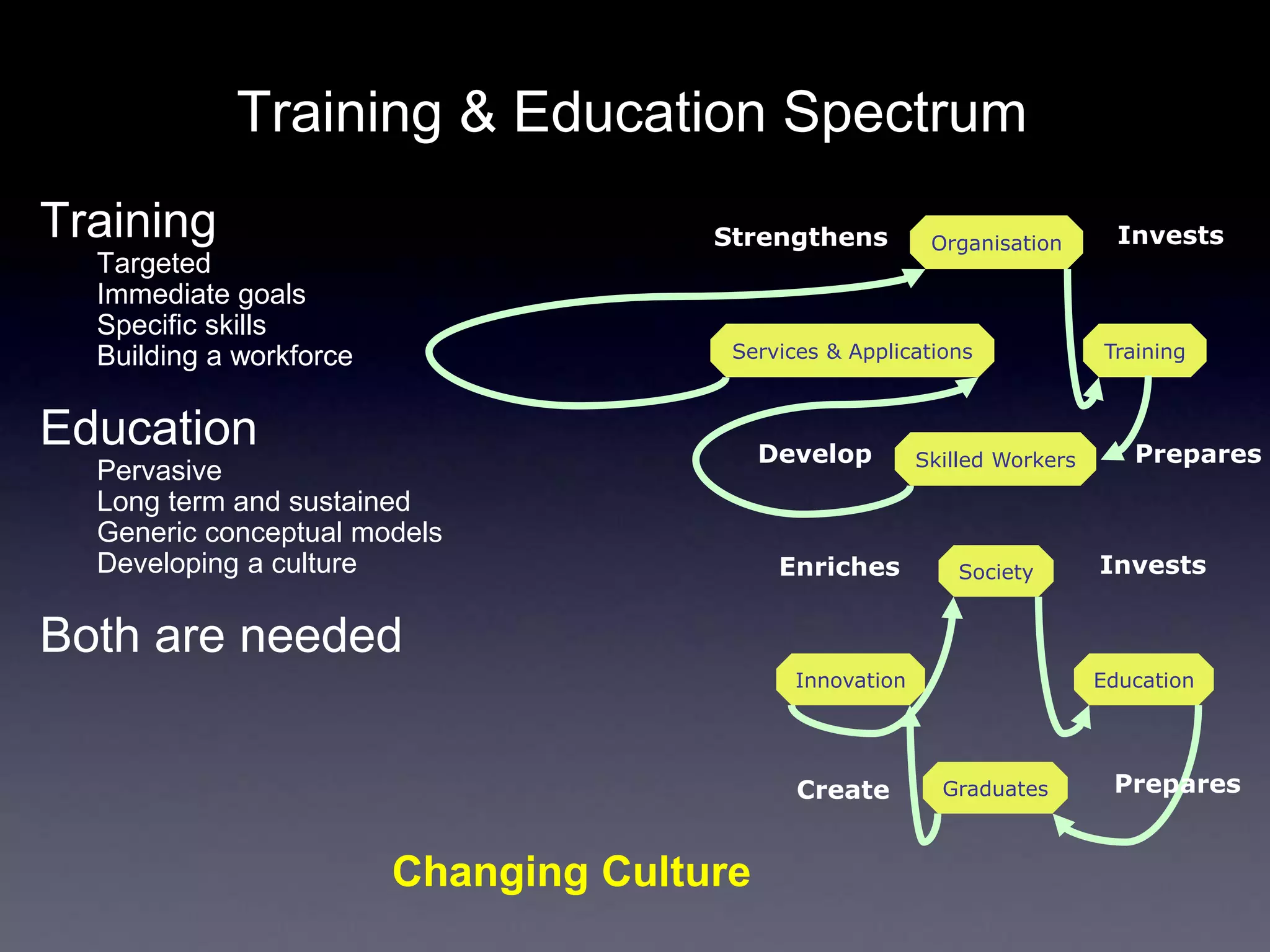
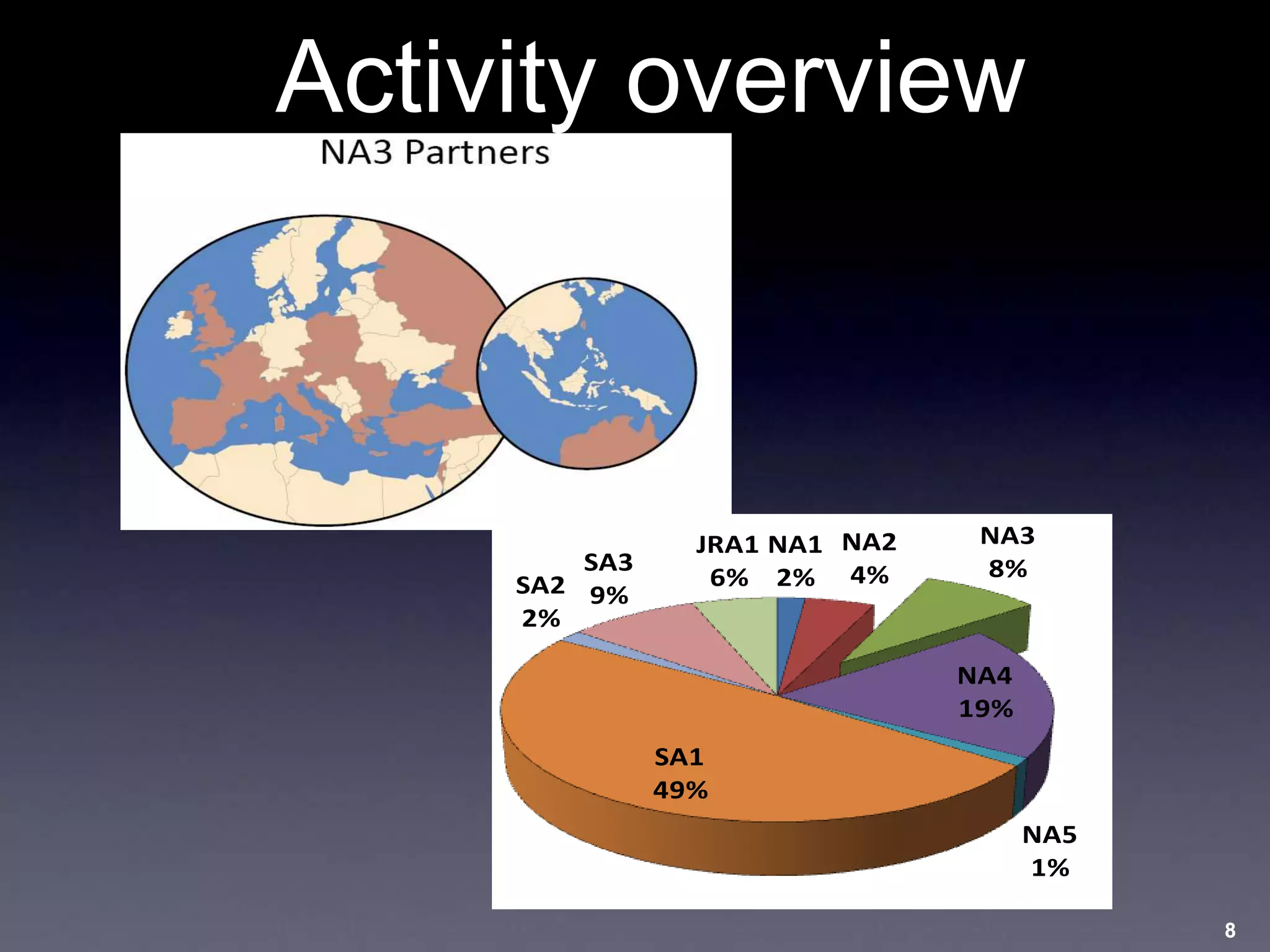
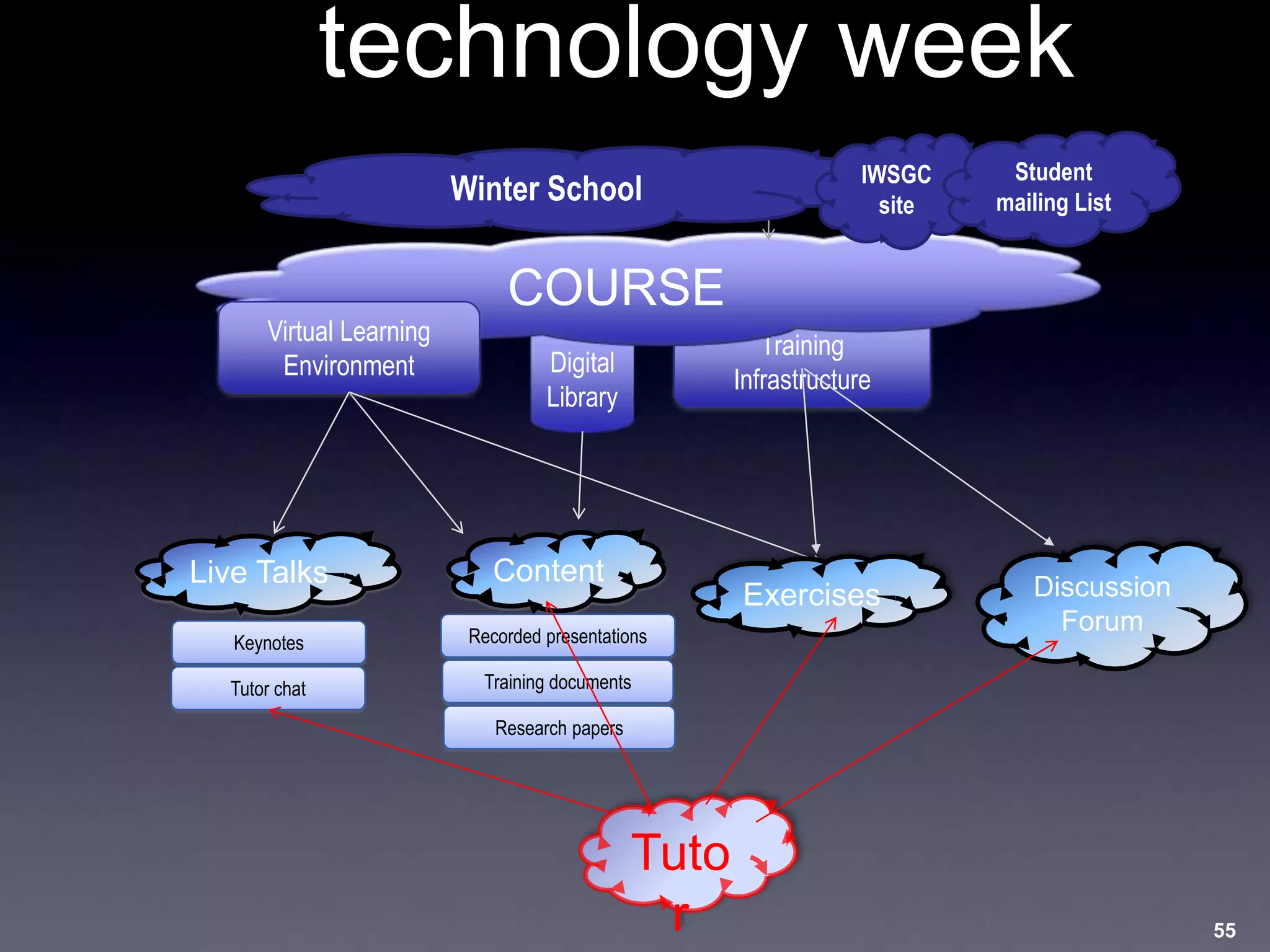
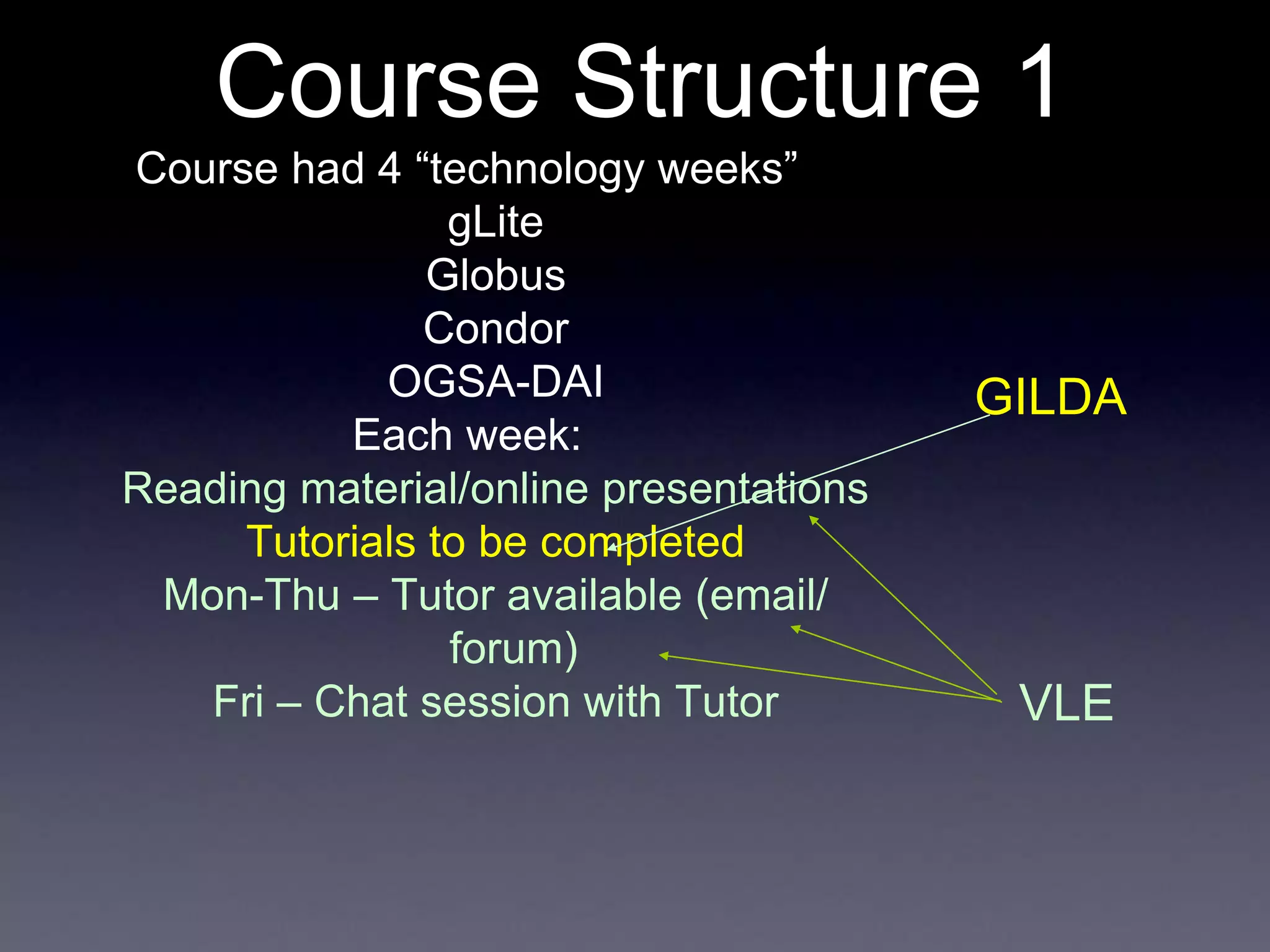
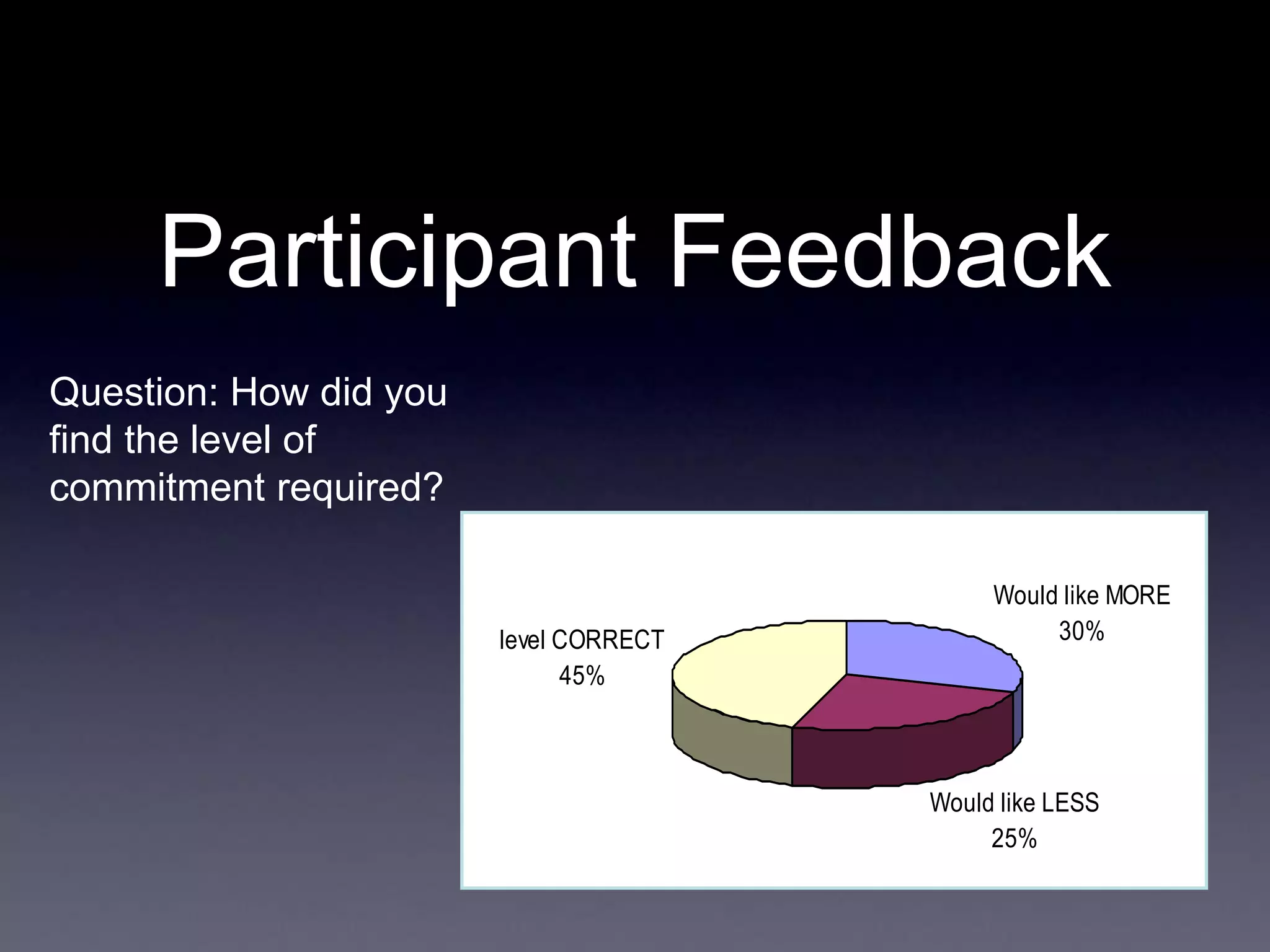
This document discusses experiences with training and technology transfer from an EU perspective regarding opportunities and challenges with cloud computing. It summarizes a European project focused on building skills through training courses in various locations worldwide. Key activities included developing online training resources and services, conducting training events, and establishing an accredited trainer program. The document also describes efforts to develop sustainable training structures and resources like a digital library as cloud computing emerges.

































![Barrier: Lack of
Awareness
Description: There seems to be a lack of systematic introduction to the services
and the training available, which results in a lack of awareness as well as a a
lack of understanding of how services and methods can facilitate research
and what different options exist.
Examples:
[MR02], [EP02], [AH04]
“one barrier is not having heard of these things” [AH03]
Candidate responses:
Boundary spanning
Opportunities for learning about e-Research / e-Infrastructure
Systematic training of young researchers
Typology:
Social Issues / Training, Education and Outreach / Early Engagement & Outreach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tien3-101114172941-phpapp02/75/Tien3-38-2048.jpg)
![Enabler: Boundary
Spanning
Description: Boundary spanning refers to the moving of people
from one discipline to another. It can help transfer ideas,
knowledge and skills across disciplinary boundaries.
Example: As one Arts and Humanities researcher put it: “before
I was at [my current institution], I was at an engineering
department at [other institution] and so I was kind of aware of
a lot of these things that we are talking about – Access Grid,
e-Science.” [AH01]
Barriers addressed:
Lack of awareness of services
Typology
Social Issues / Individual / Career Choices
Training, Education and Outreach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tien3-101114172941-phpapp02/75/Tien3-39-2048.jpg)



























![NGS 3 EWP2
“NGS Agile Deployment Environments”
EPSRC funded, 2 years
People
Matteo Turilli (OeRC, Oxford) [0.75 FTE]
Steve Thorn (NeSC, Edinburgh) [0.5 FTE]
David Fergussion (NeSC, Edinburgh) [WP Leader]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tien3-101114172941-phpapp02/75/Tien3-70-2048.jpg)




