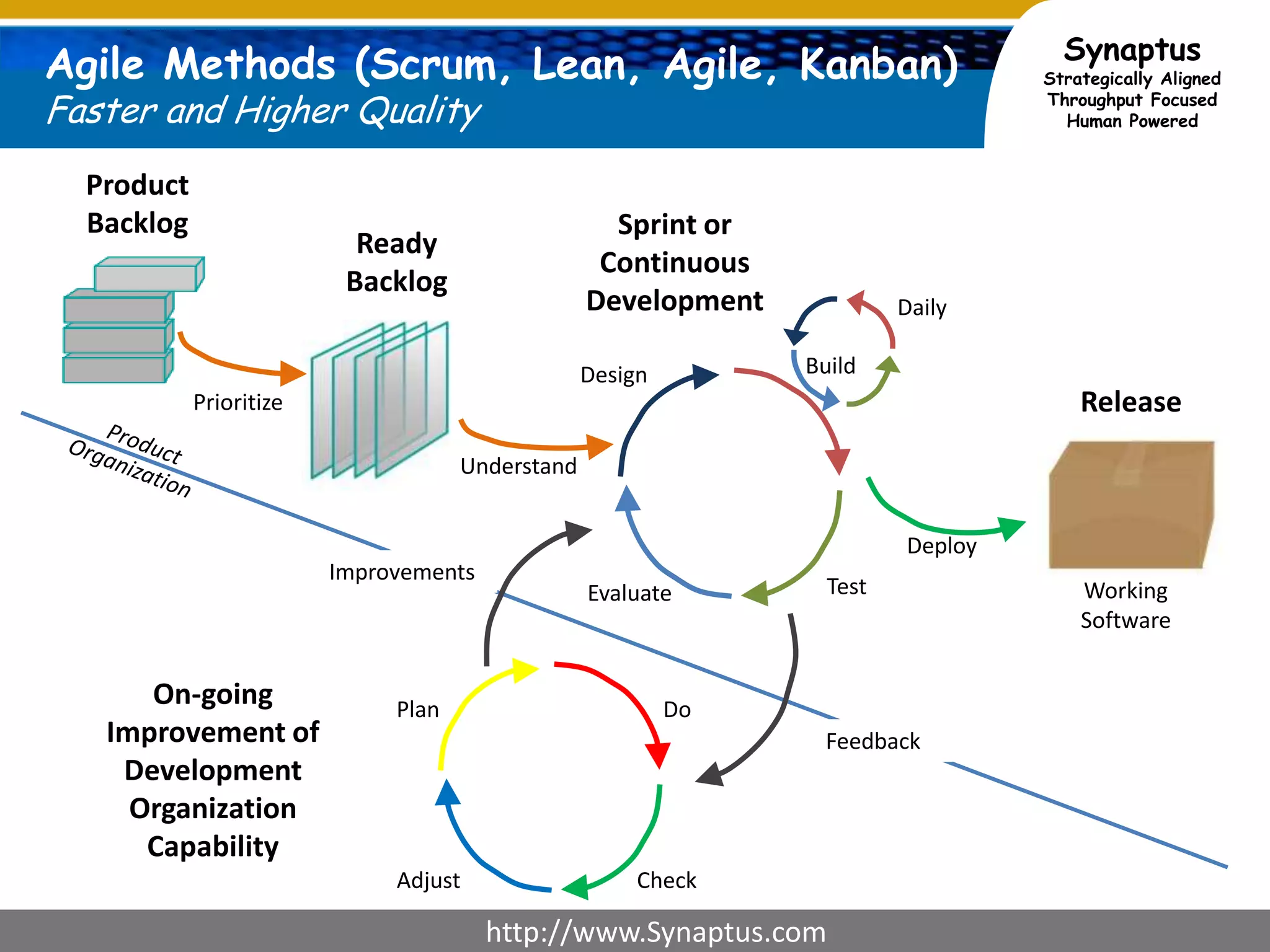
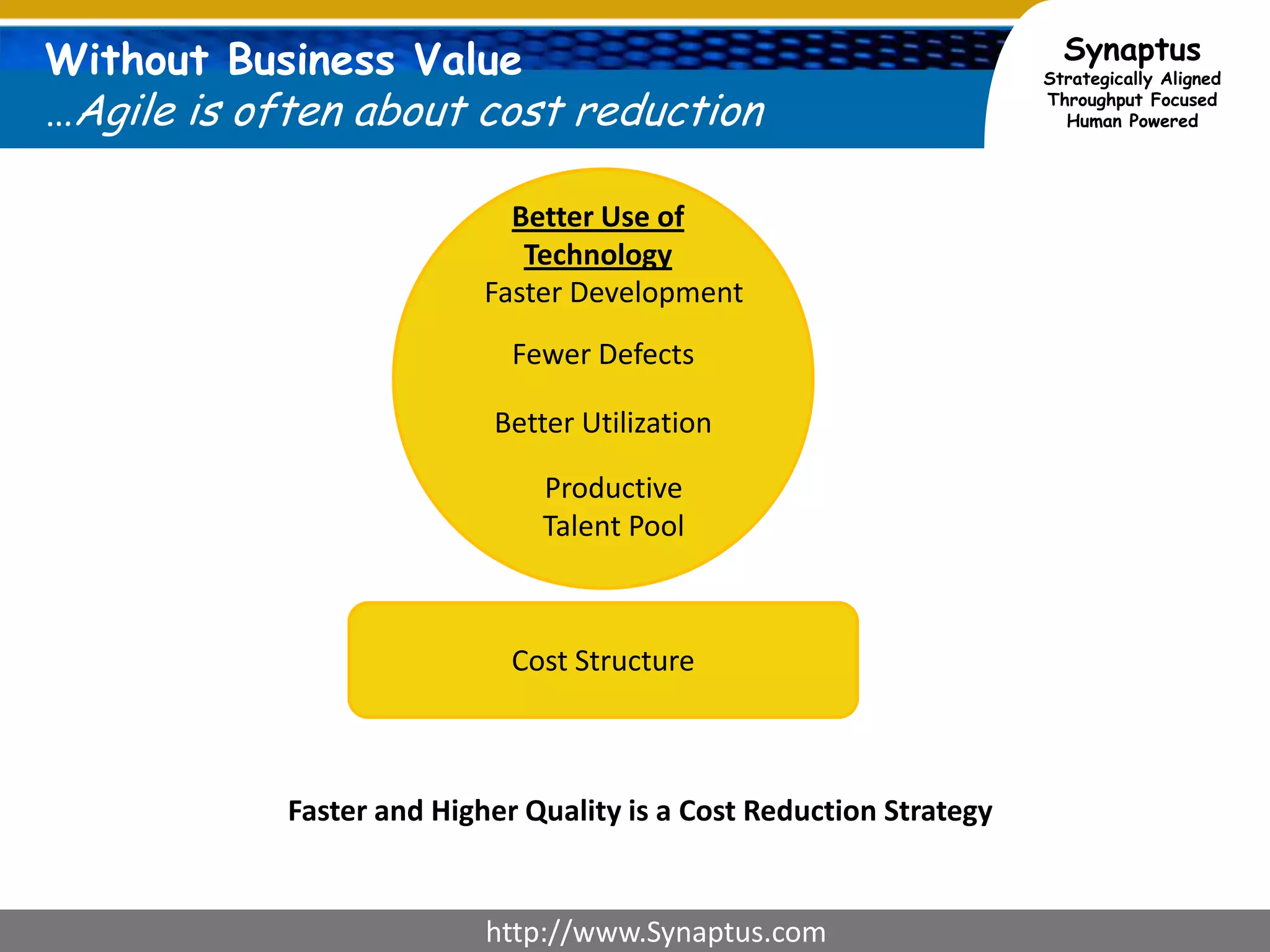
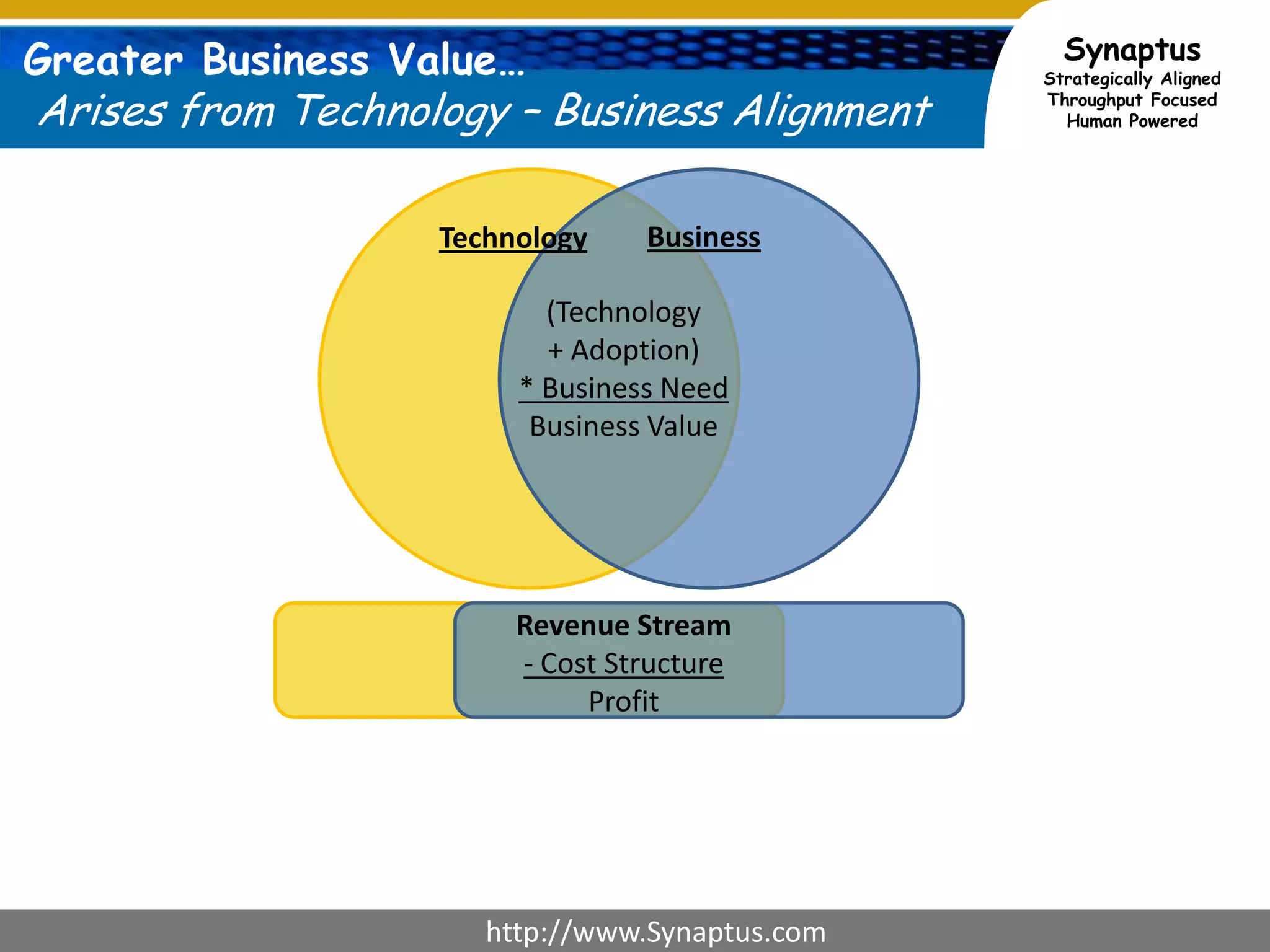
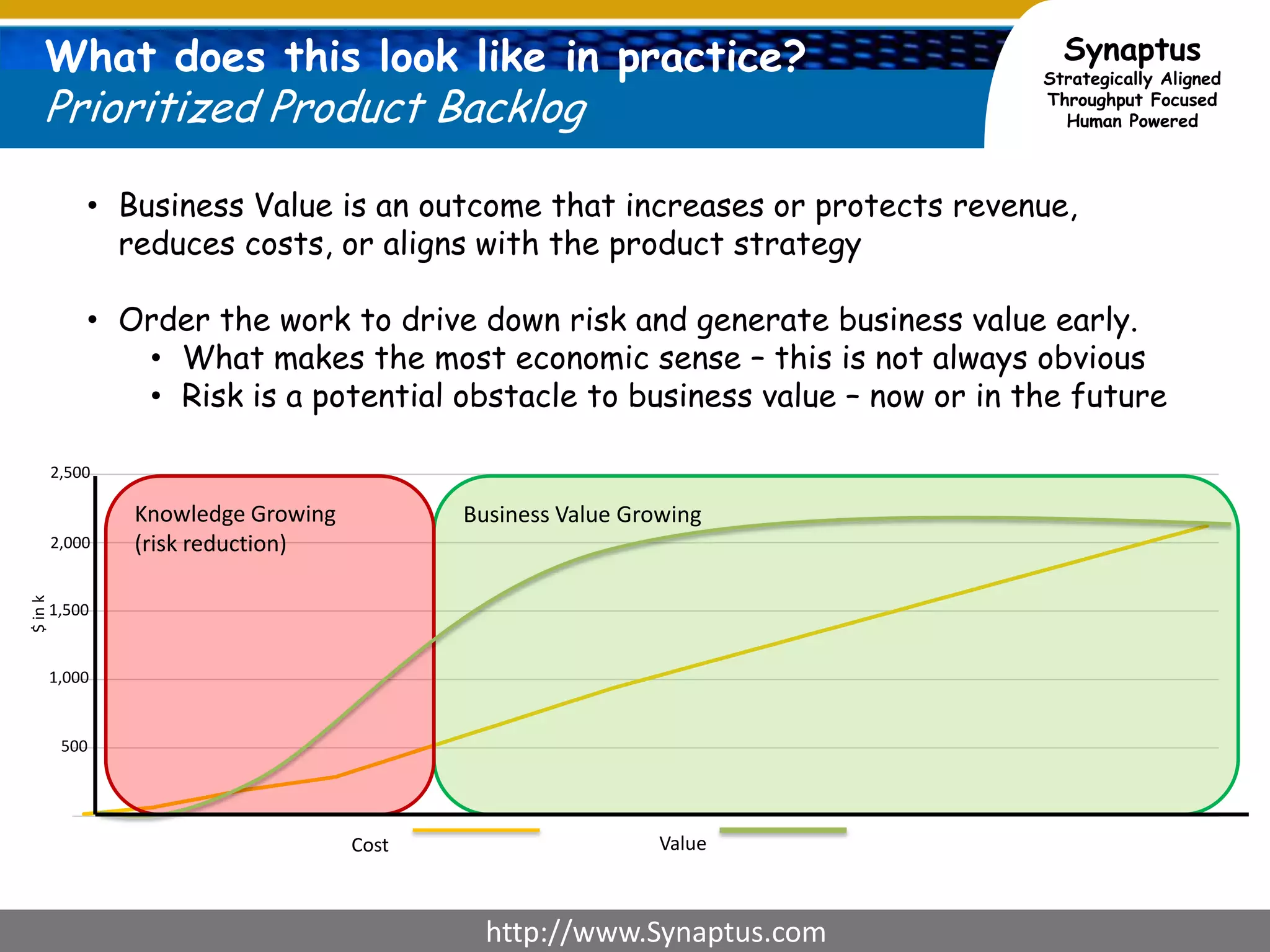
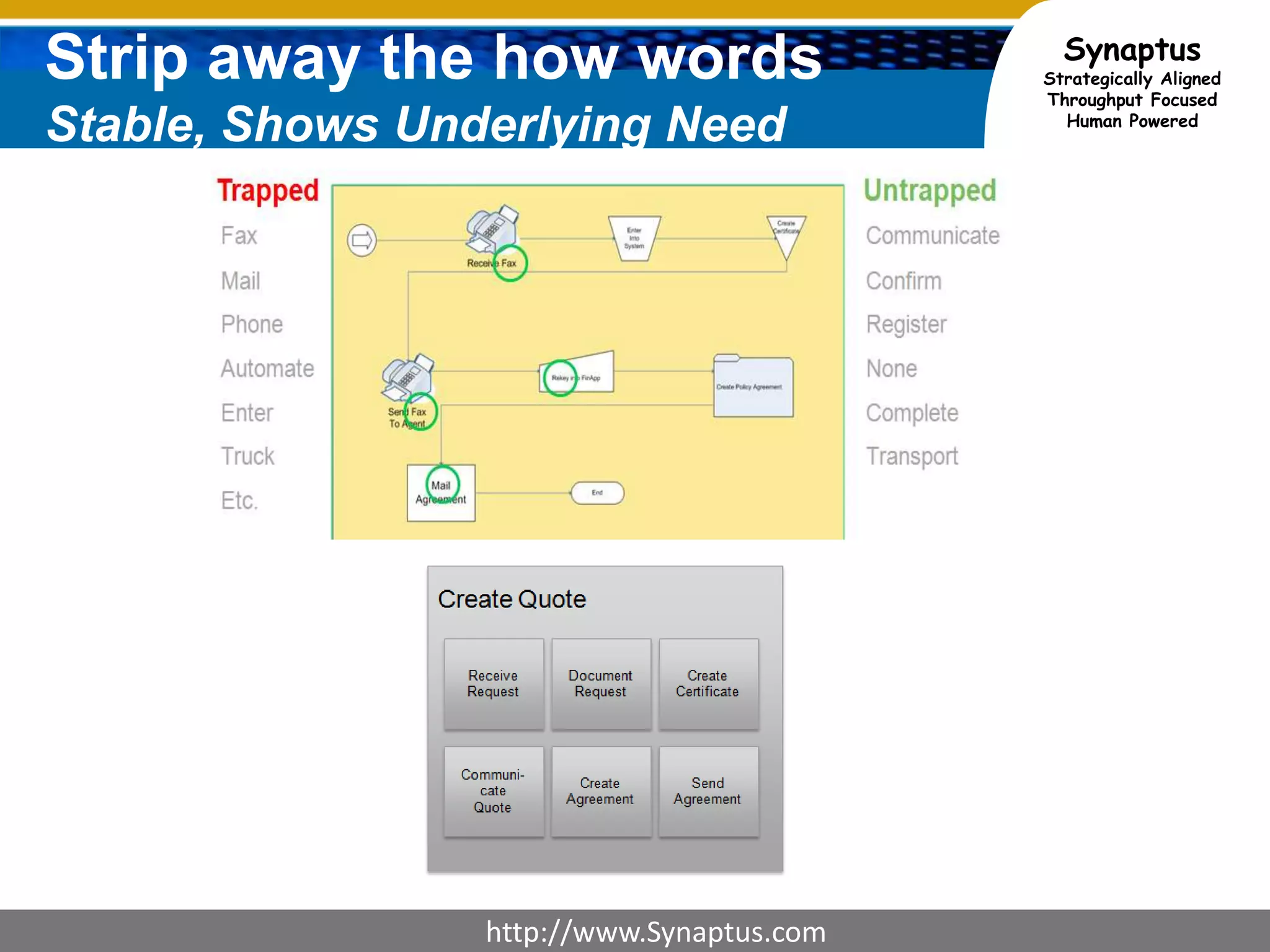
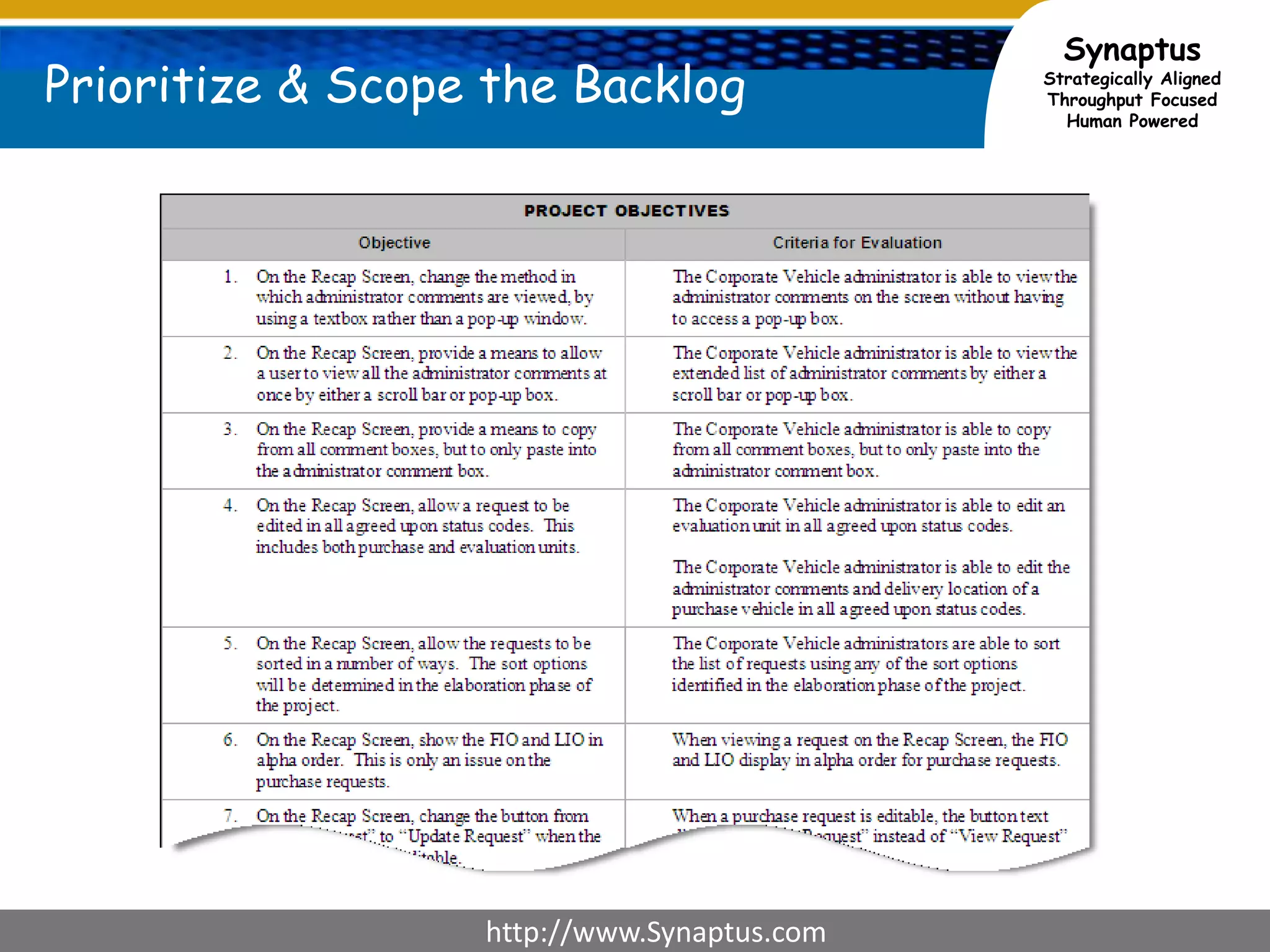
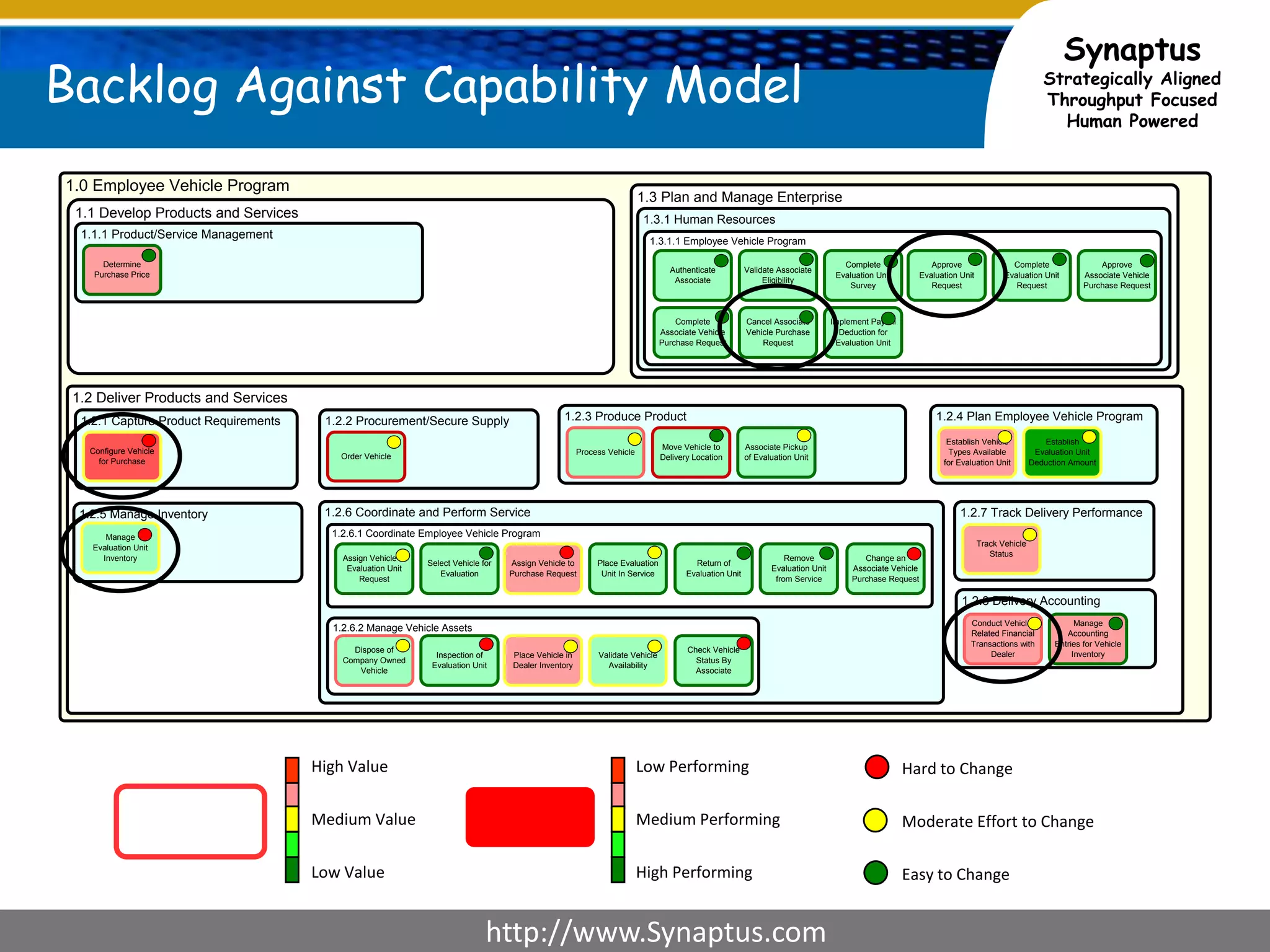
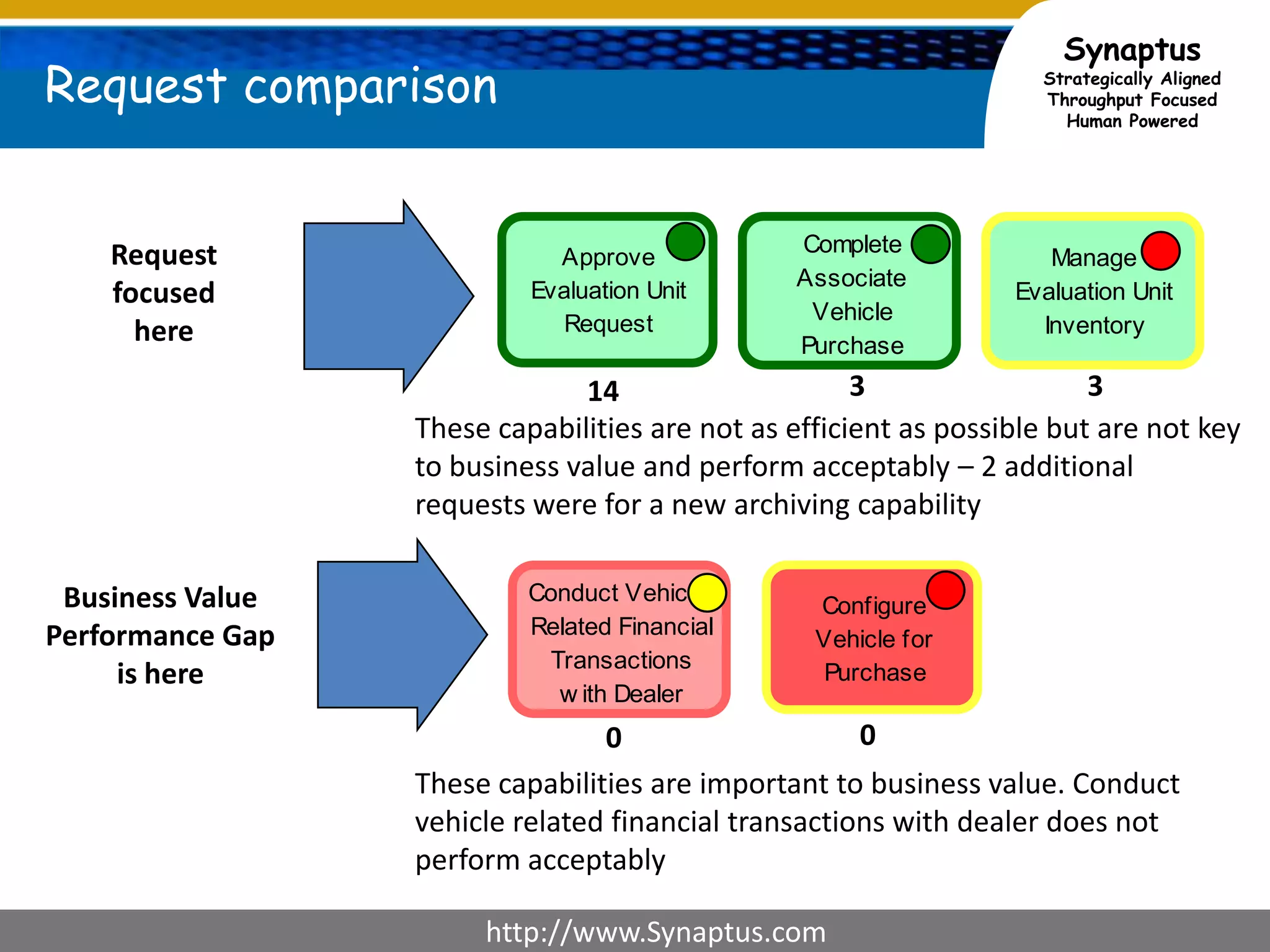
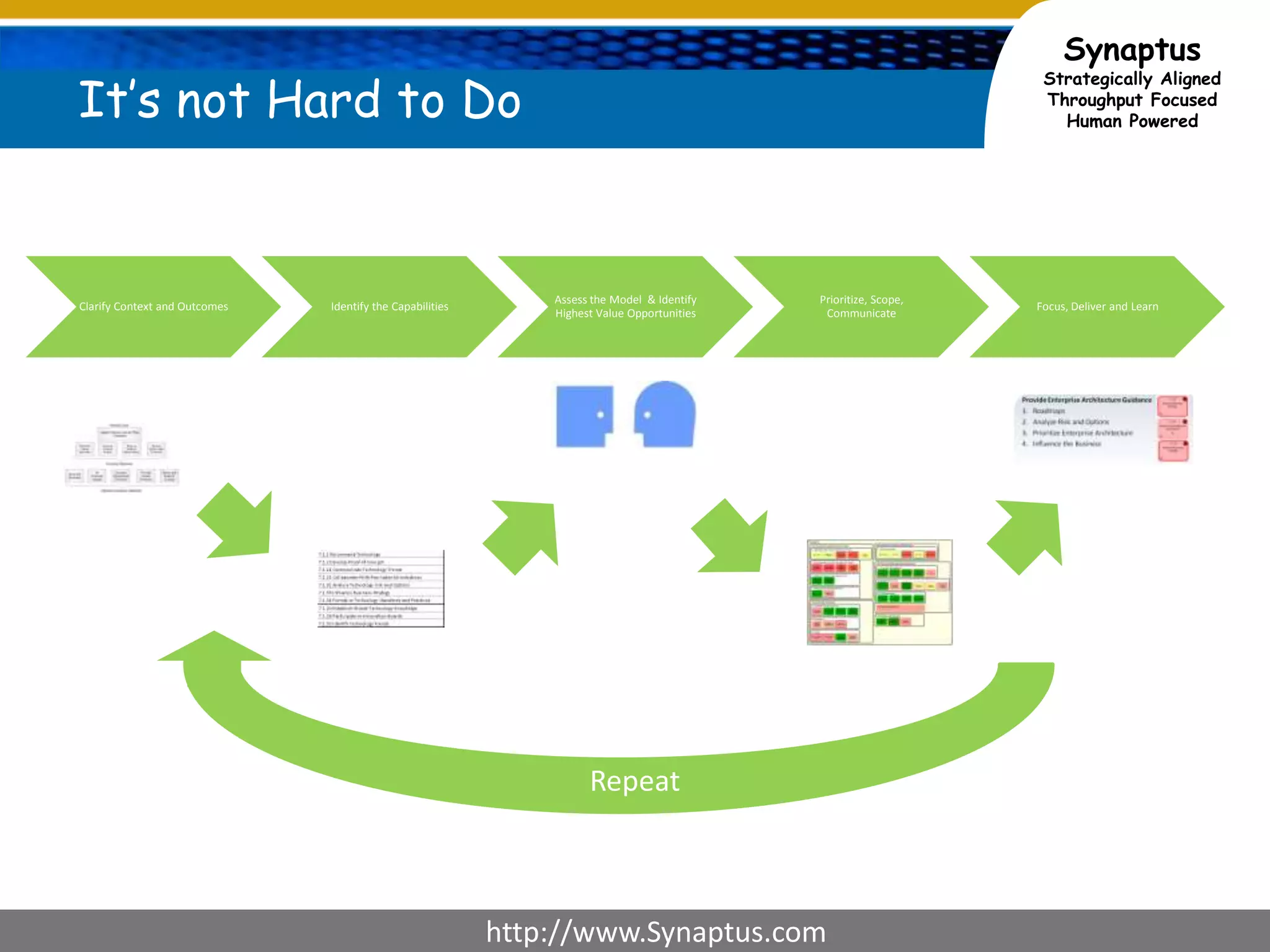
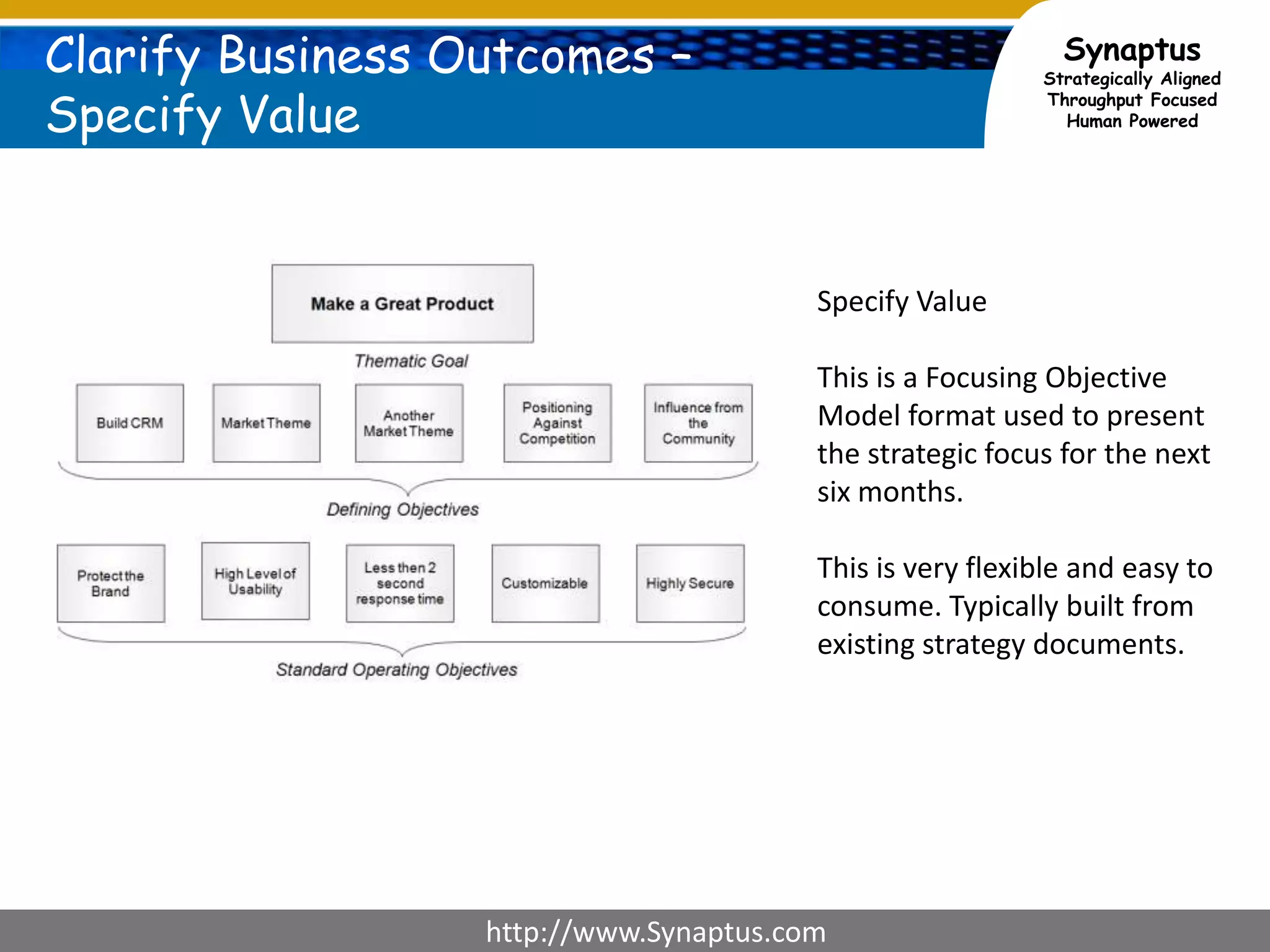
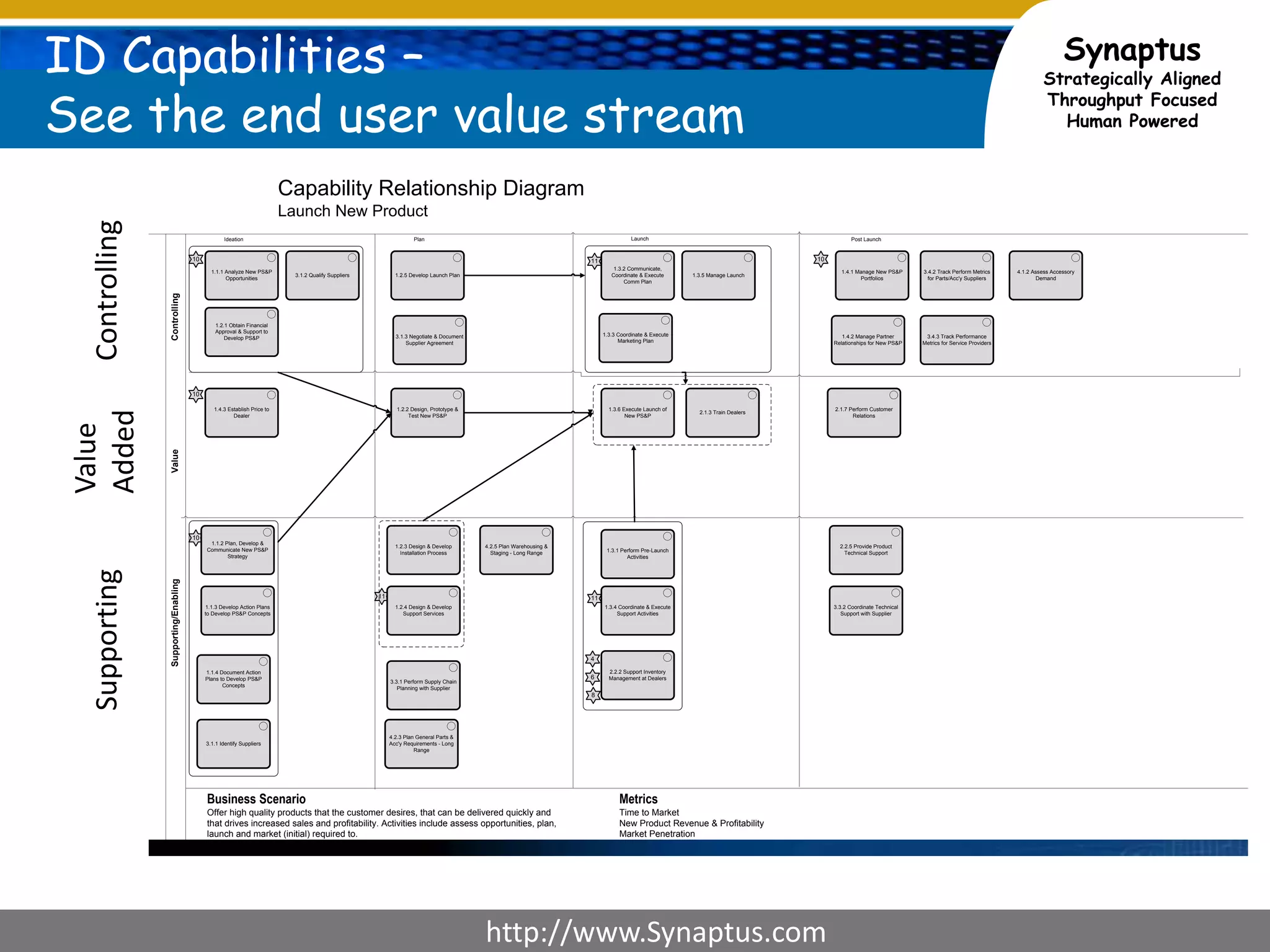
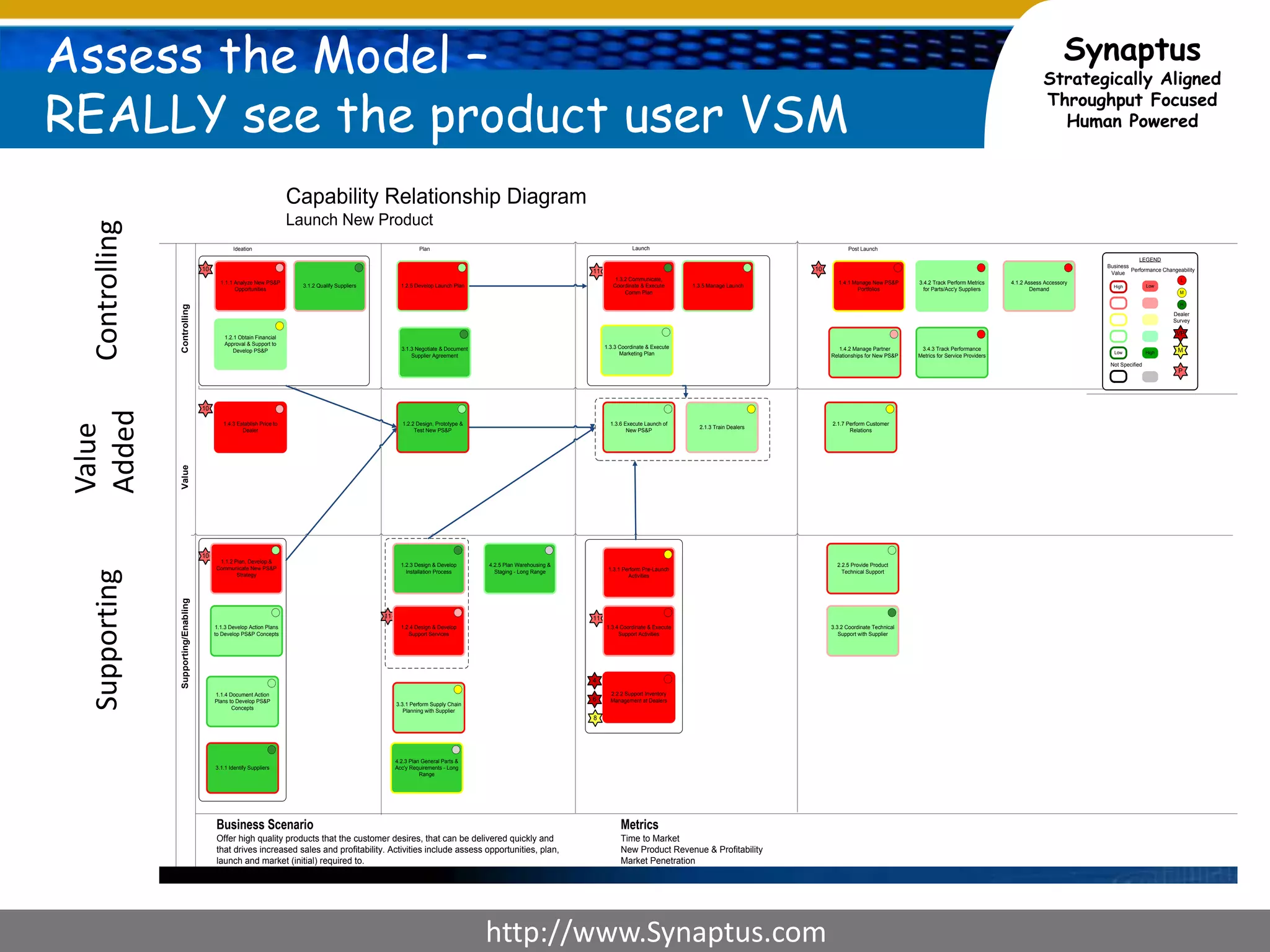
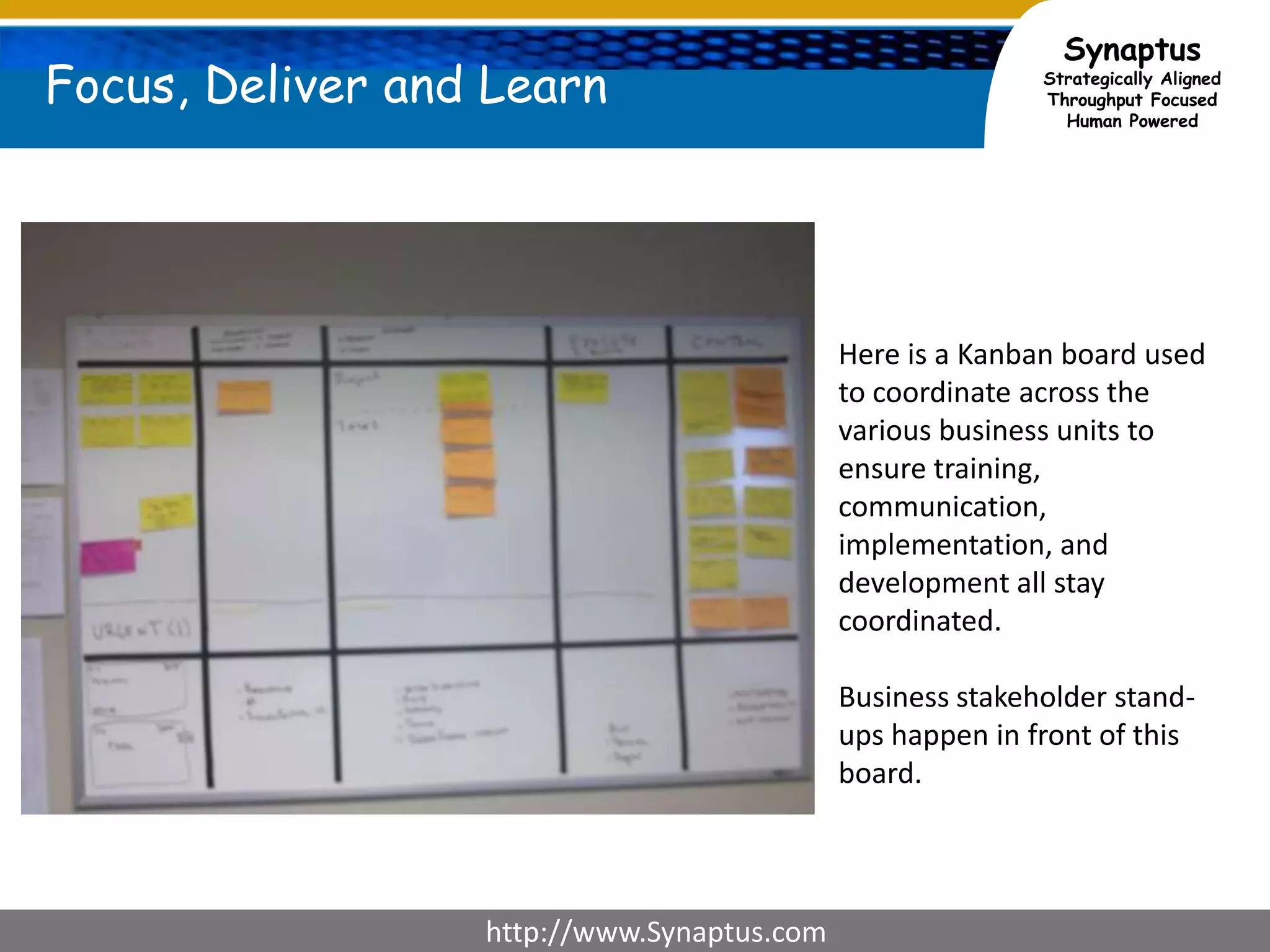
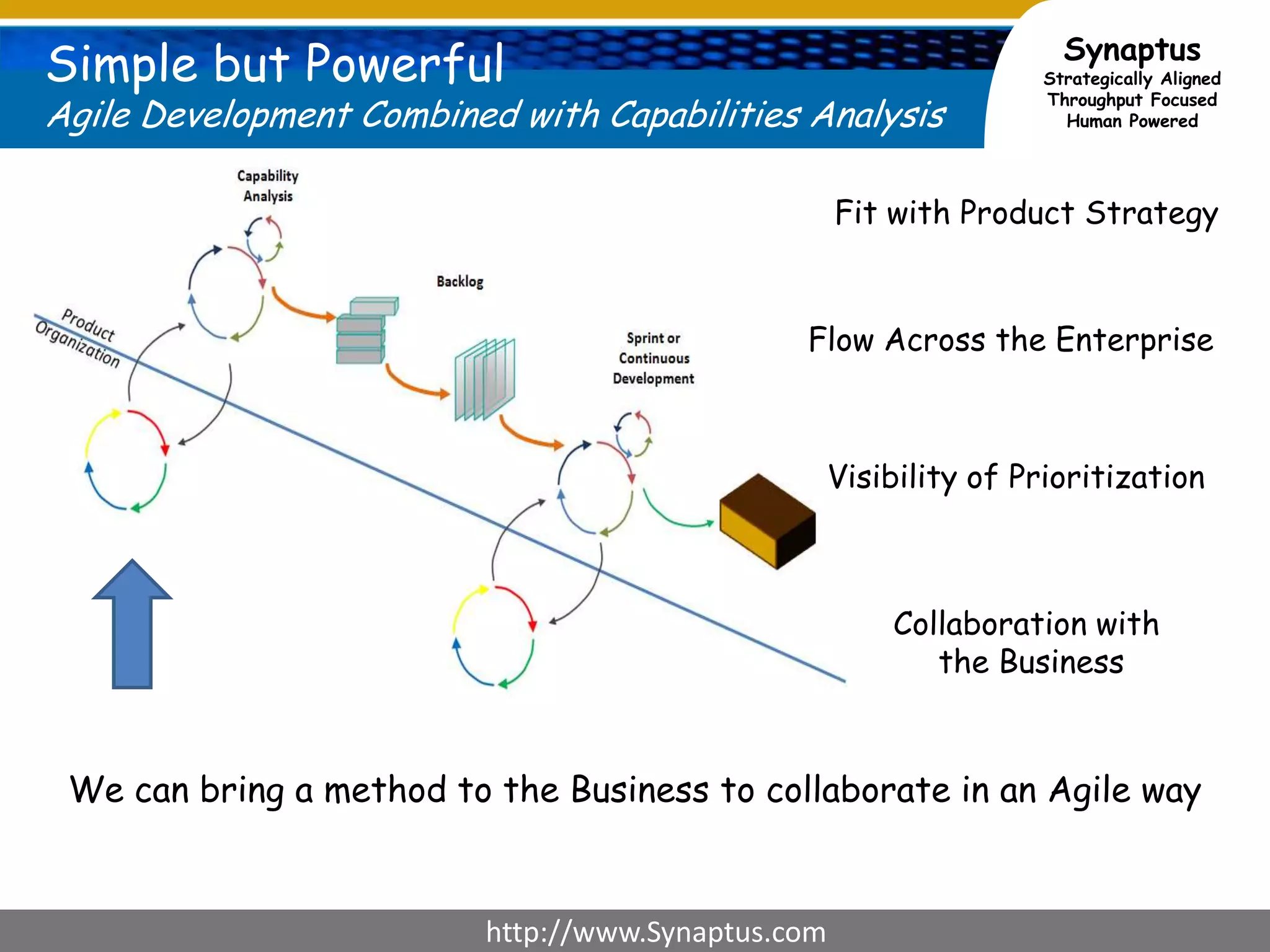
The document discusses enhancing agile development methodologies to focus on delivering business value by aligning technology with business needs and prioritizing high-value outcomes. It emphasizes the importance of collaboration, visibility, and effective prioritization to drive down risks and ensure economic returns. The new approach to agile aims to deliver faster, higher quality results while fostering a culture of trust and continuous improvement within teams.