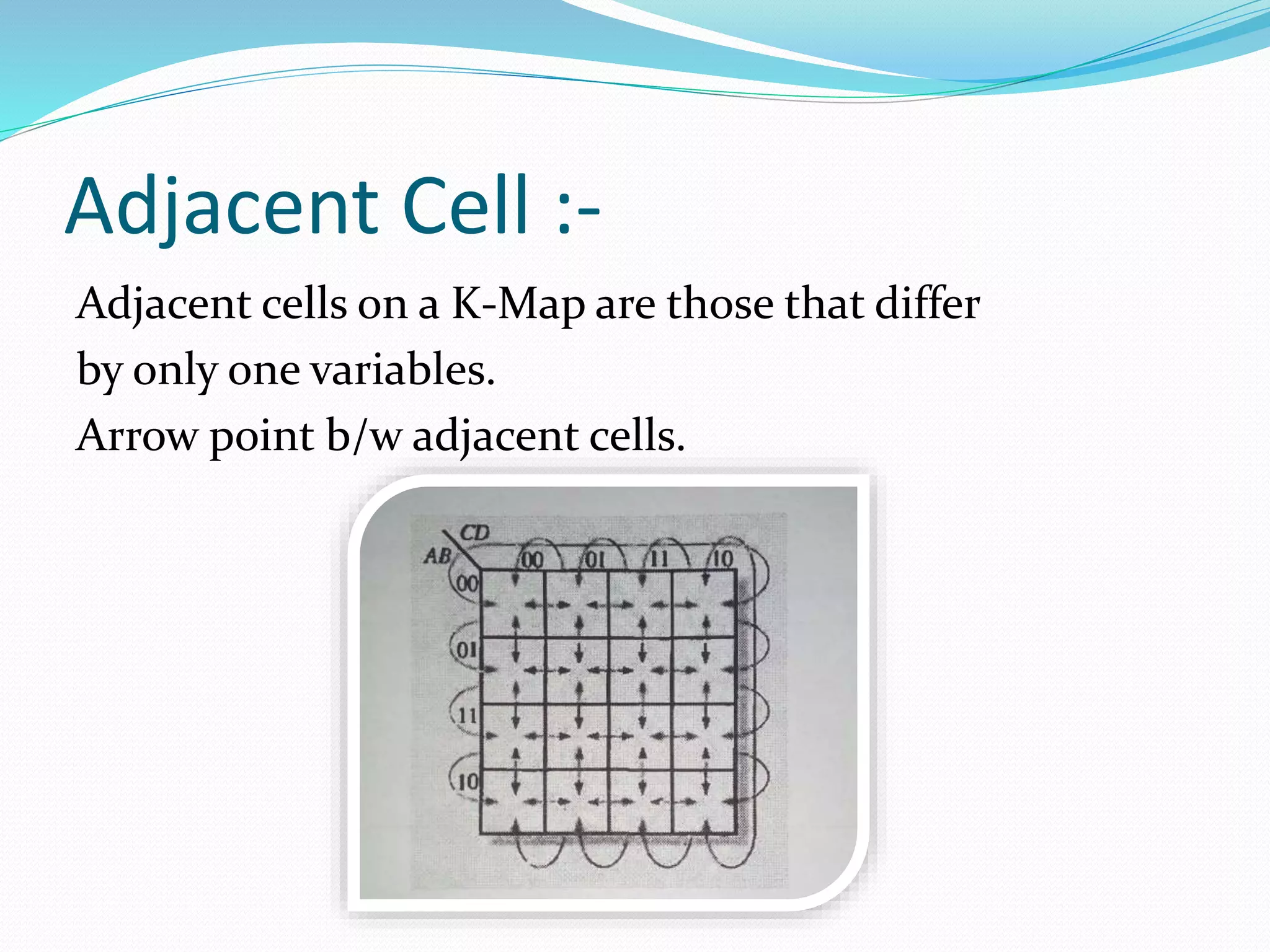
Karnaugh maps (K-maps) are graphical representations used to simplify Boolean algebra expressions. K-maps arrange variables in a grid with cells representing combinations. Adjacent cells differ by one variable. Expressions are plotted on K-maps by placing 1's in cells for each product term. Adjacent 1's can be grouped to form new product terms, simplifying the expression. K-maps exist for 2, 3, and 4 variables. "Don't care" conditions represented by X allow further simplification by ignoring unspecified minterms.