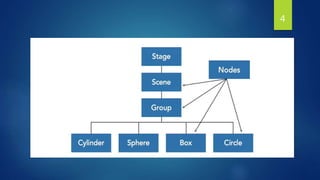
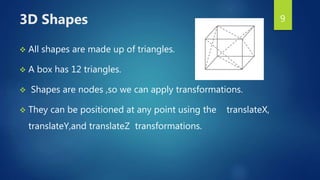
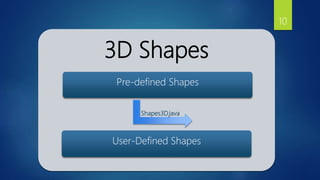
This document provides an overview of JavaFX 3D graphics. It discusses 3D shapes in JavaFX, how to add a camera and lighting, apply materials to shapes, and interact with 3D shapes. 3D shapes in JavaFX include boxes, spheres, and user-defined meshes. A camera must be added to view shapes in the third dimension. Lighting, including ambient and point lights, can be added to illuminate shapes. Materials use shading to mix light and color for a 3D effect. Interaction with 3D shapes allows manipulating them in the 3D scene.