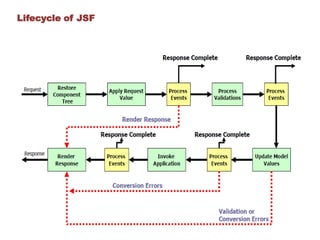
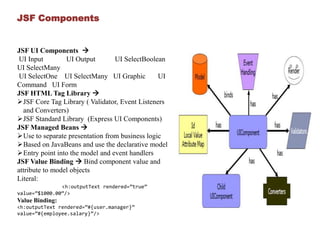
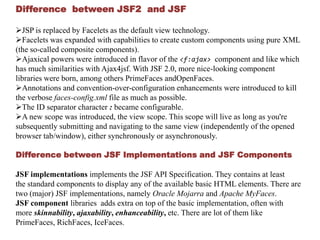
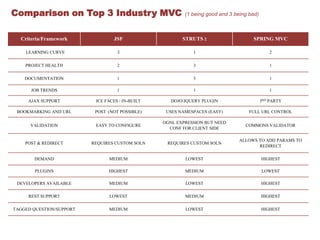
Java Server Faces (JSF) is a component-based MVC framework for building user interfaces in Java web applications. JSF provides UI components that can be used in JSP or Facelets views. It follows a request response lifecycle where the controller handles gathering input, validating, updating models, and rendering responses. Popular JSF components include inputs, outputs, selects, forms, and commands. Facelets is the default view technology in JSF 2 and provides templating capabilities. Key differences between JSF and JSF 2 include replacing JSP with Facelets and adding Ajax and annotation support. Spring MVC has the highest demand and documentation quality while Struts 2 has the lowest learning curve and JSF is in