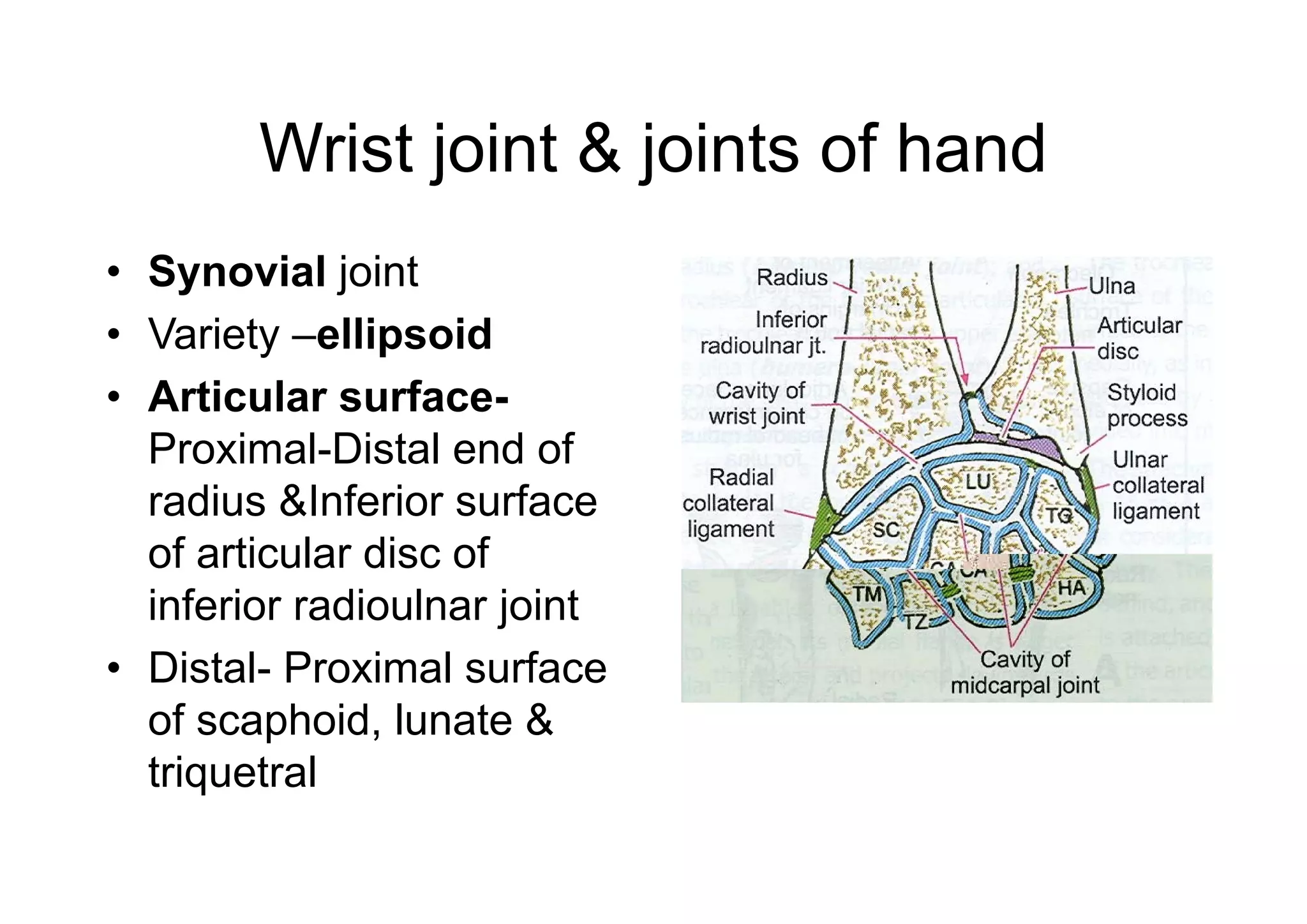
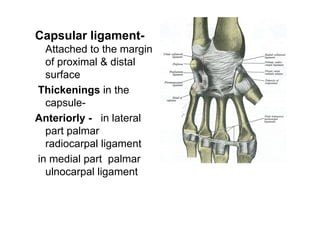
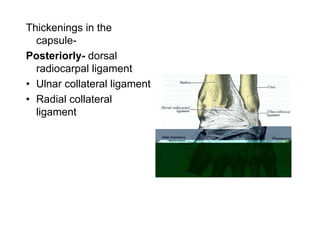
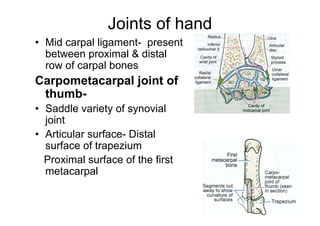
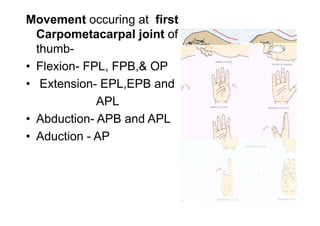
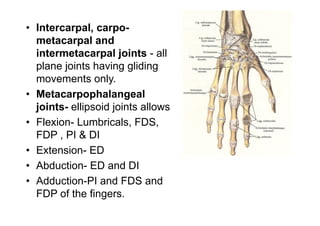
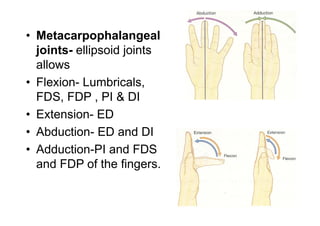
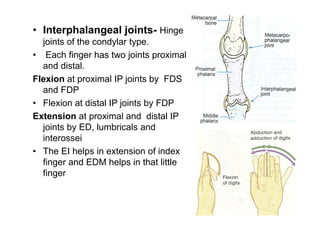
The document describes the anatomy of the wrist joint and joints of the hand. It notes that the wrist joint is a synovial ellipsoid joint that allows flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction. It is supported by collateral ligaments and surrounded by a capsular ligament. The joints of the hand include carpometacarpal, intercarpal, carpometacarpal, intermetacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints, each with their own movements and ligamentous support. Muscles are also described that facilitate the various movements at each joint.