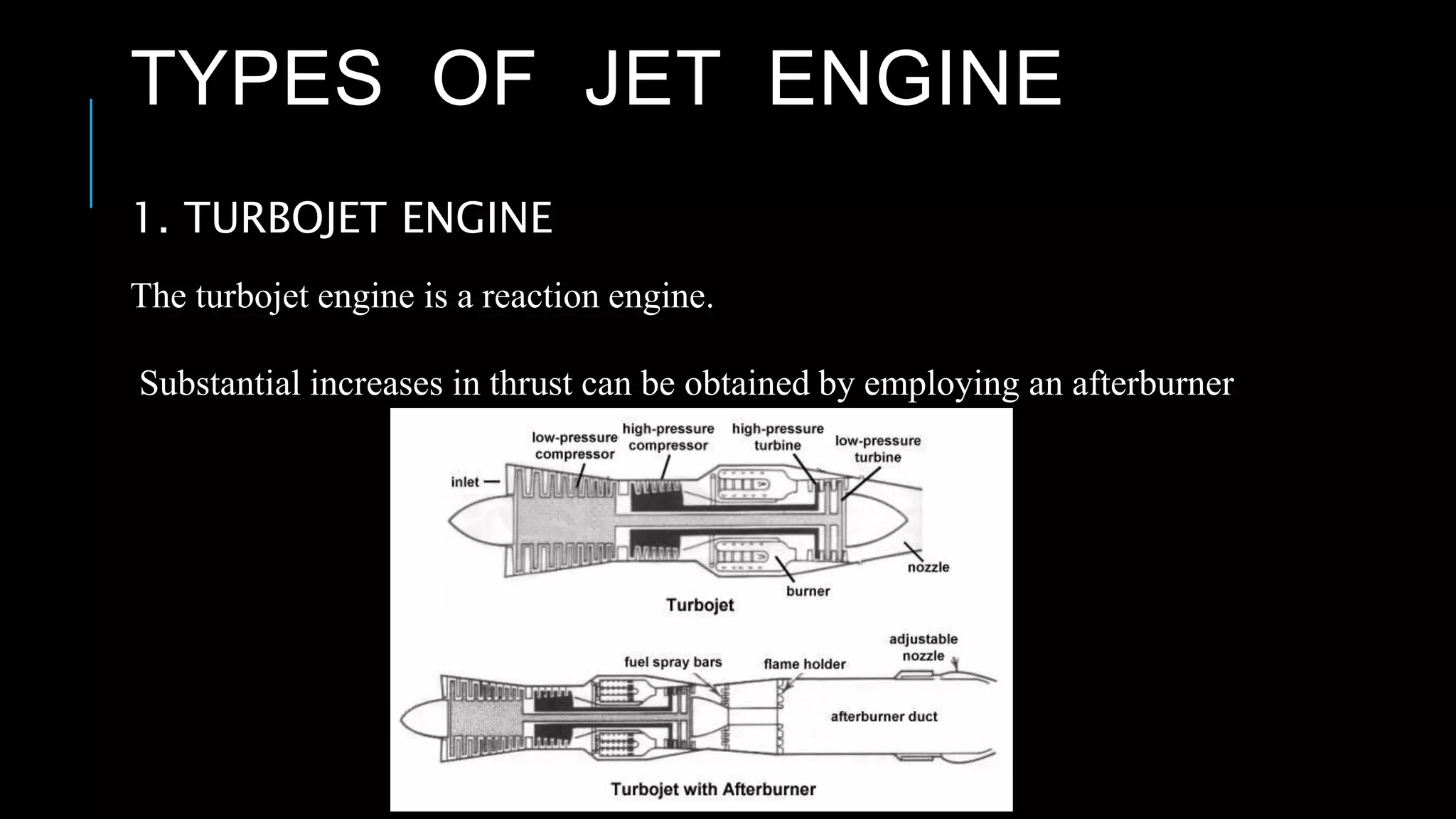
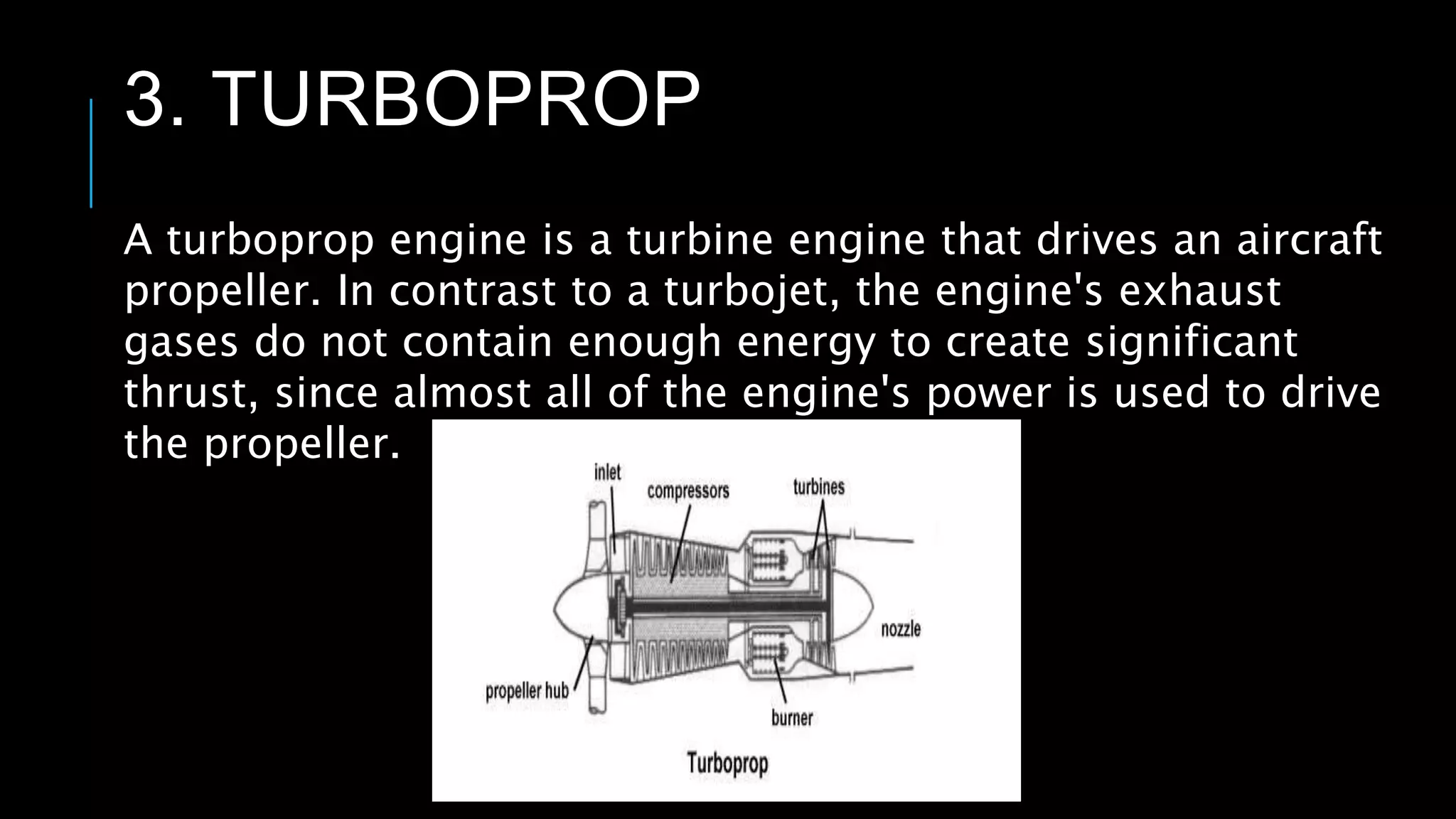
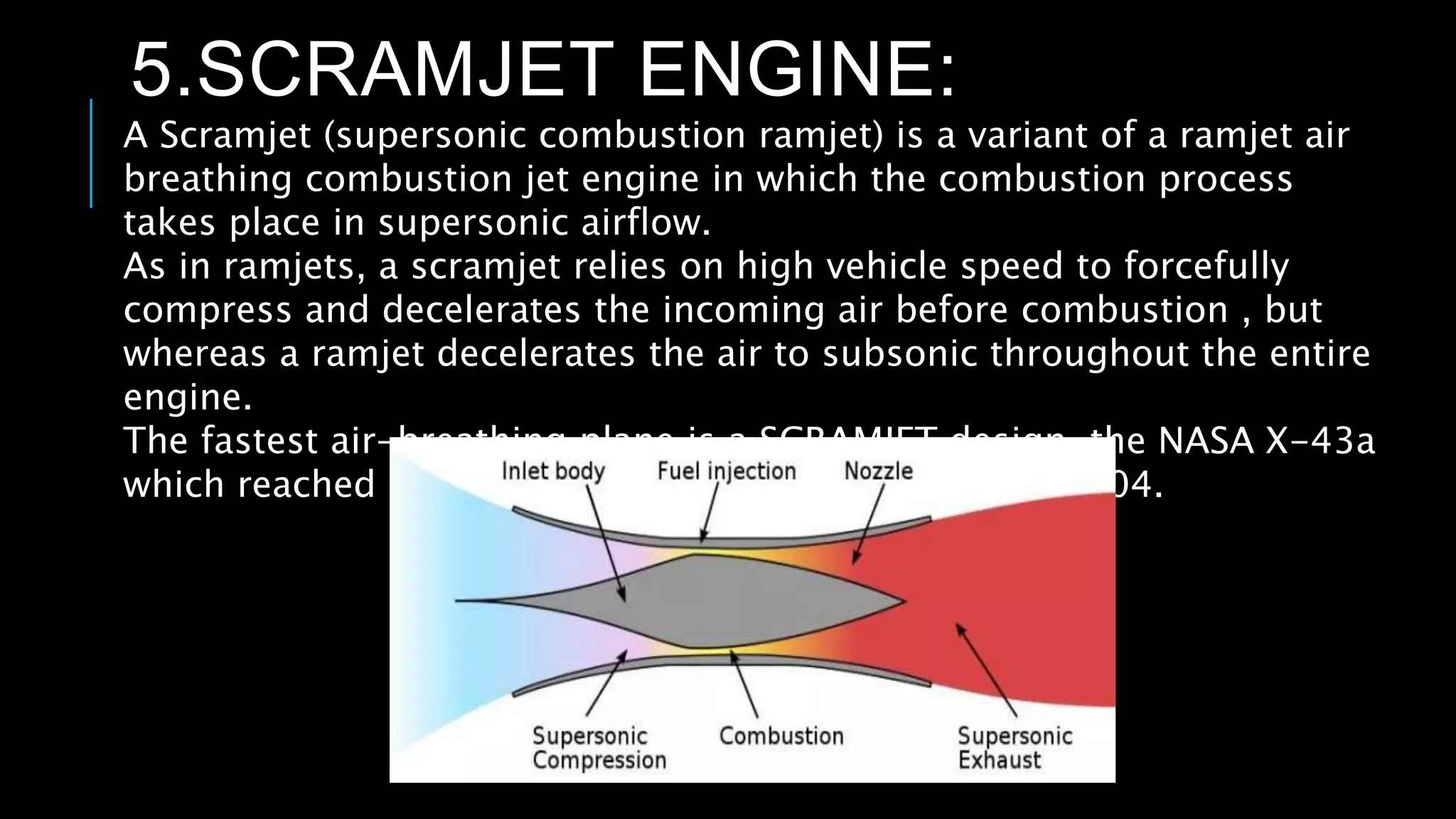
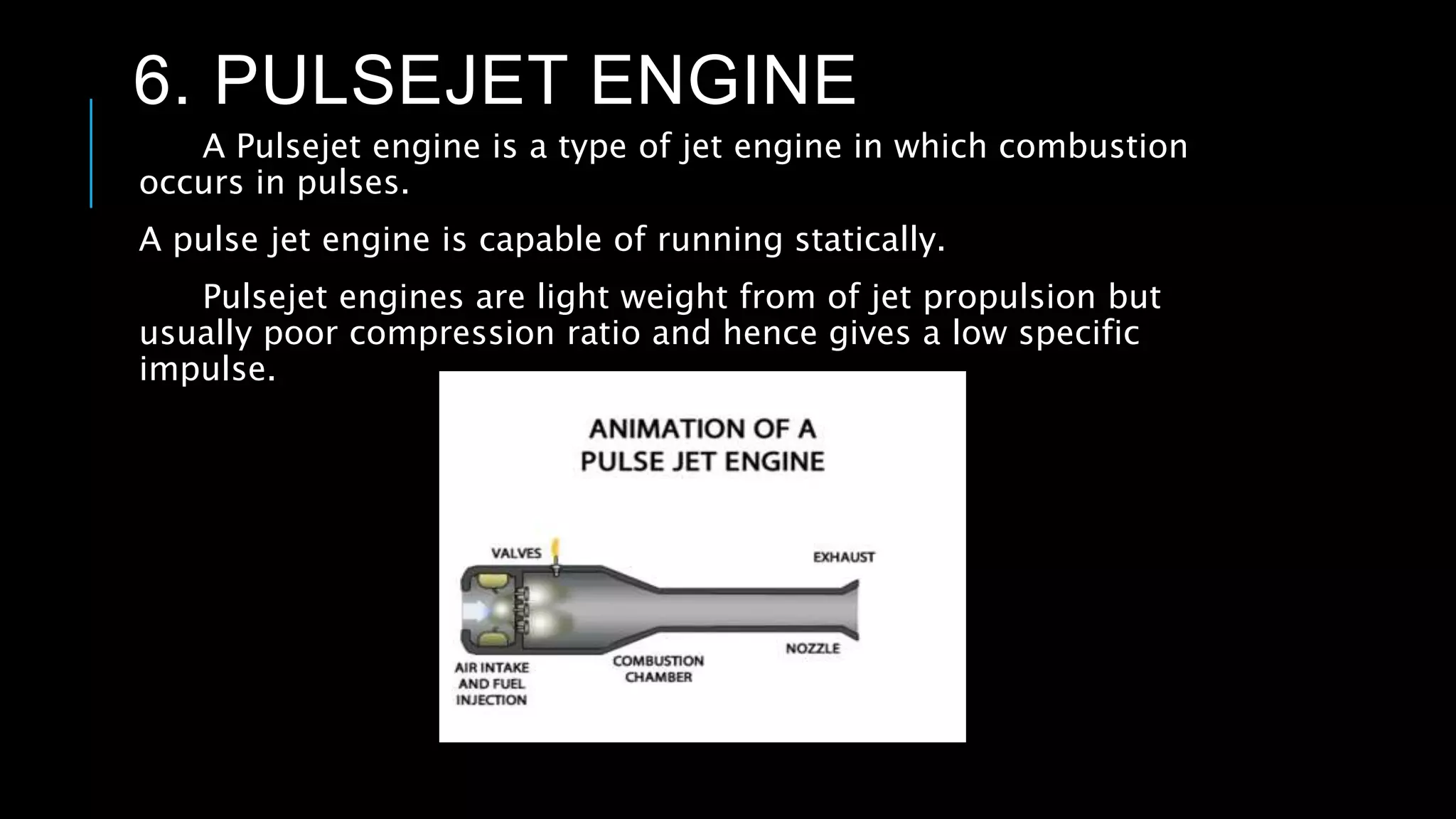
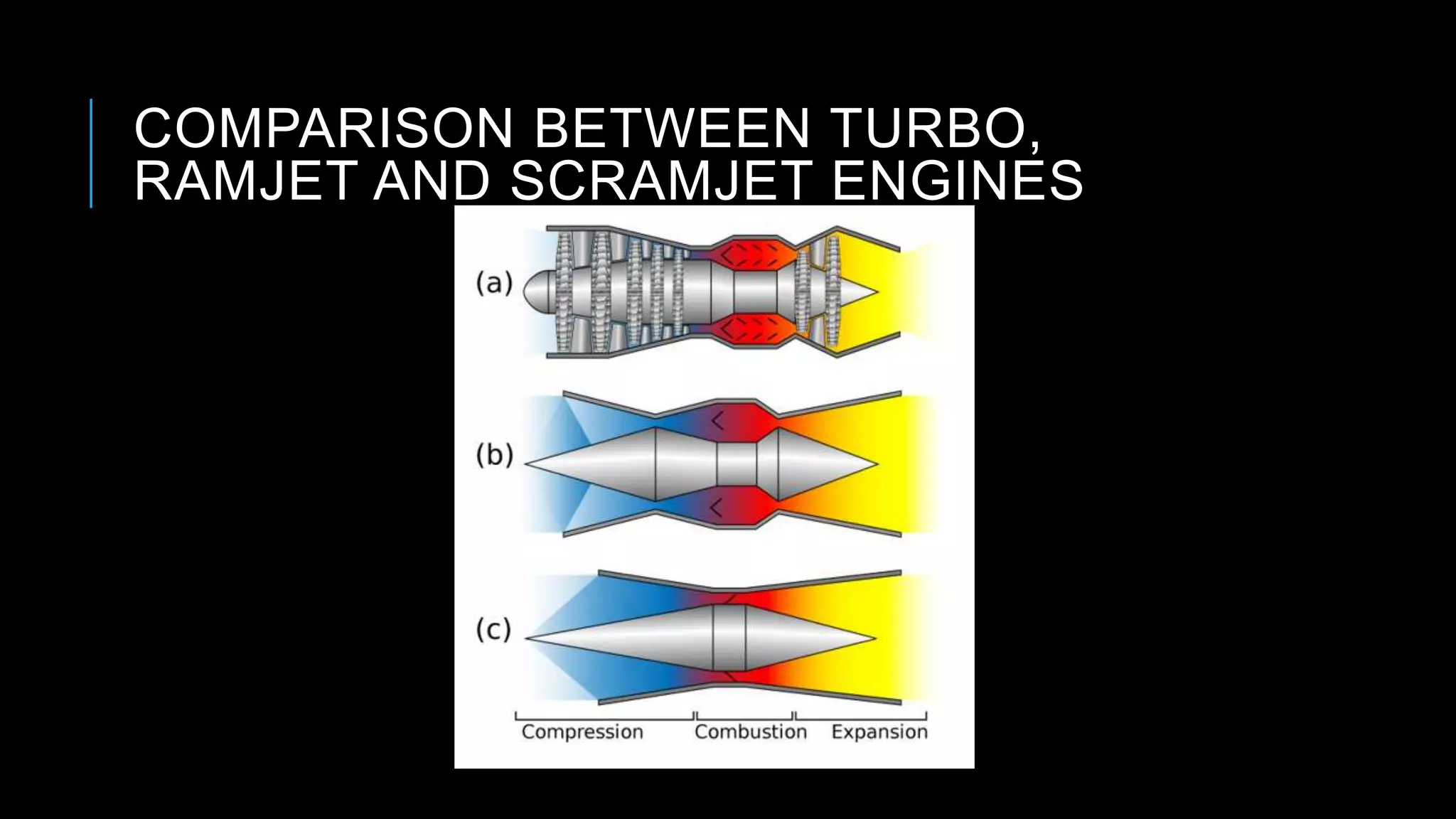
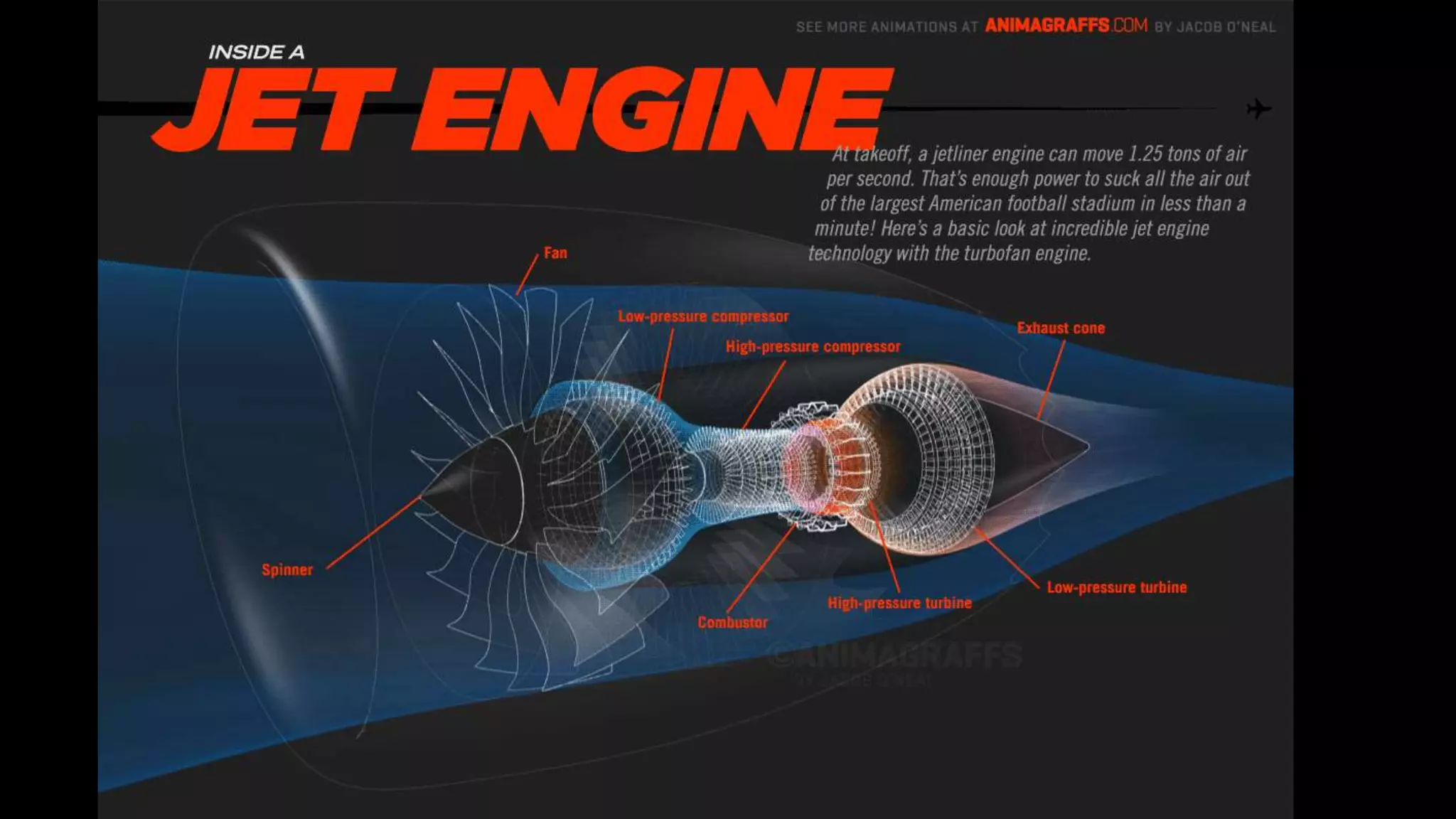
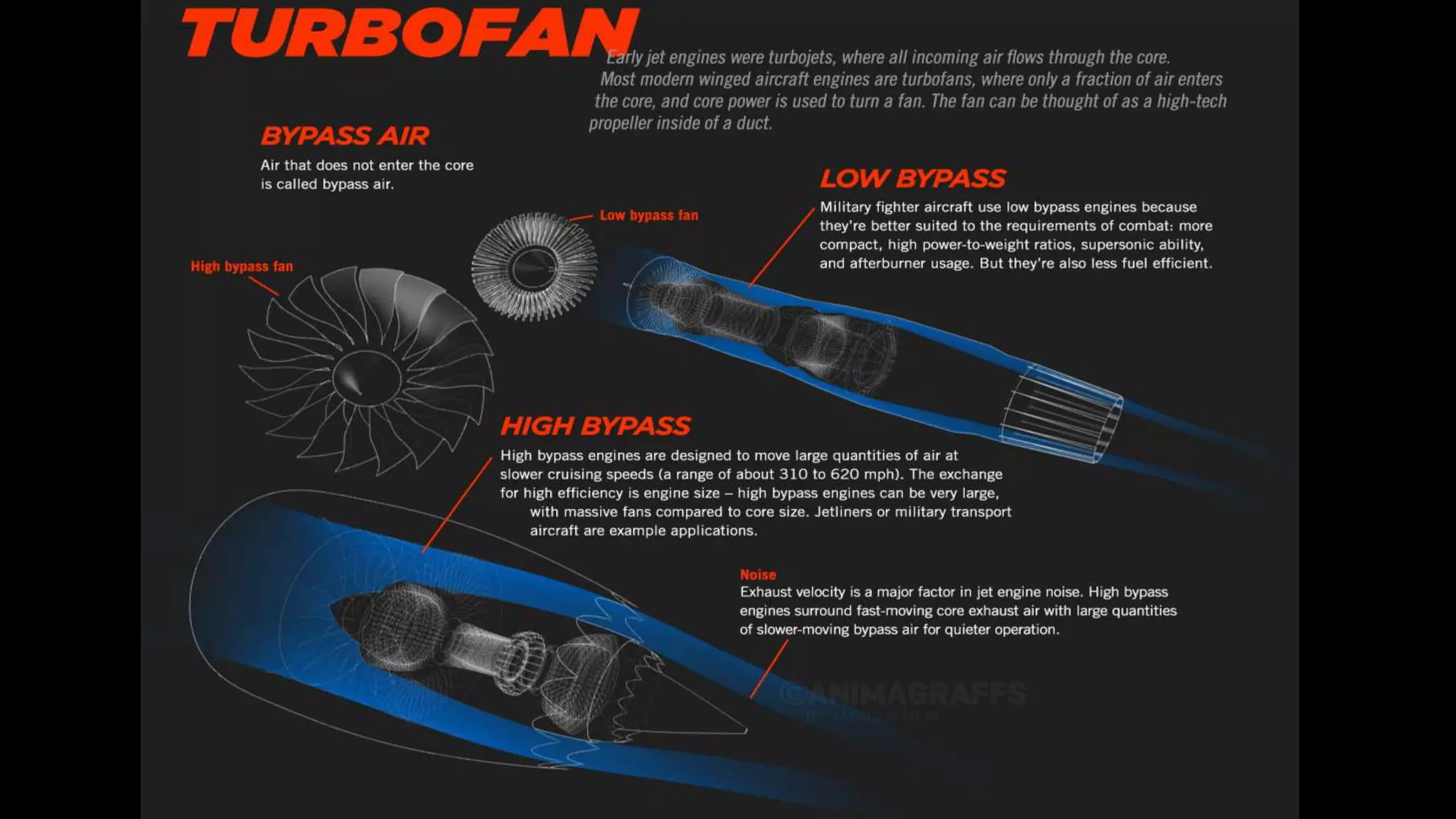
This presentation summarizes the key aspects of jet engines. It introduces jet engines as reaction engines that generate thrust from ejecting a fast moving jet of exhaust gases according to Newton's laws of motion. The principle of jet engines is then explained based on Newton's second and third laws of motion. Finally, the presentation describes the main types of jet engines - turbojet, turbofan, turboprop, ramjet, scramjet, and pulsejet - and provides a comparison of turbojet, ramjet, and scramjet engines.