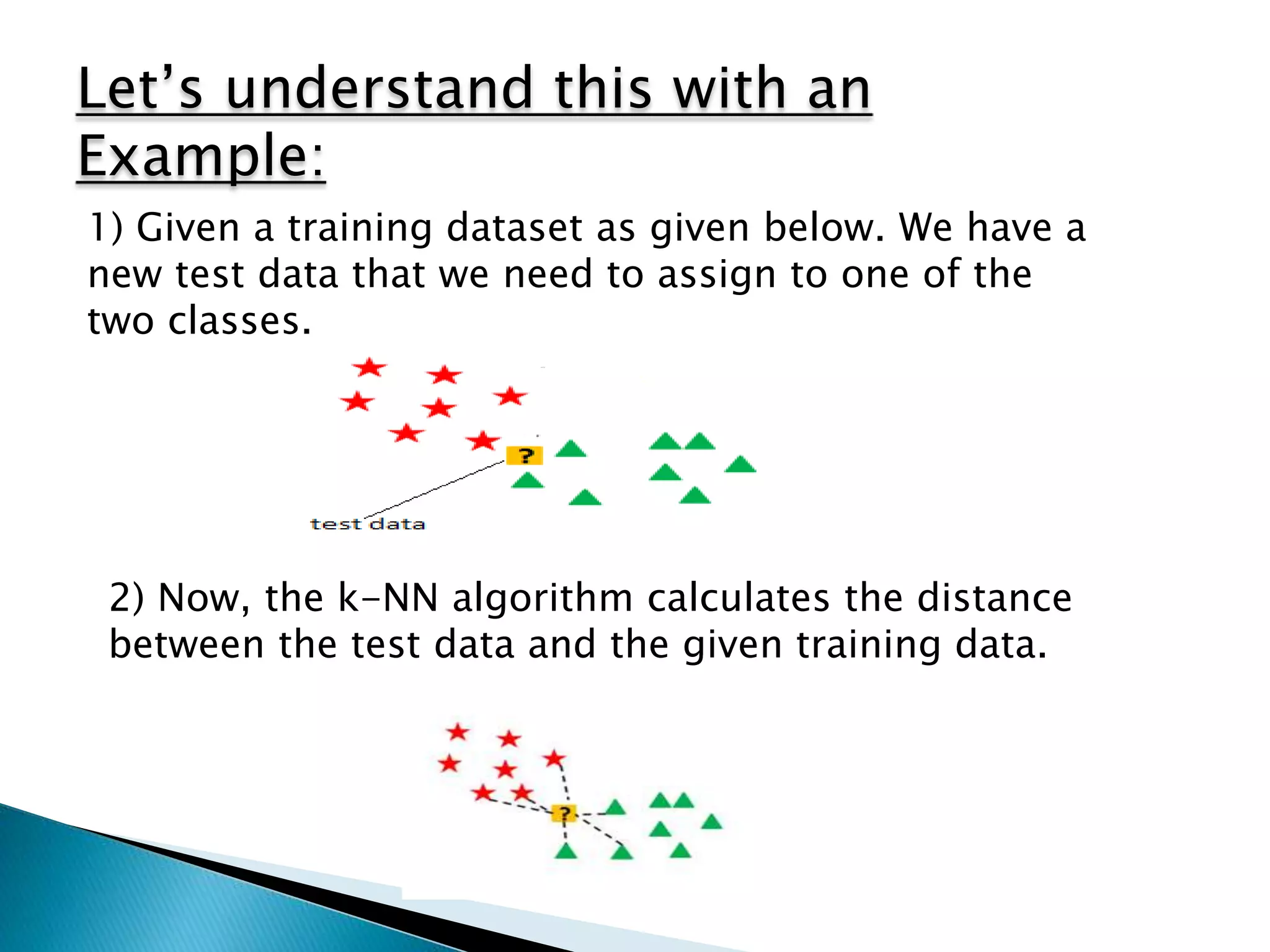
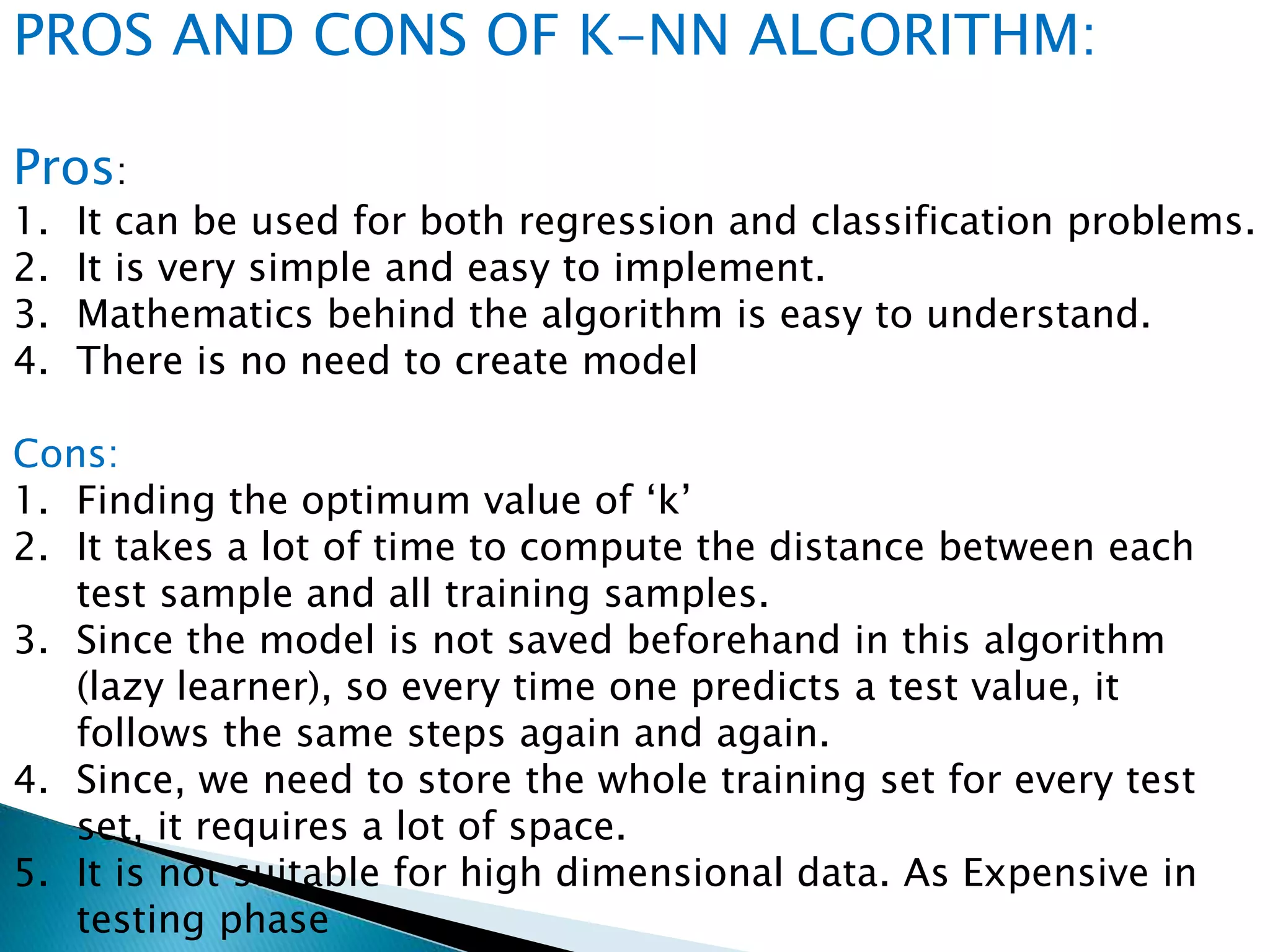
This document provides an overview of the K-nearest neighbors (KNN) machine learning algorithm. It defines KNN as a supervised learning method used for both regression and classification. The document explains that KNN finds the k closest training examples to a test data point and assigns the test point the majority class of its neighbors (for classification) or the average of its neighbors (for regression). An illustrative example is provided. Key properties of KNN discussed include distance metrics, choosing k, and that it is a lazy learner. The pros and cons of KNN are summarized. Finally, the document states it will provide an implementation of KNN on a diabetes dataset.