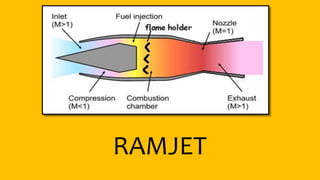
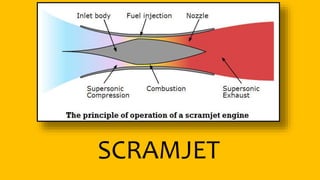
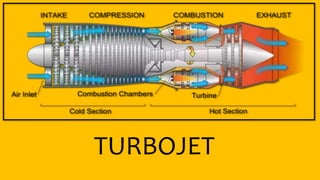
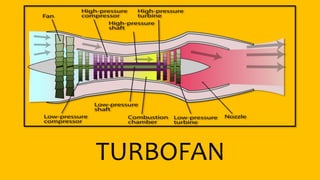
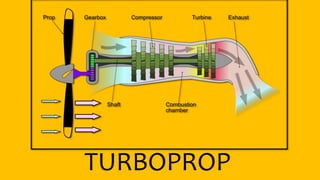
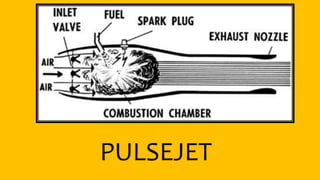
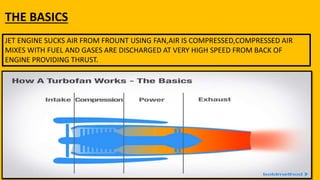
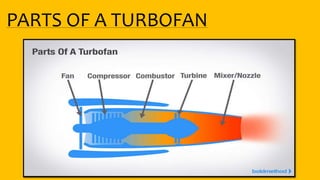
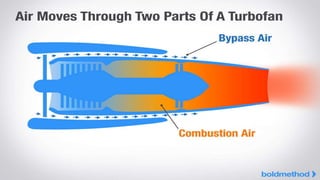
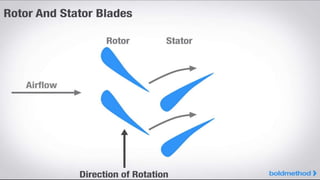
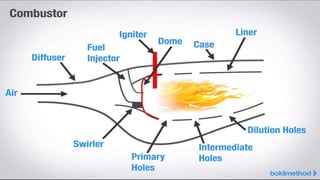
This document provides an overview of the turbofan jet engine, including its basic workings and key components. It explains that a turbofan engine works by sucking in air using a fan, compressing the air, mixing it with fuel and combusting it to discharge hot gases through the turbine and nozzle, generating thrust. It then describes the main parts of a turbofan engine in more detail: the fan, compressor, combustor, turbine and nozzle.