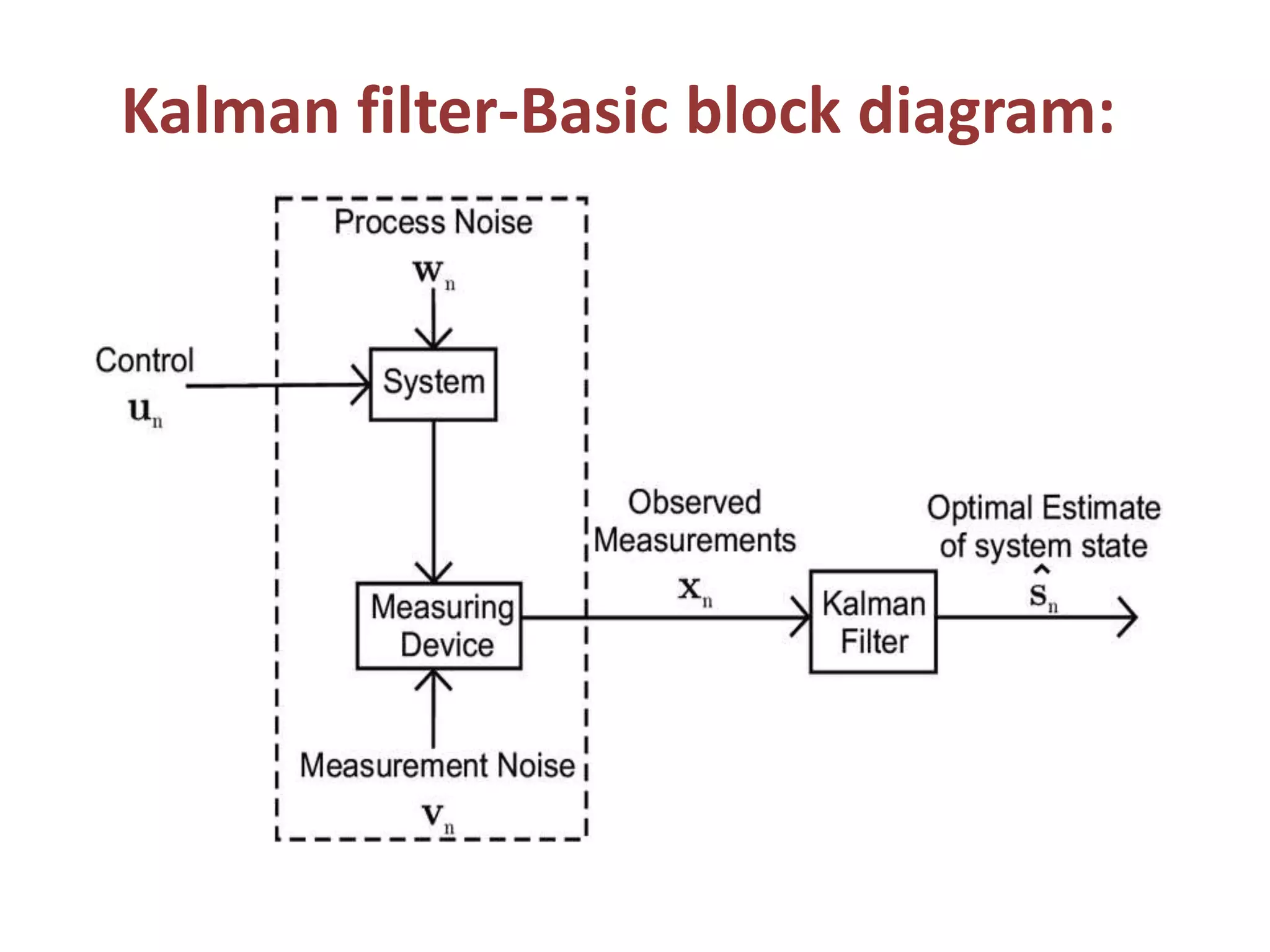
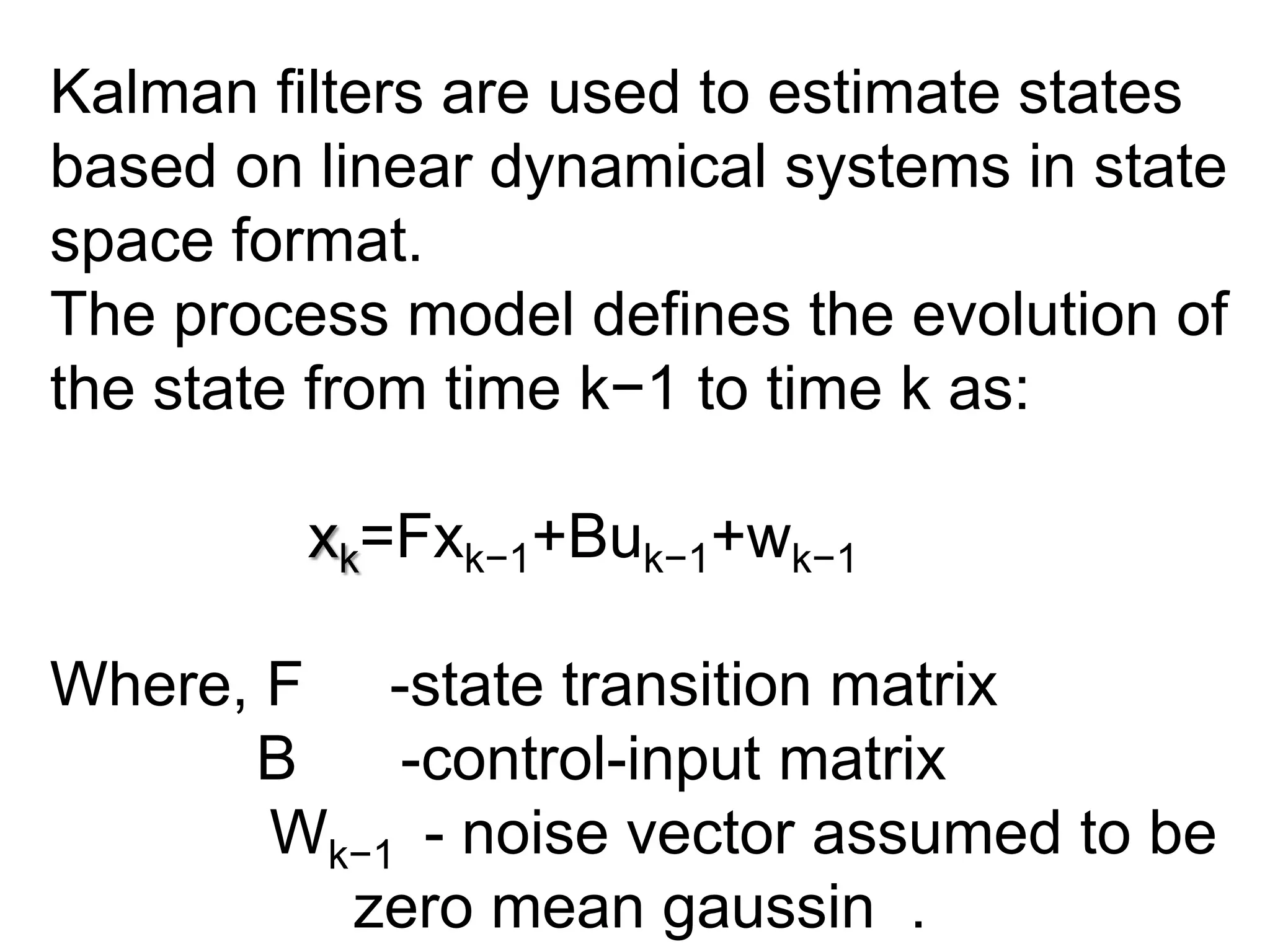
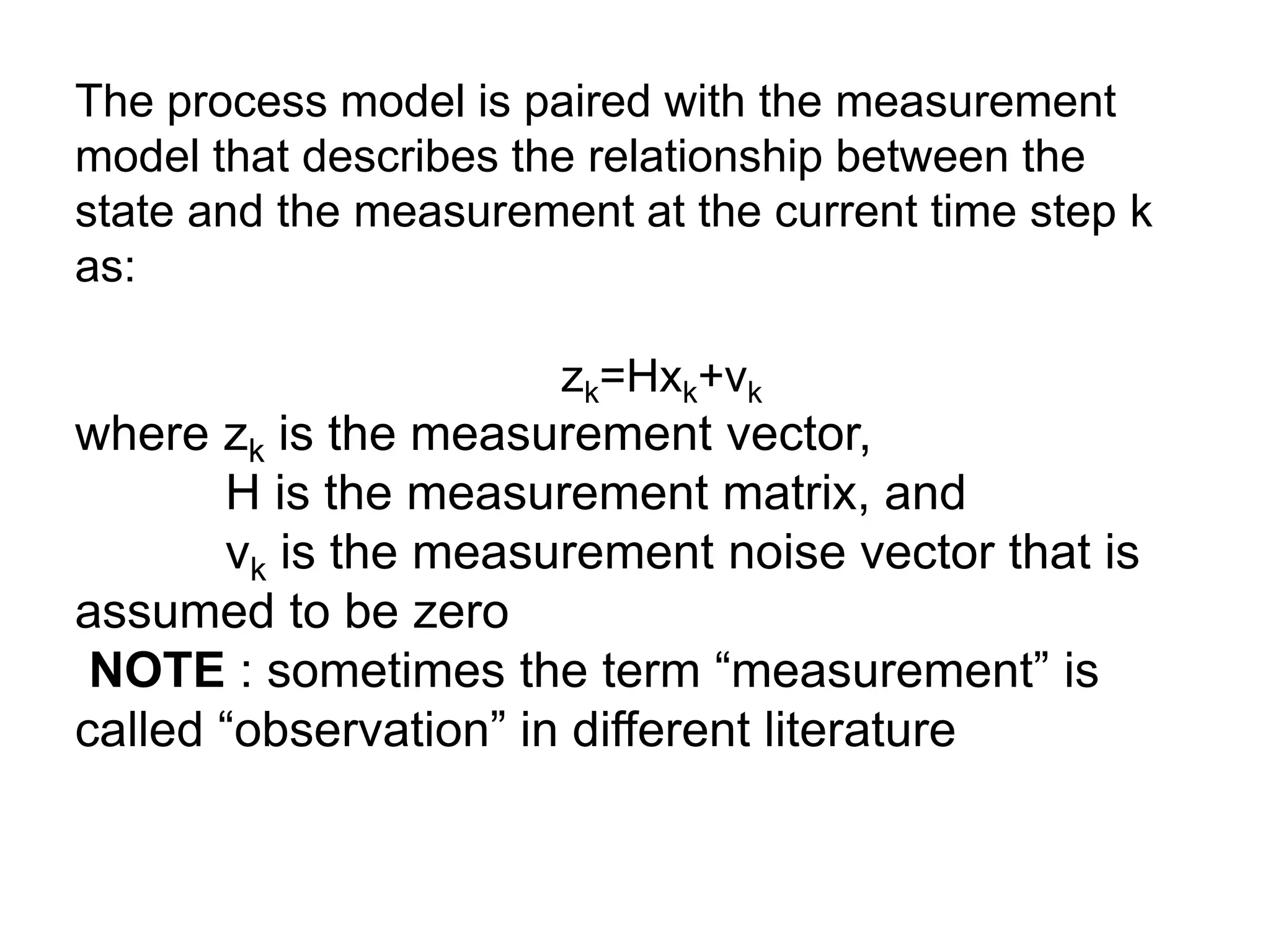
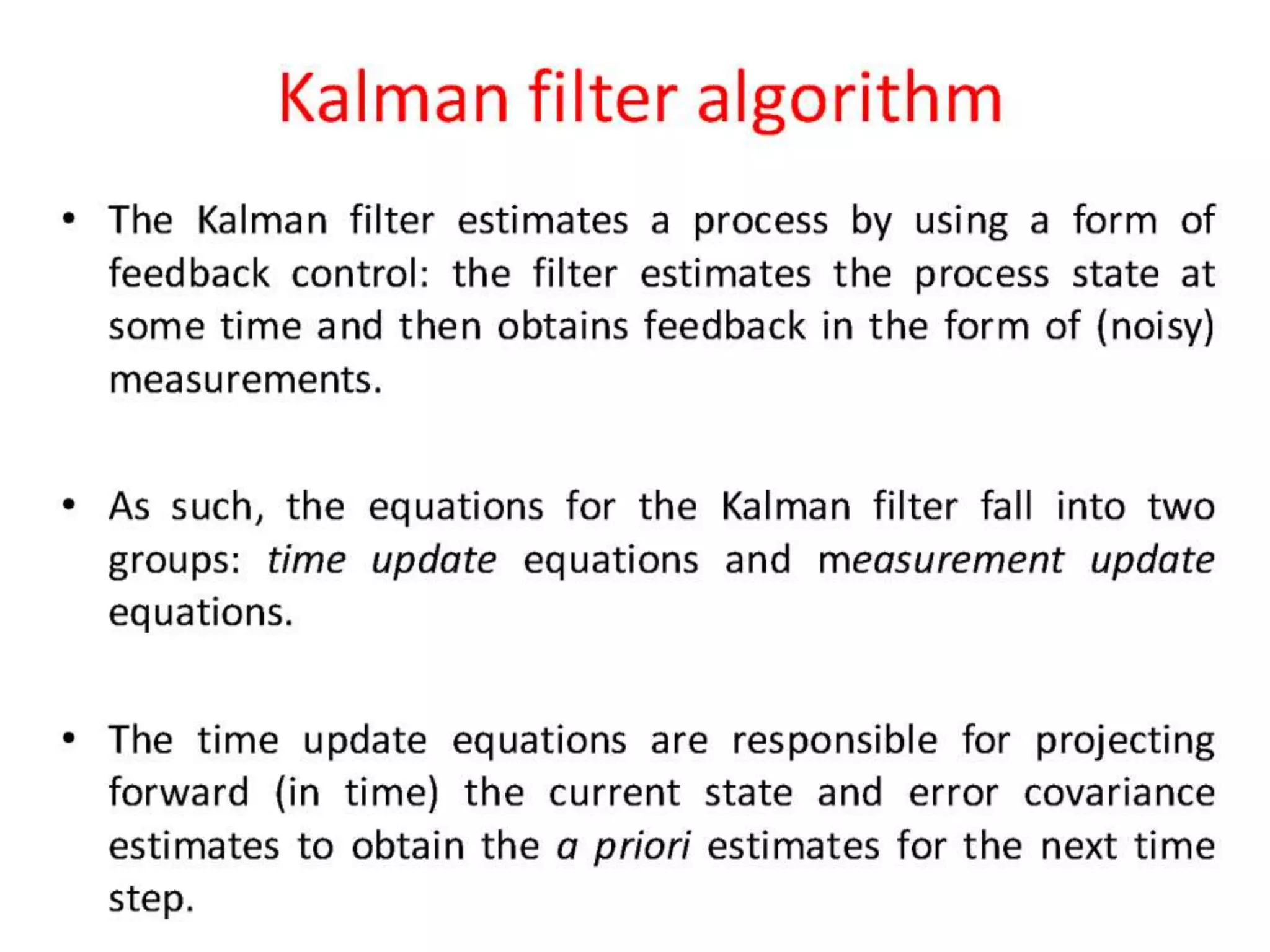
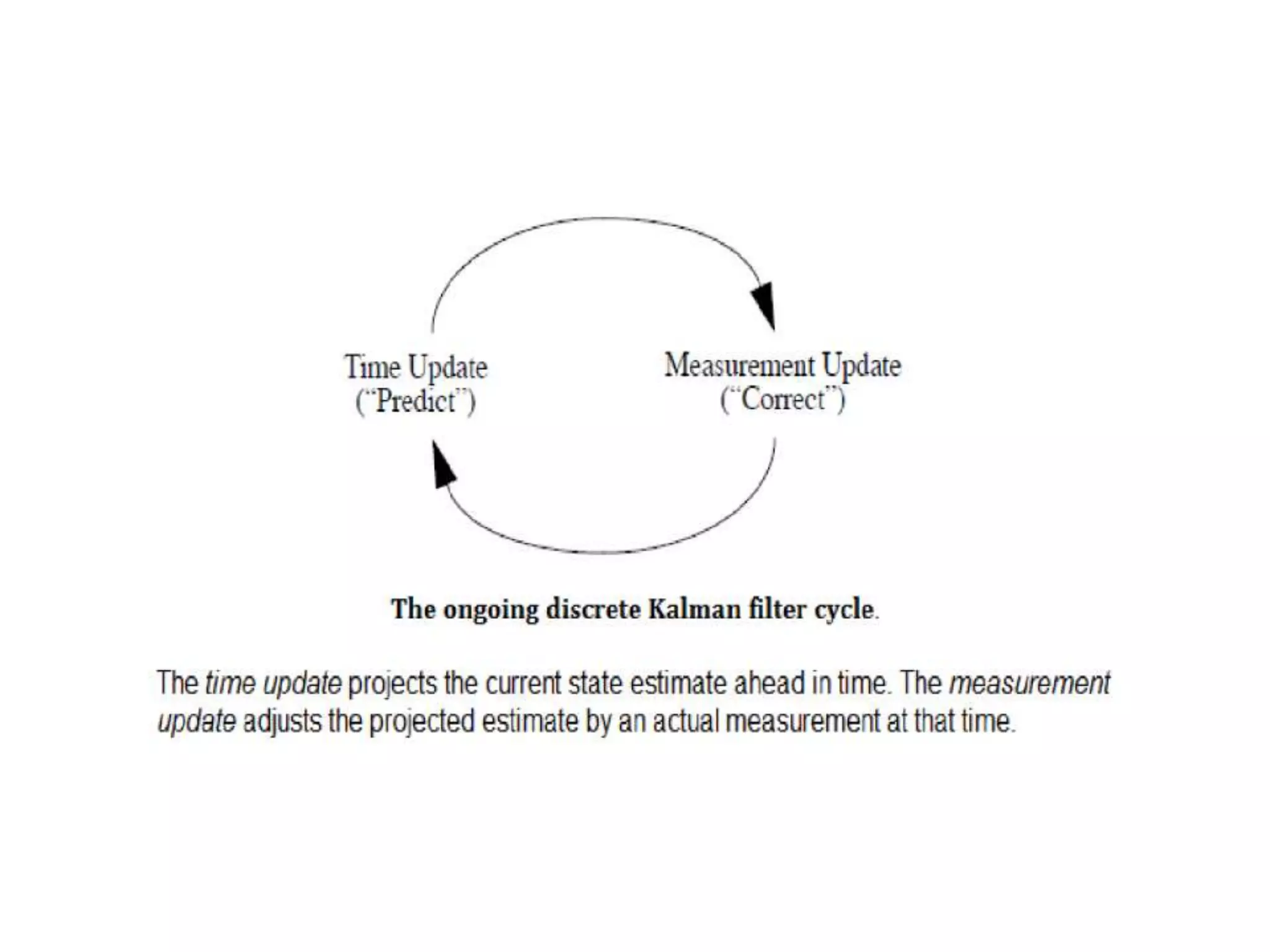
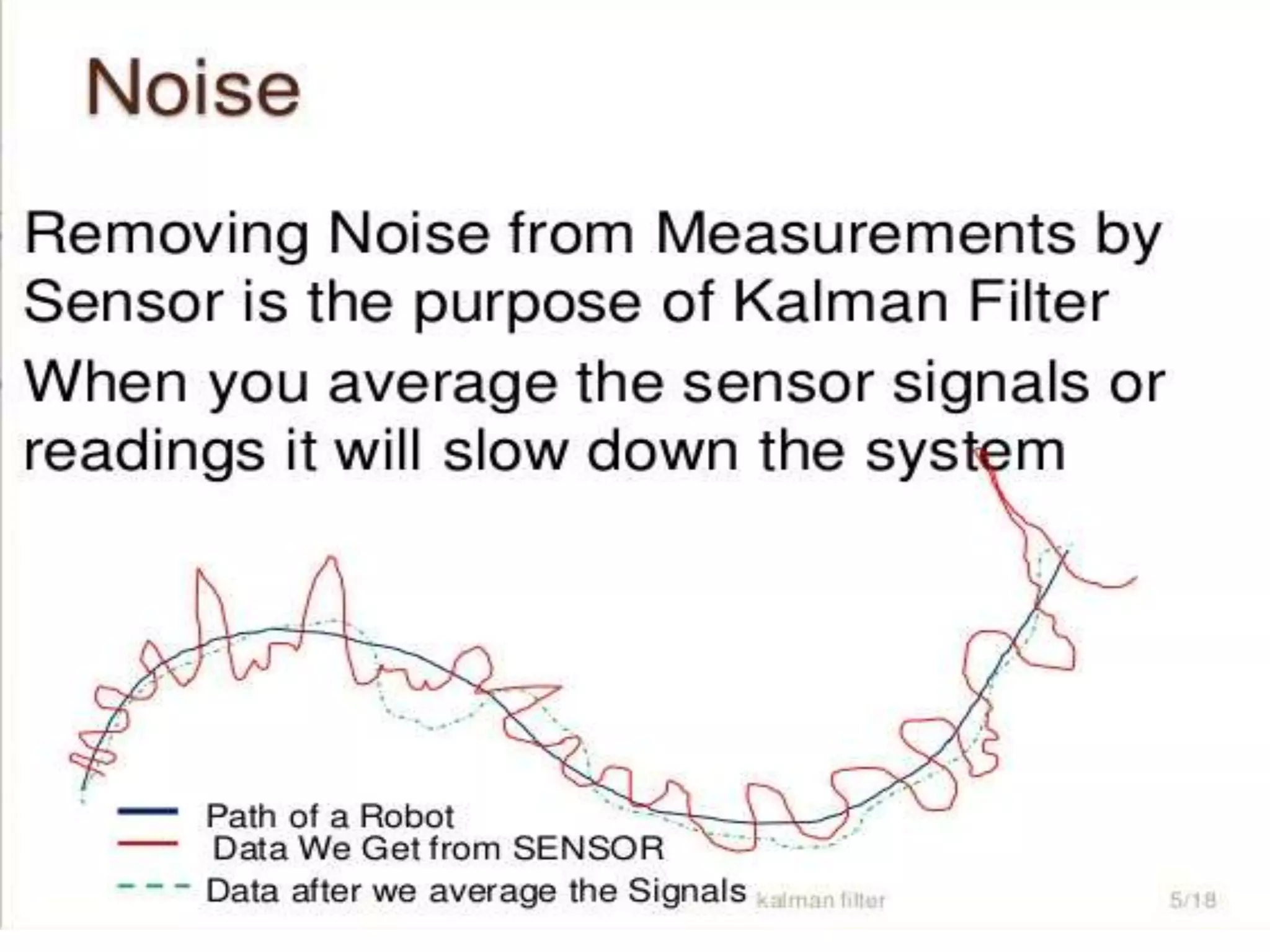
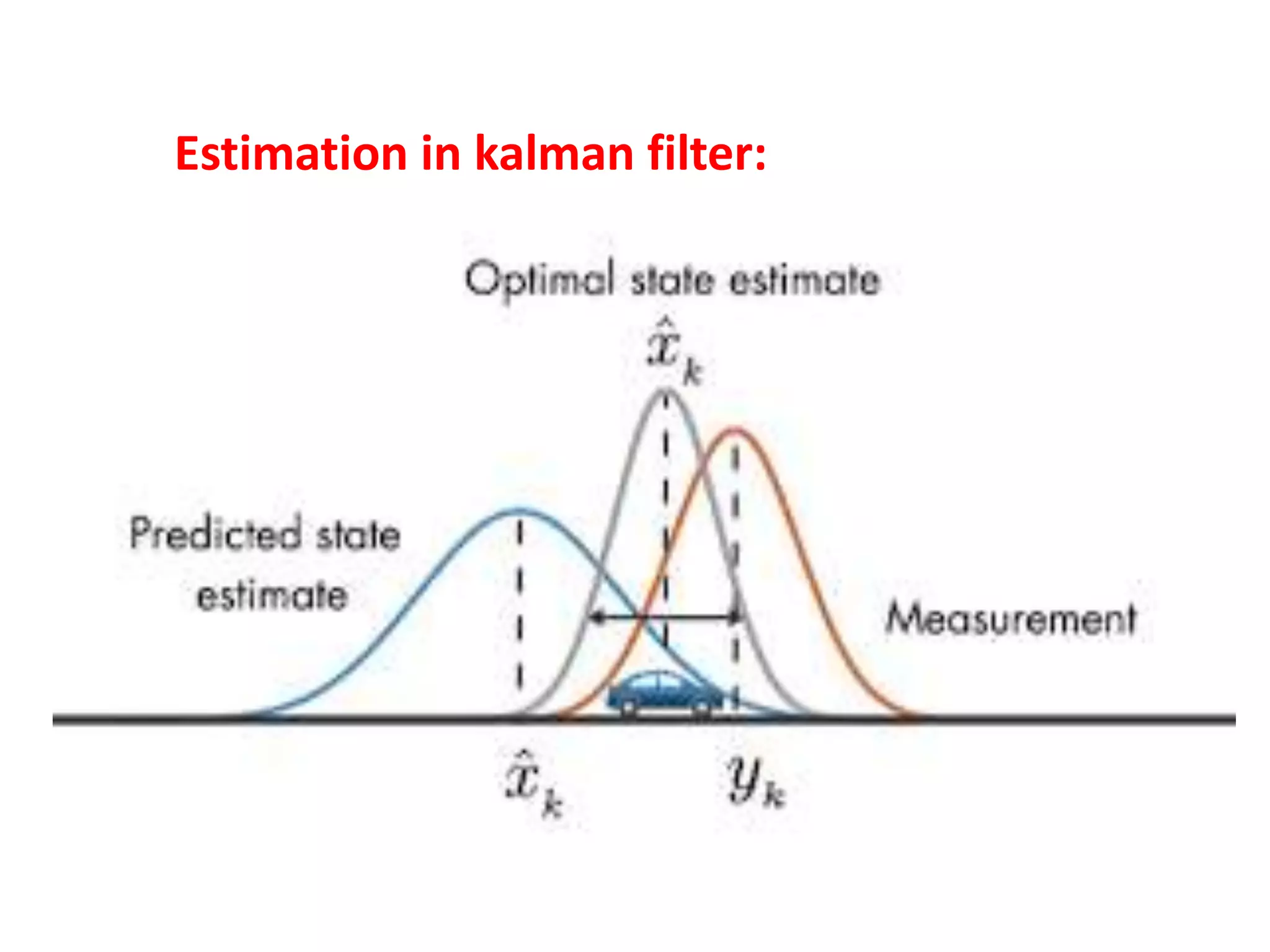
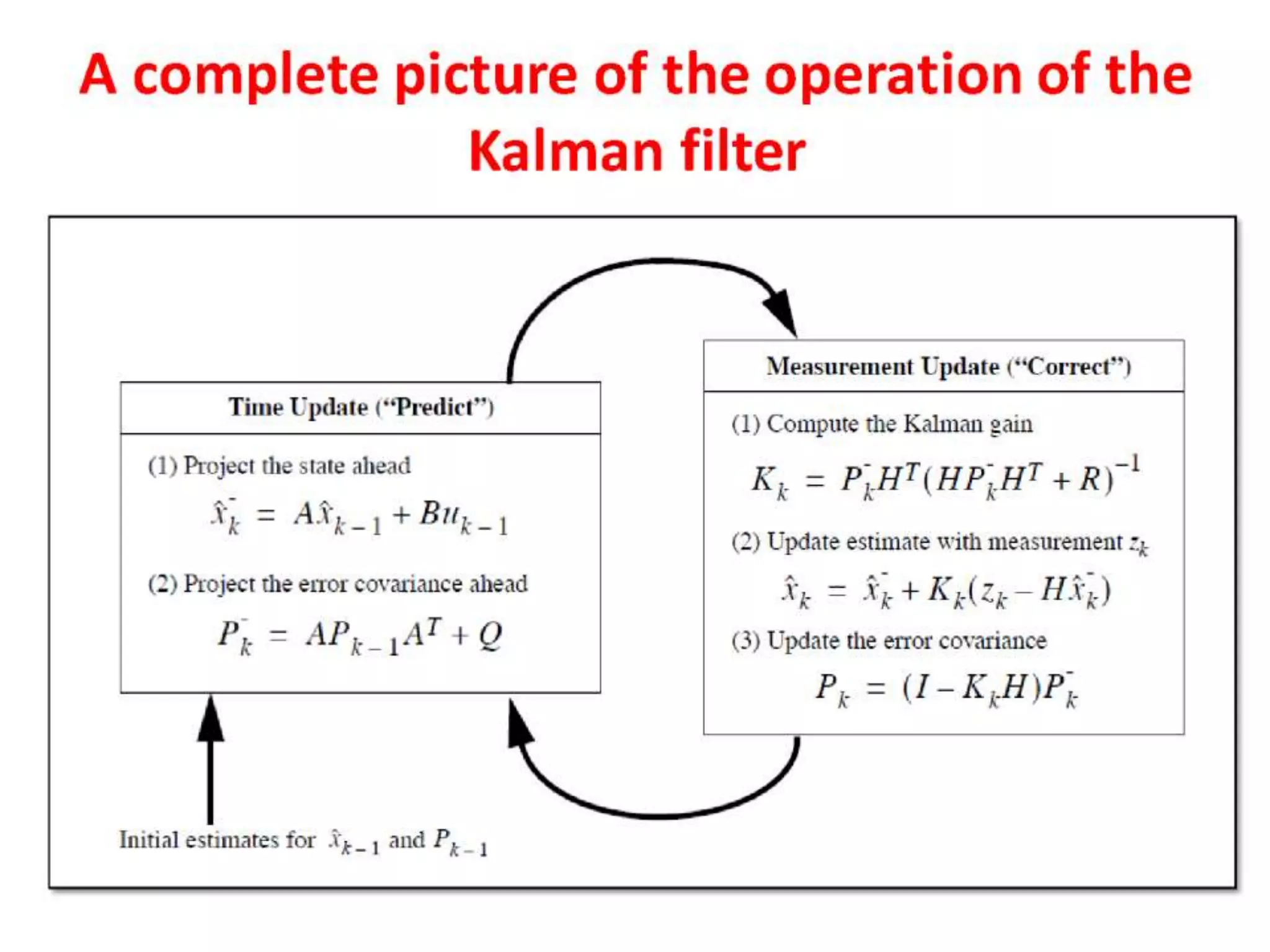
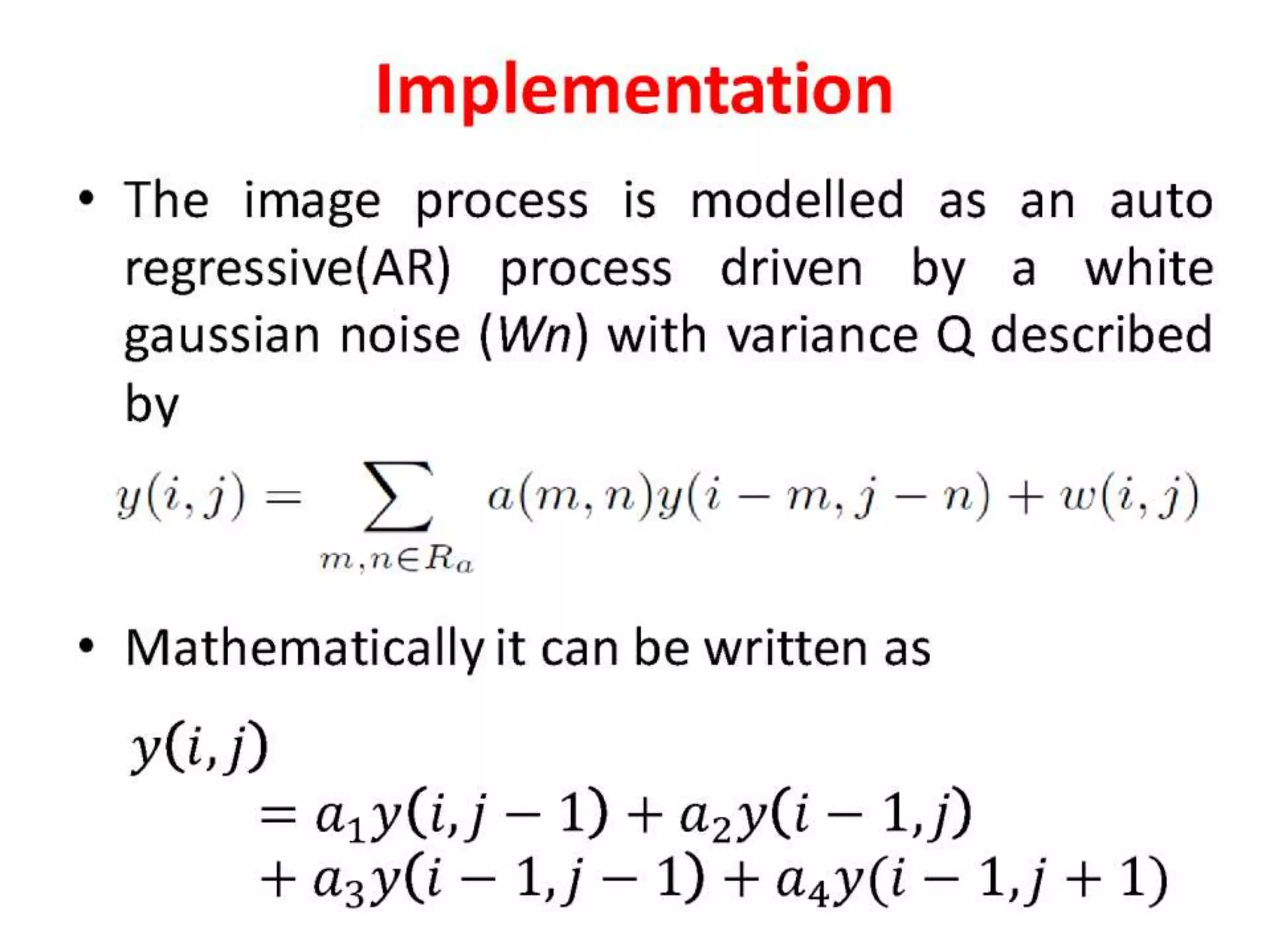
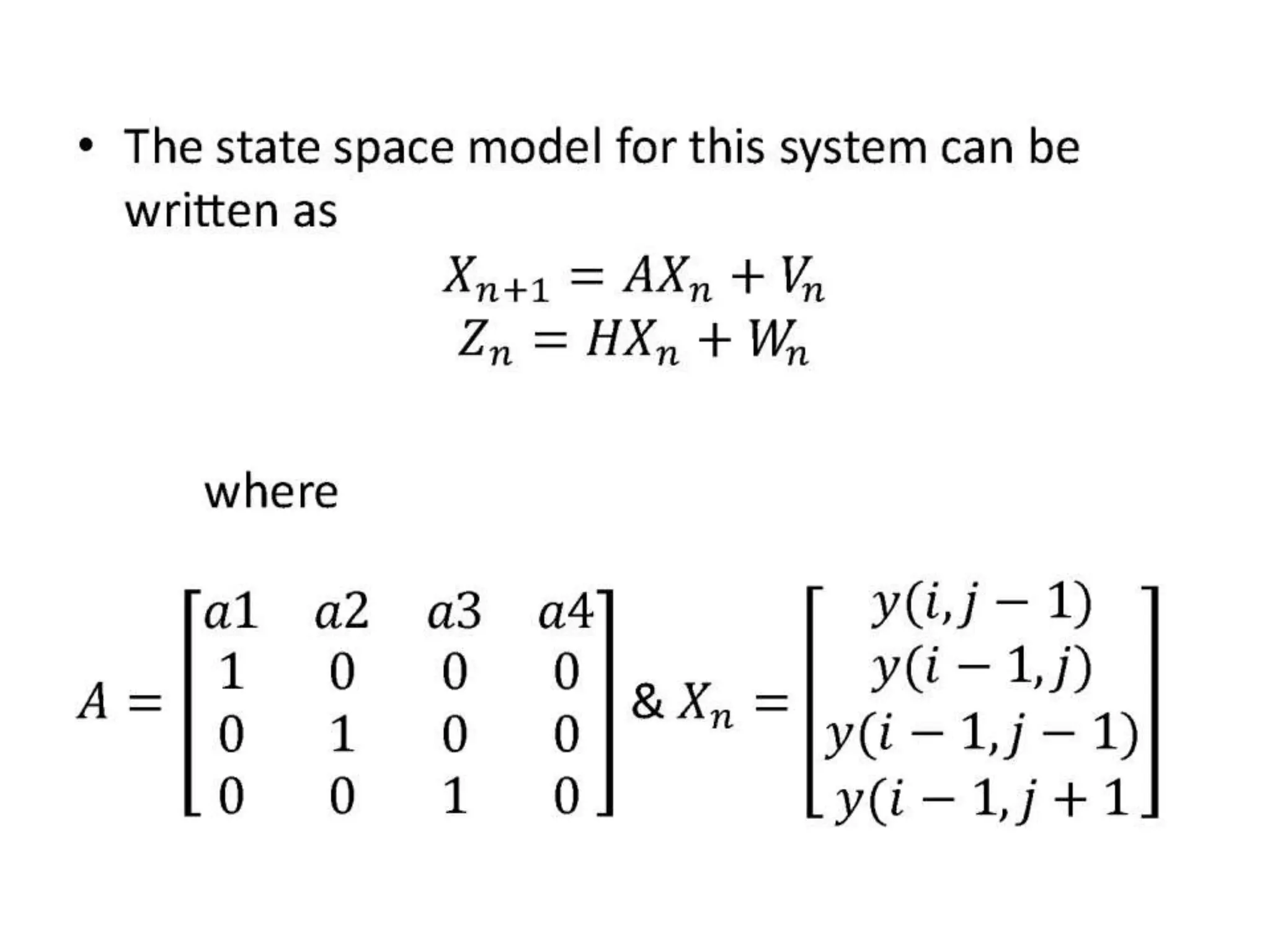
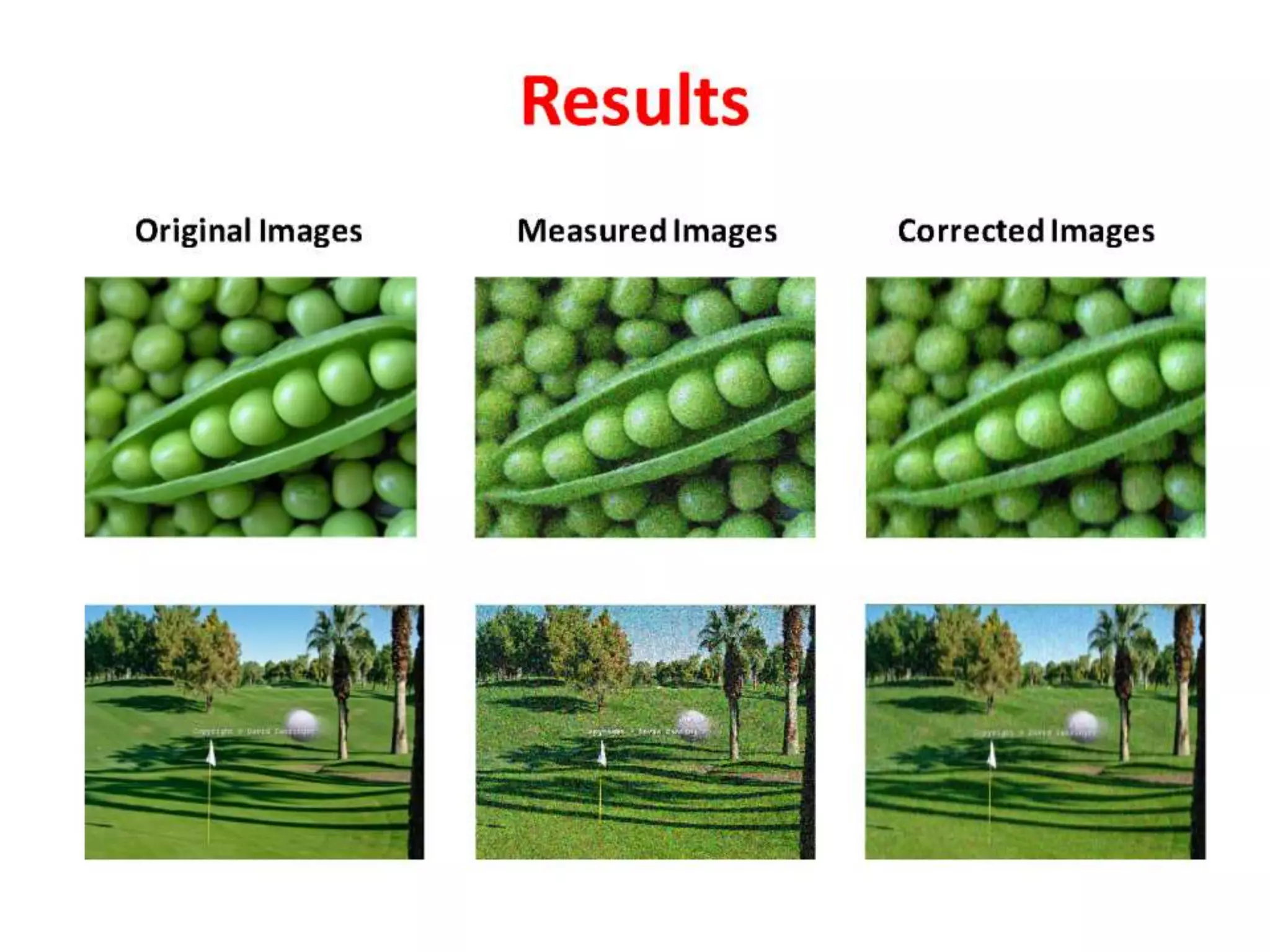
The document discusses the development and theory of Kalman filtering, an algorithm that provides more accurate estimates of unknown variables through a series of measurements over time despite statistical noise. It covers its background, including Rudolf Kalman's contributions and the mathematical models behind the filtering process. Additionally, it highlights several applications of Kalman filters, such as image processing, GPS tracking, and terrain-referenced navigation.