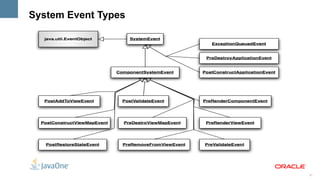
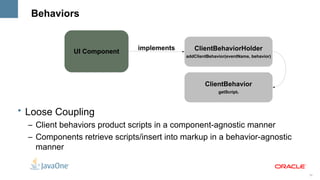
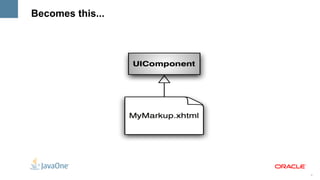
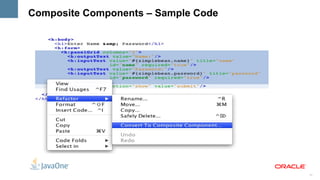
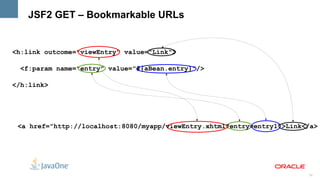
The document outlines the key features and enhancements of Java Server Faces 2.0, including improved ease of development through Facelets and composite components, integrated Ajax support, HTTP GET support, validation integration with Bean Validation, and runtime performance improvements through partial state saving and behaviors. It provides code samples to illustrate many of the new capabilities.

















![Validation – Sample Code
<h:inputText value="#{address.zip}">
<f:validateBean validationGroups="myGroup"/>
</h:inputText>
<h:input id="zip" value="#{address.zip}">
<f:validateRequired />
</h:input>
<h:input id="zip" value="#{address.zip}" required=”true”/>
<h:input id="zip" value="#{address.zip}">
<f:validateRegex pattern="/^d{5}([-]d{4})?$/" />
</h:input>
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneindia-2011-jsf2-110513122718-phpapp02/85/JavaServer-Faces-2-0-JavaOne-India-2011-27-320.jpg)

![Resource EL – Sample Code
• Syntax
– #{resource['<resource>']}
– #{resource['<library>:<resource>']}
• Examples of use
– <a href="#{resource['header.jpg']}"/>
– <h:graphicImage value="#{resource['corp:header.jpg']}"/>
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneindia-2011-jsf2-110513122718-phpapp02/85/JavaServer-Faces-2-0-JavaOne-India-2011-29-320.jpg)