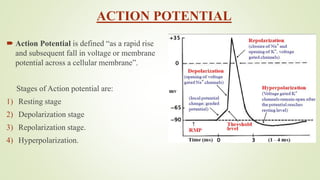
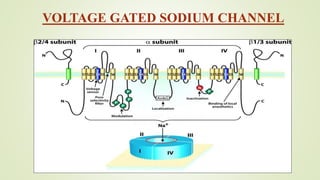
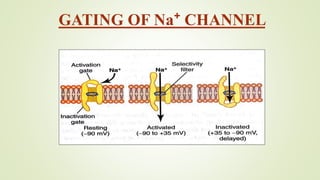
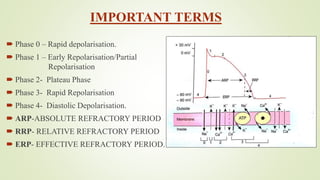
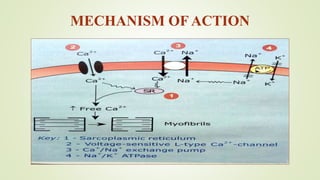
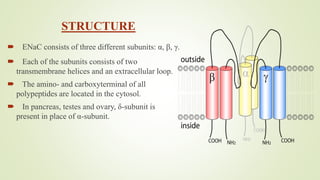
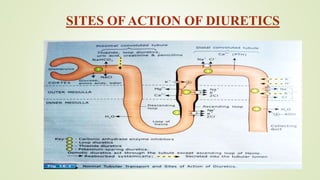
This document discusses sodium channel modulators. It begins by explaining ion channels and their role in establishing concentration gradients across cell membranes. It then focuses on sodium channels, describing the main types which include voltage-gated sodium channels. Voltage-gated sodium channels are responsible for generating action potentials in neurons and other excitable cells. The document explains the structure and gating of voltage-gated sodium channels, and how they play a role in the stages of the action potential. It discusses various drugs that can act as activators or blockers of sodium channels, including local anesthetics and class I antiarrhythmic agents. Finally, it briefly covers ligand-gated sodium channels such as nicotinic acetylcholine receptors