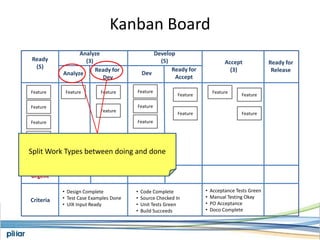
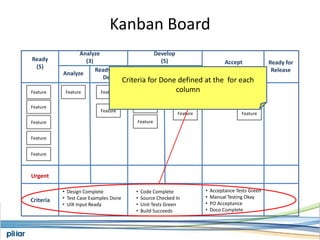
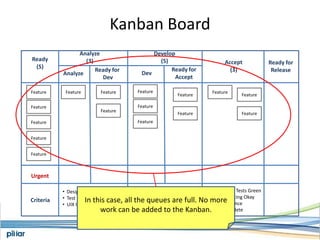
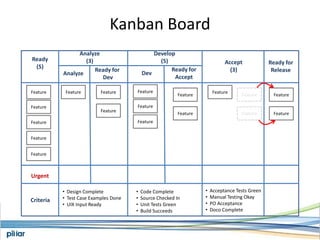
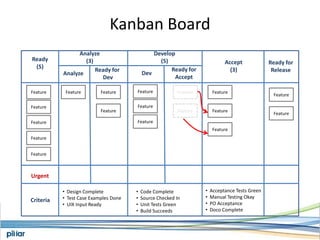
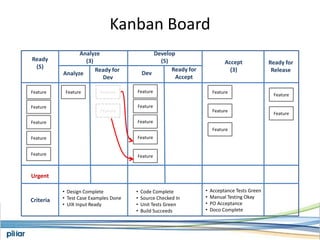
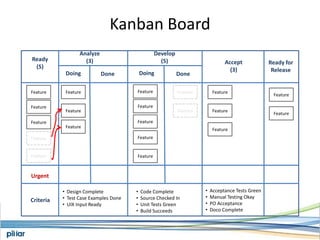
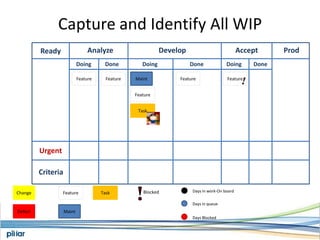
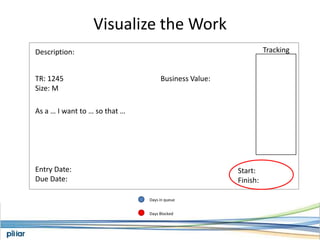
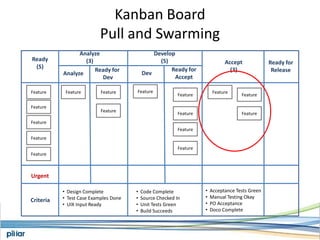
- A Kanban board is used to visualize work with limits on work-in-progress for each stage to highlight bottlenecks and encourage swarming to flow of work.
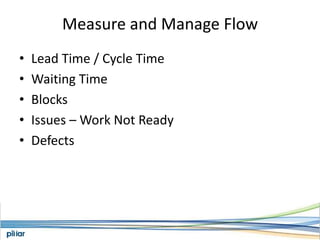
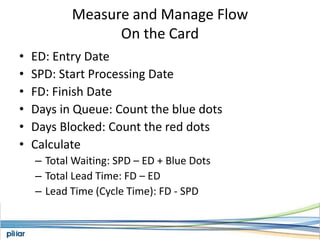
- Metrics like lead time, wait time and blocks are measured to manage flow and continue improving the process over time