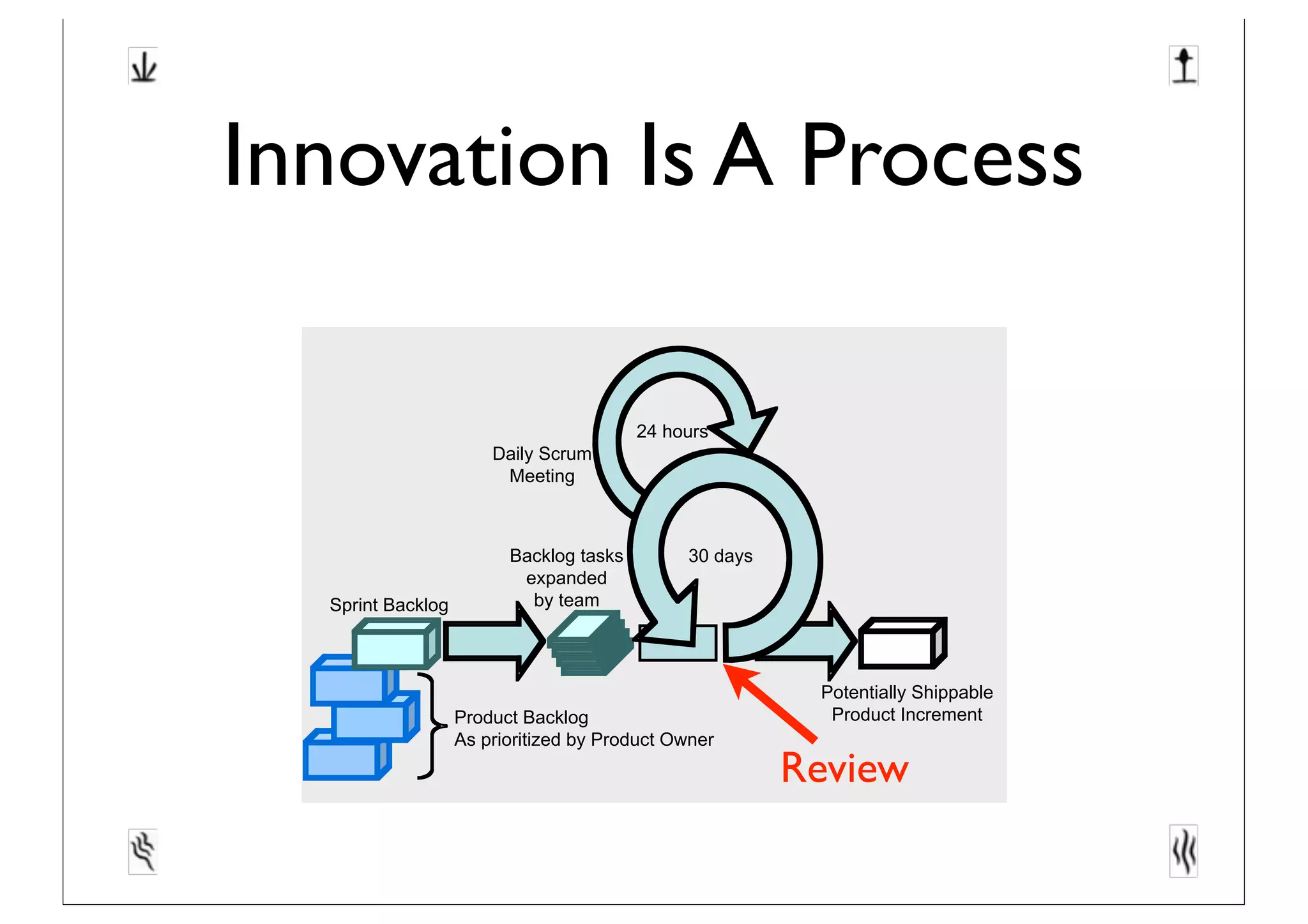
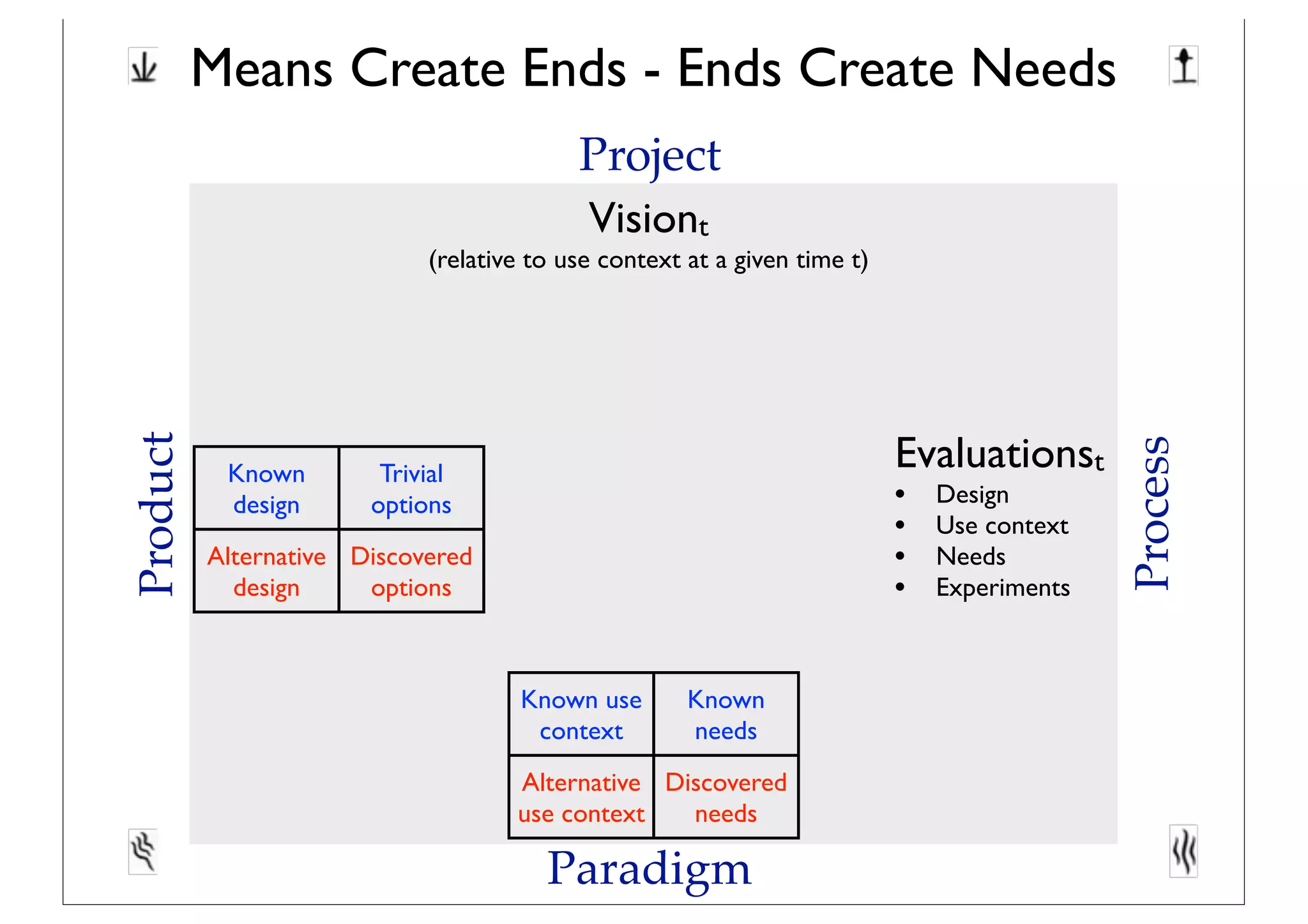
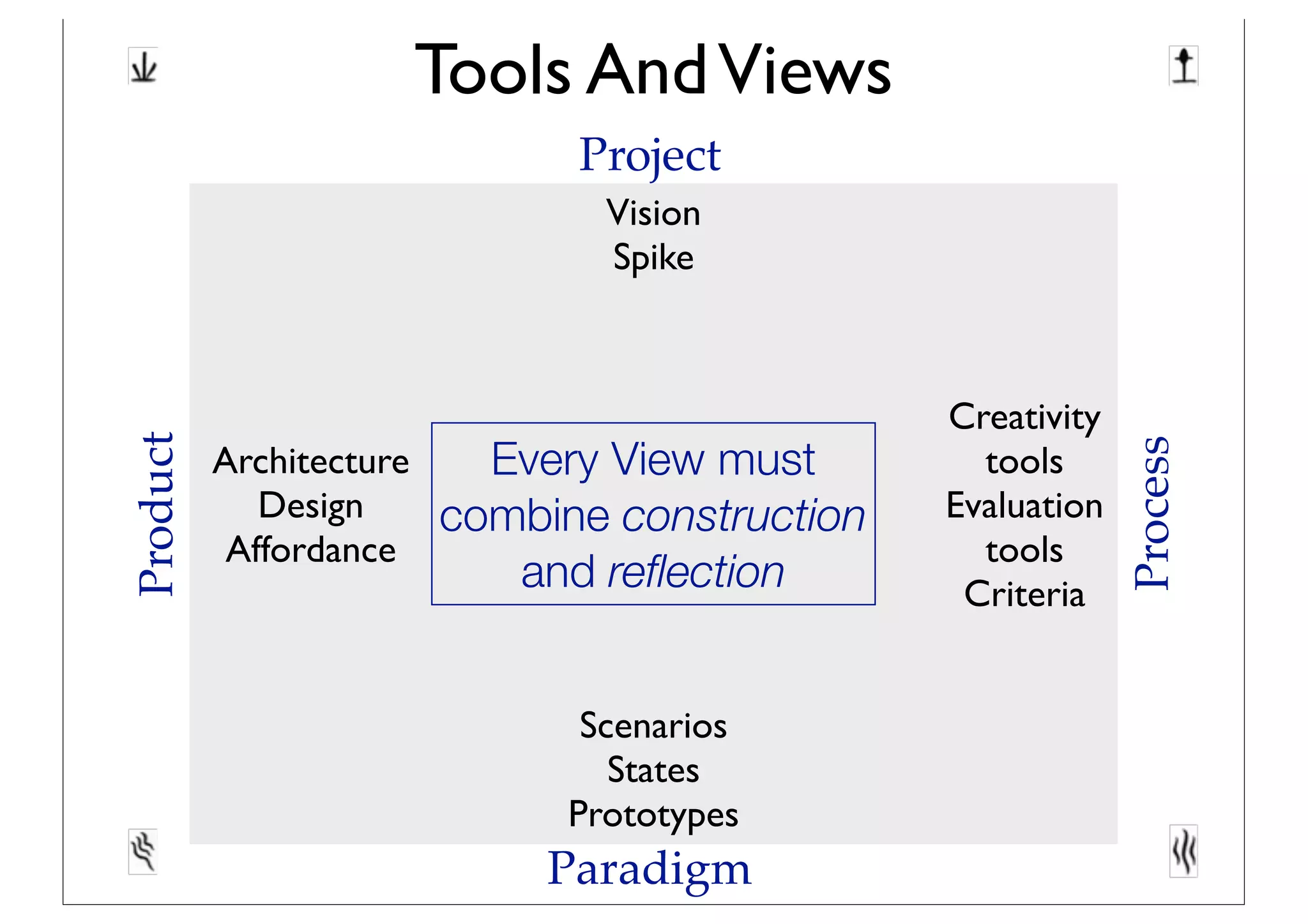
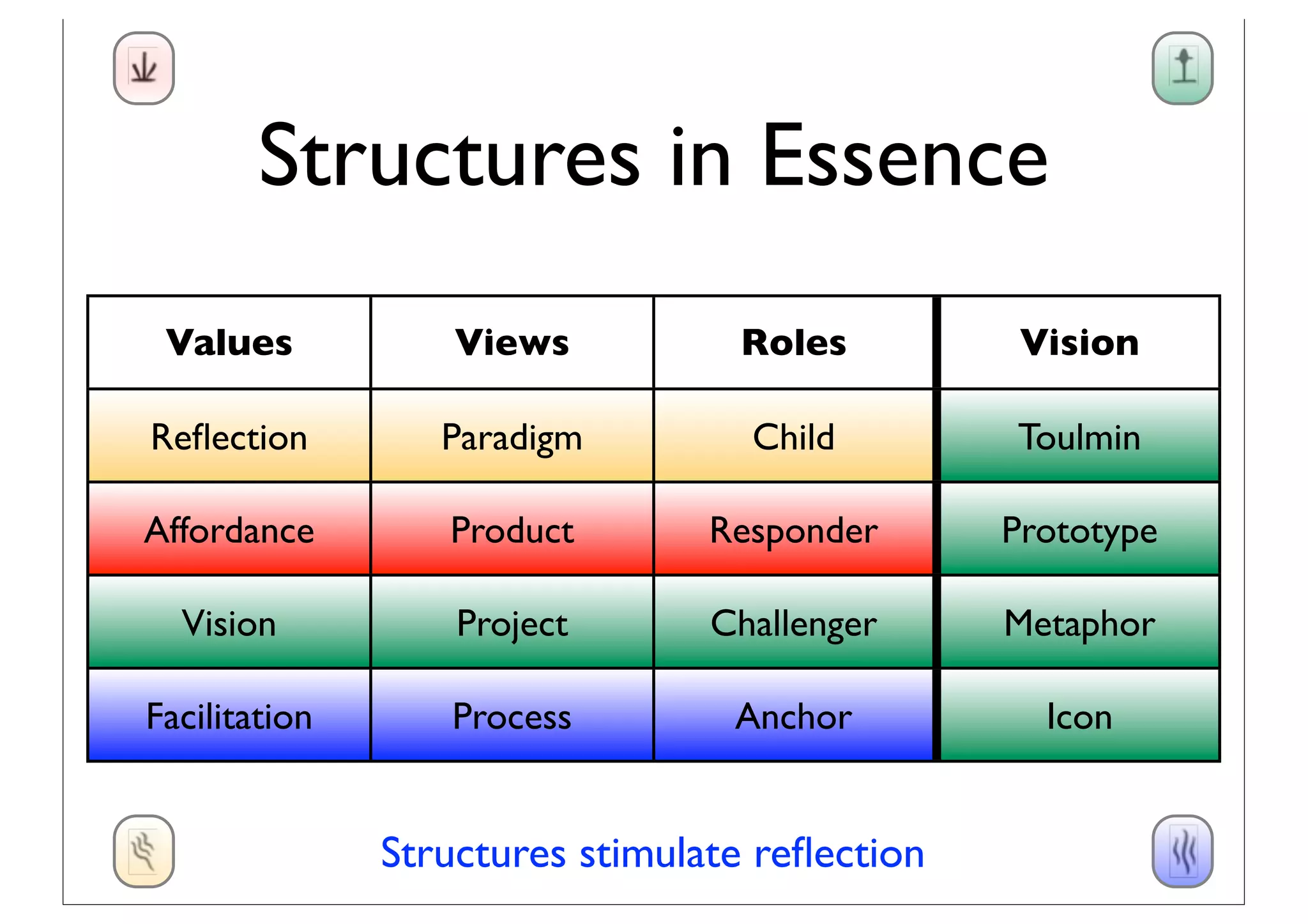
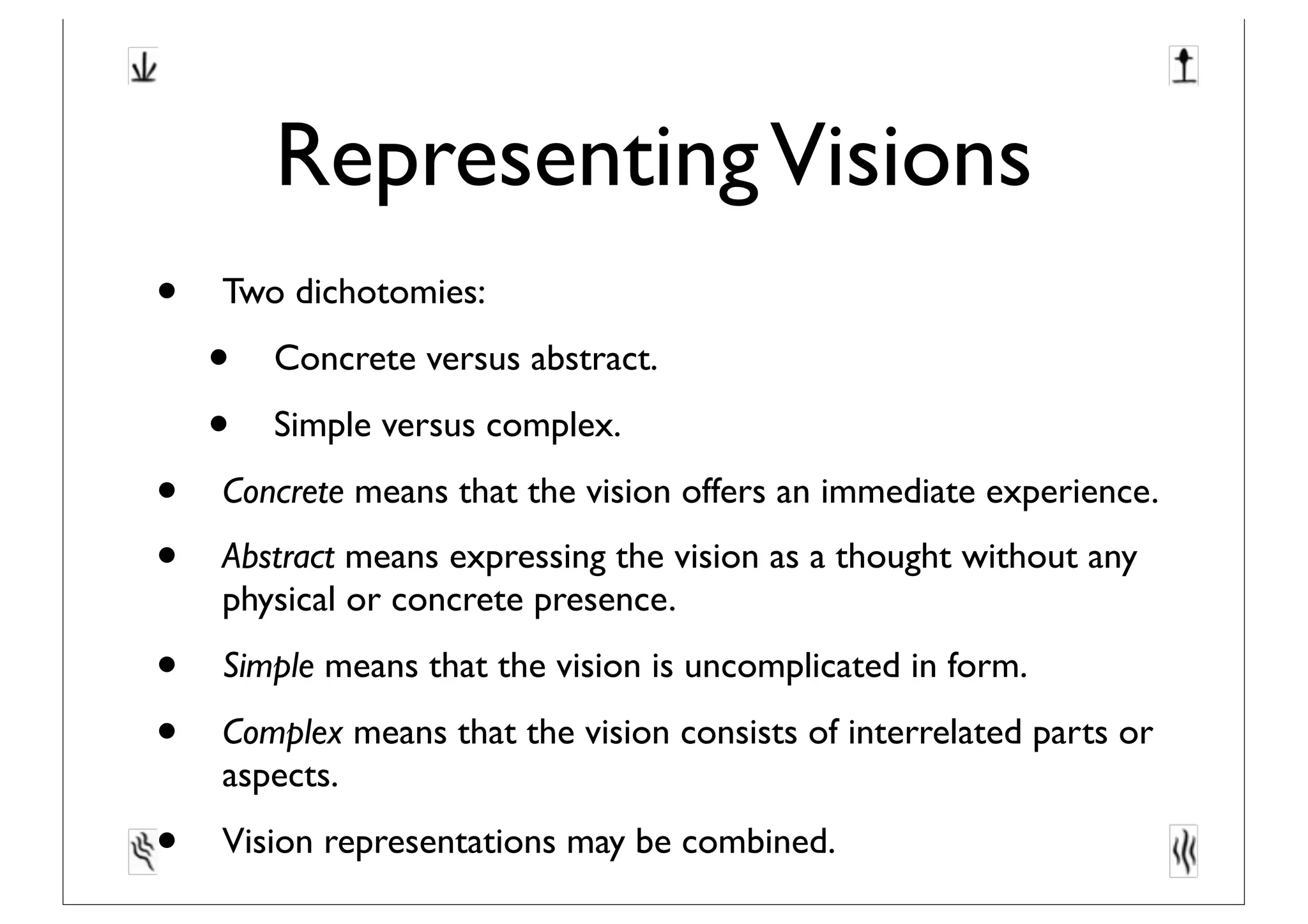
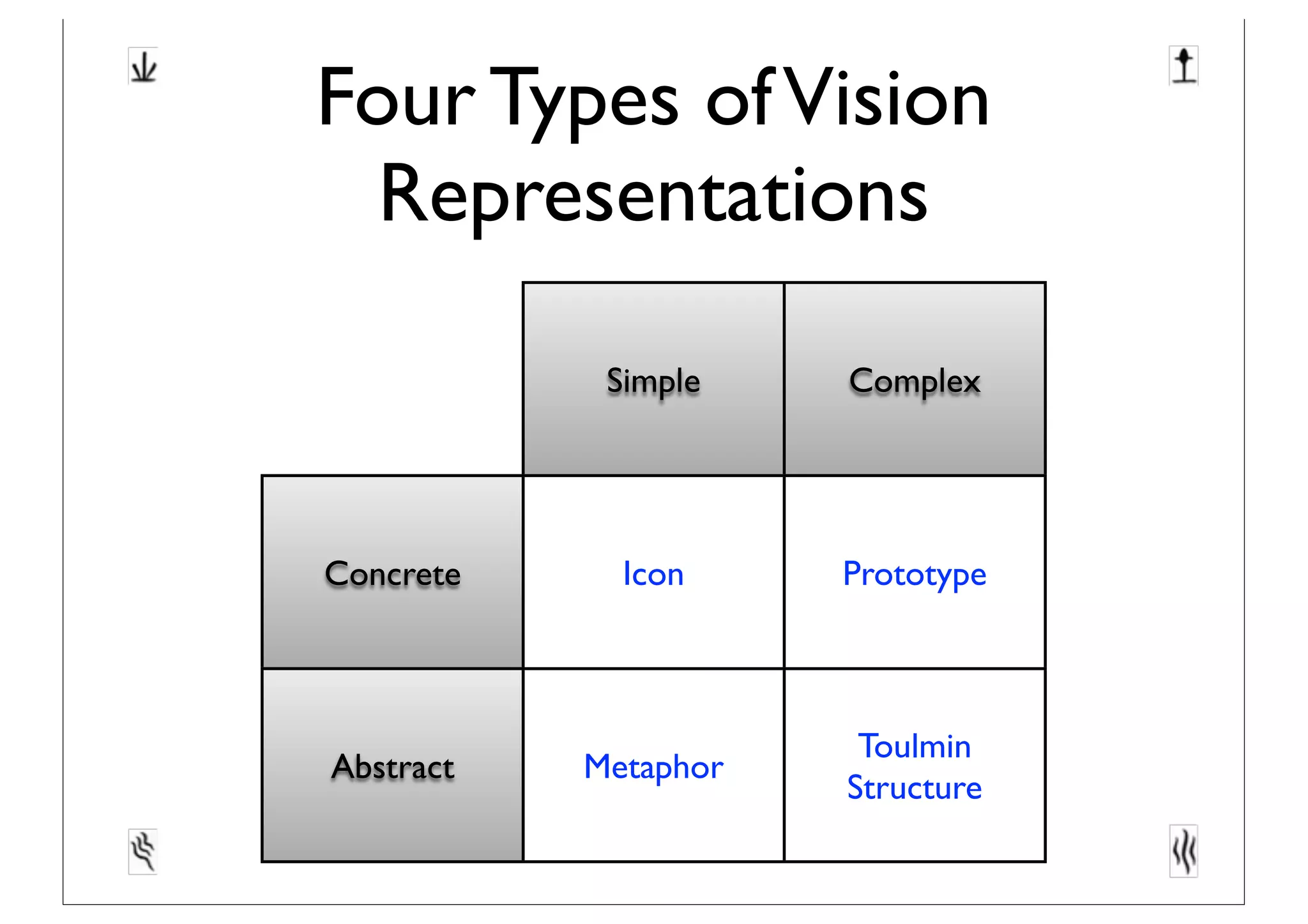
This document discusses software innovation and principles of agile development. It notes that innovation is a process involving a product backlog, sprints, daily standups, and incremental releases. It emphasizes discovering needs through experimentation and evaluating options. The document also discusses representing and maturing visions over time through various structures, including icons, prototypes, metaphors, and Toulmin structures, to facilitate team convergence. Visions should stimulate reflection and be both persistent yet dynamic.