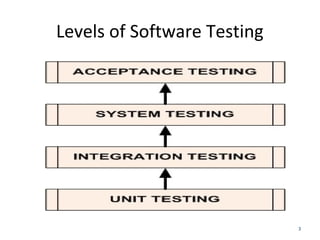
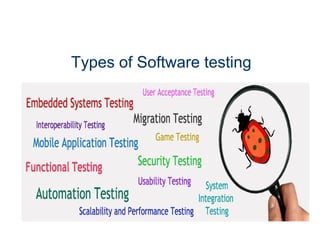
This document discusses different types of software testing including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing, functional testing, non-functional testing, user interface testing, usability testing, accessibility testing, localization testing, performance testing, load testing, stress testing, compatibility testing, cross-browser testing, security testing, negative testing, re-testing, and regression testing. It provides details on the purpose and goals of each testing type.