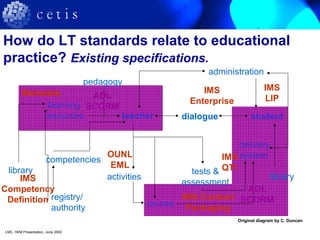
The document provides an overview of learning technology interoperability standards, detailing their development, importance in preventing content 'lock-in', and facilitating content reuse and sharing. It outlines various organizations involved in the creation of these standards, such as IMS Global Learning and the IEEE Learning Technology Standards Committee, and their specific focus areas. The CETIS supports the UK higher education sector in adopting these interoperability standards and tracks their relevance and implementation.