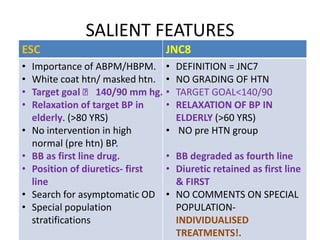
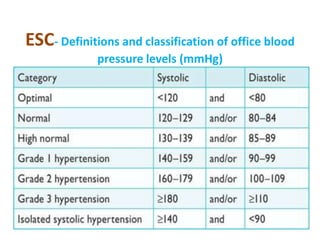
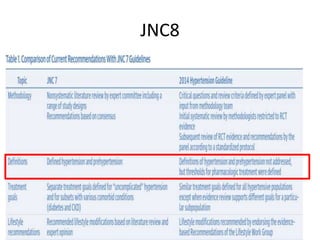
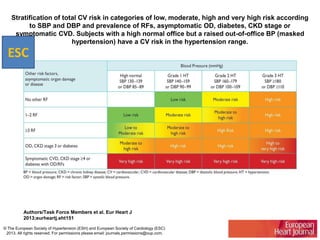
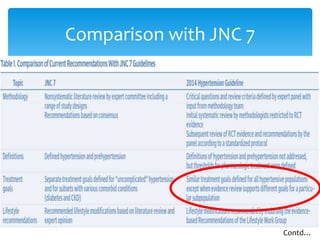
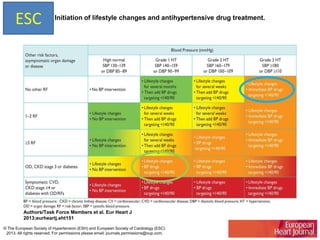
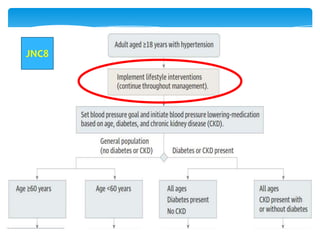
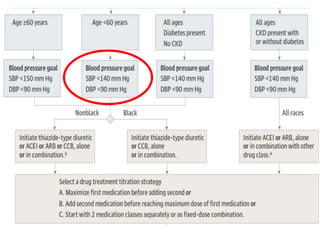
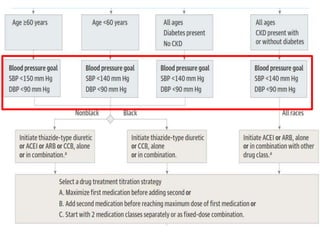
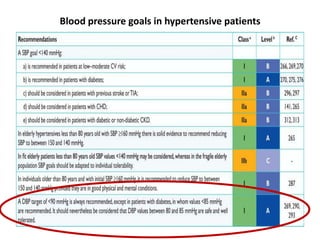
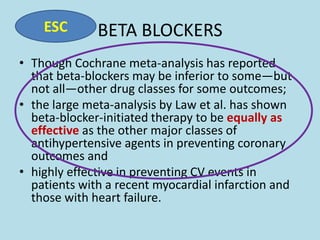
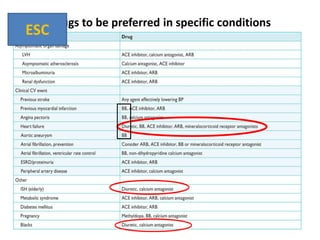
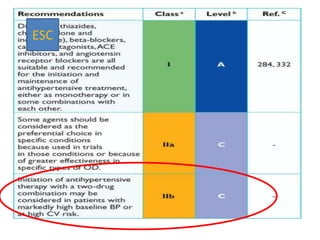
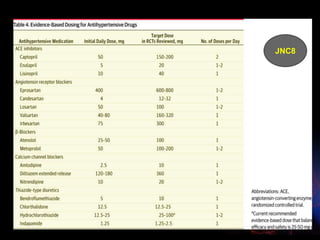
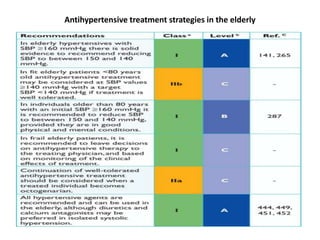
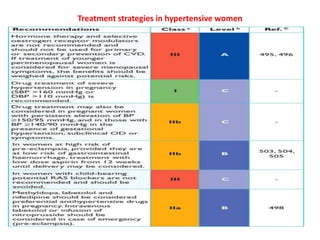
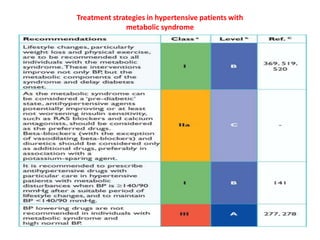
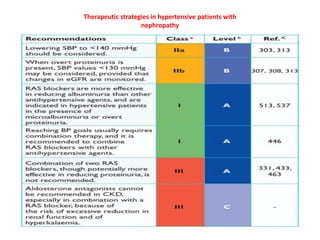
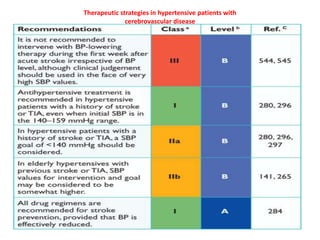
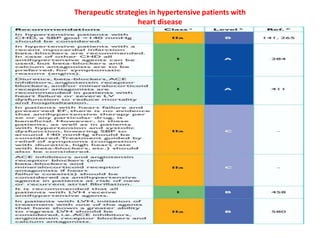
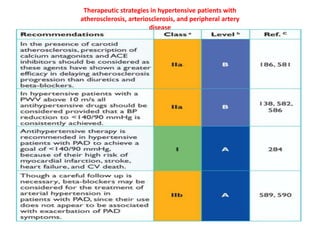
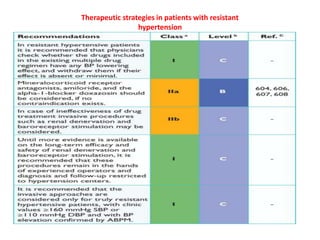
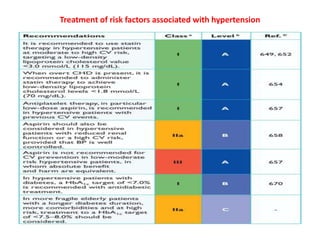
The document compares the 2013 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) hypertension guidelines to the 2014 Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8) guidelines. Some key differences include: ESC defines pre-hypertension while JNC 8 does not, ESC recommends lifestyle changes for pre-hypertension while JNC 8 does not, and ESC recommends beta-blockers as first-line treatment while JNC 8 recommends thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or CCBs as first-line based on clinical trials. Both guidelines relax blood pressure targets for elderly patients over 60 or 80 years old, respectively.