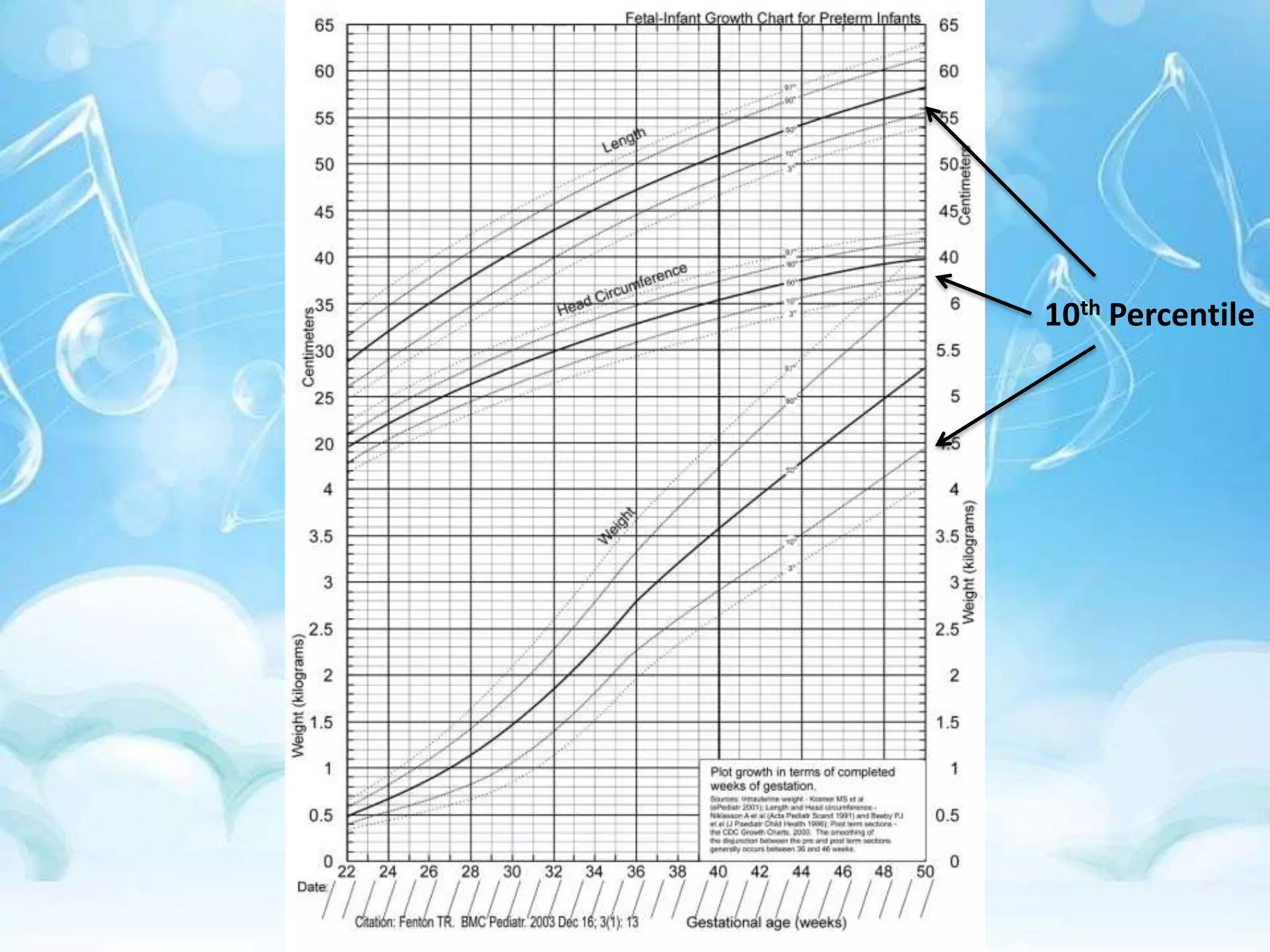
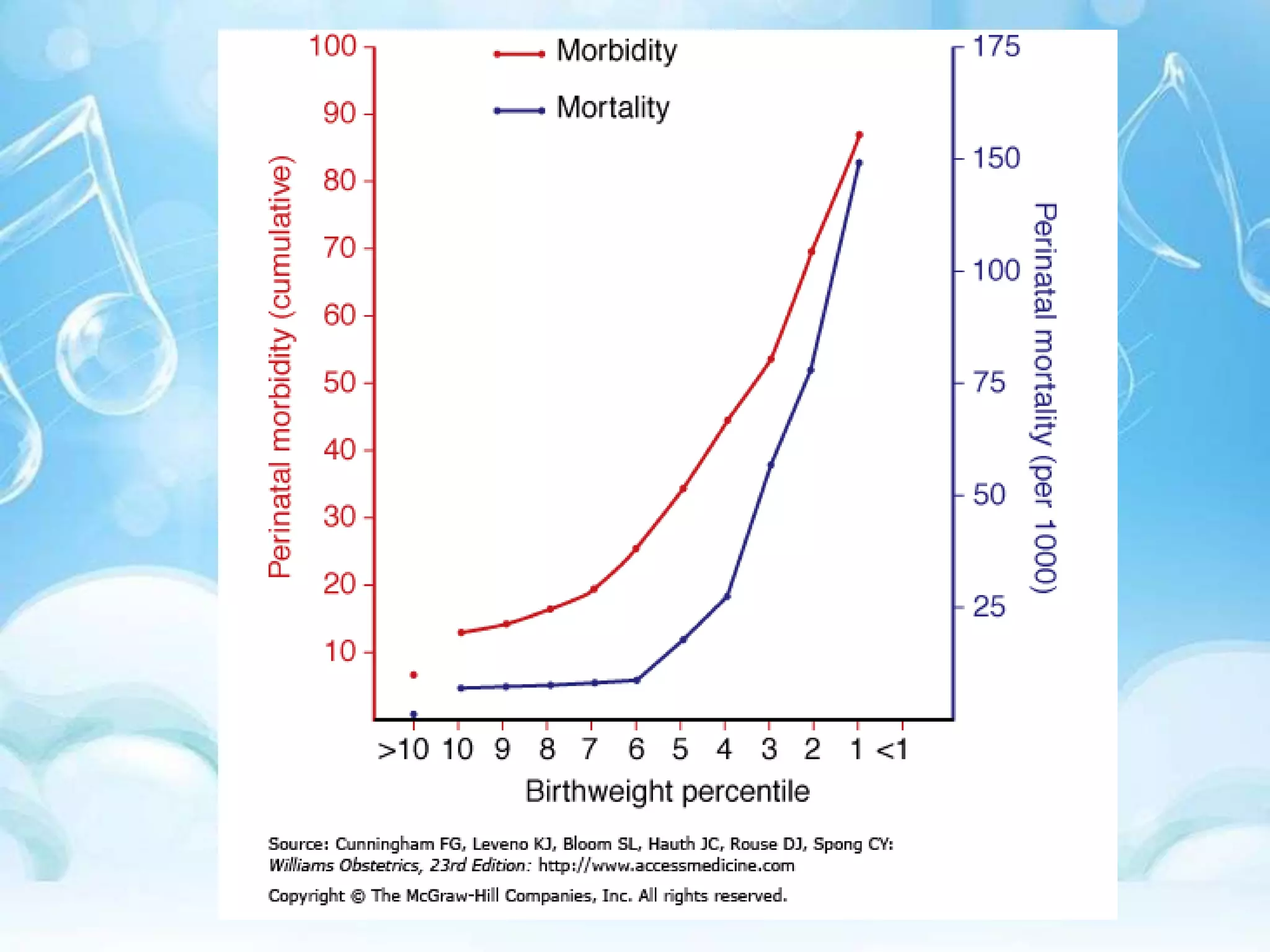
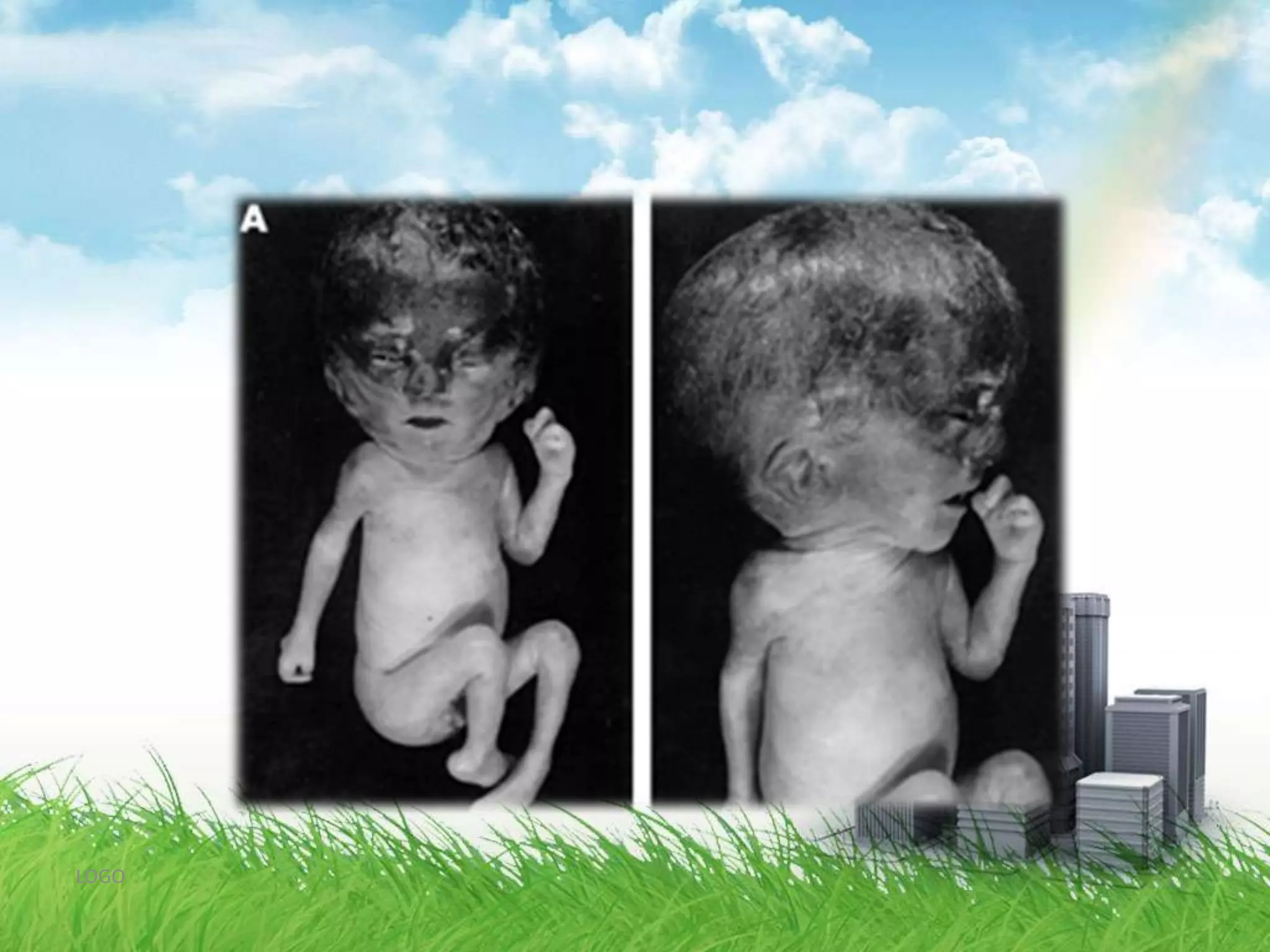
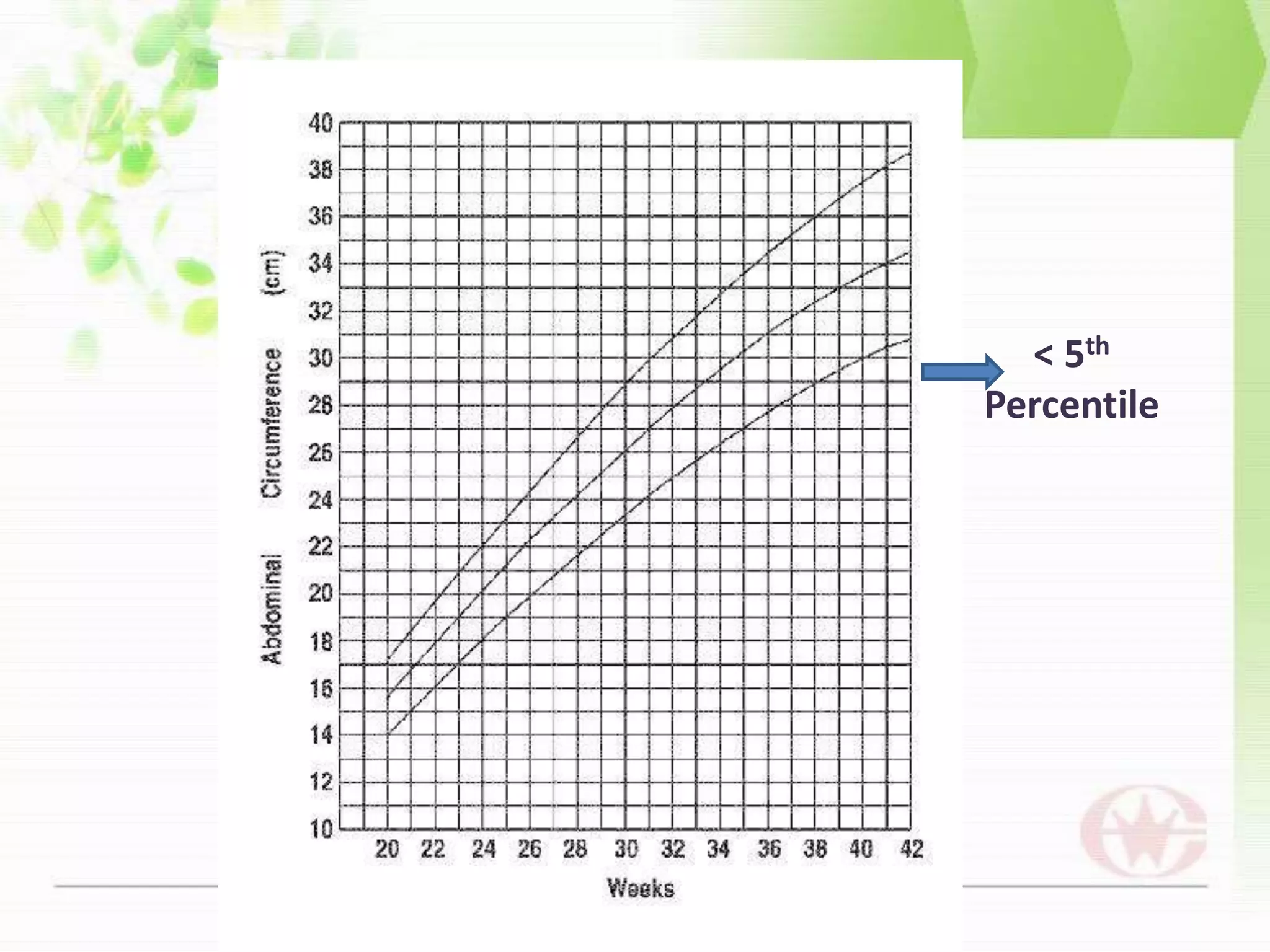
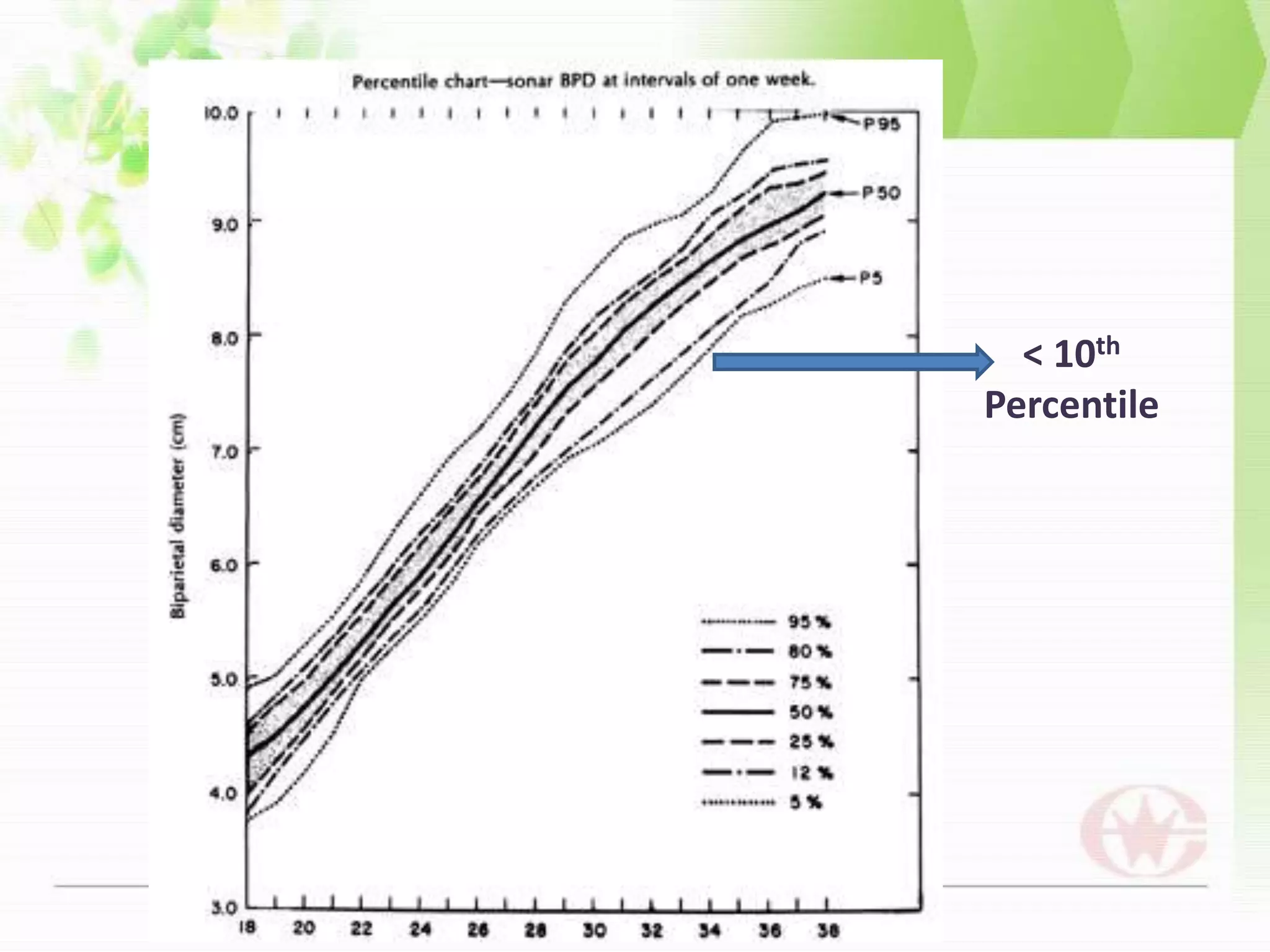
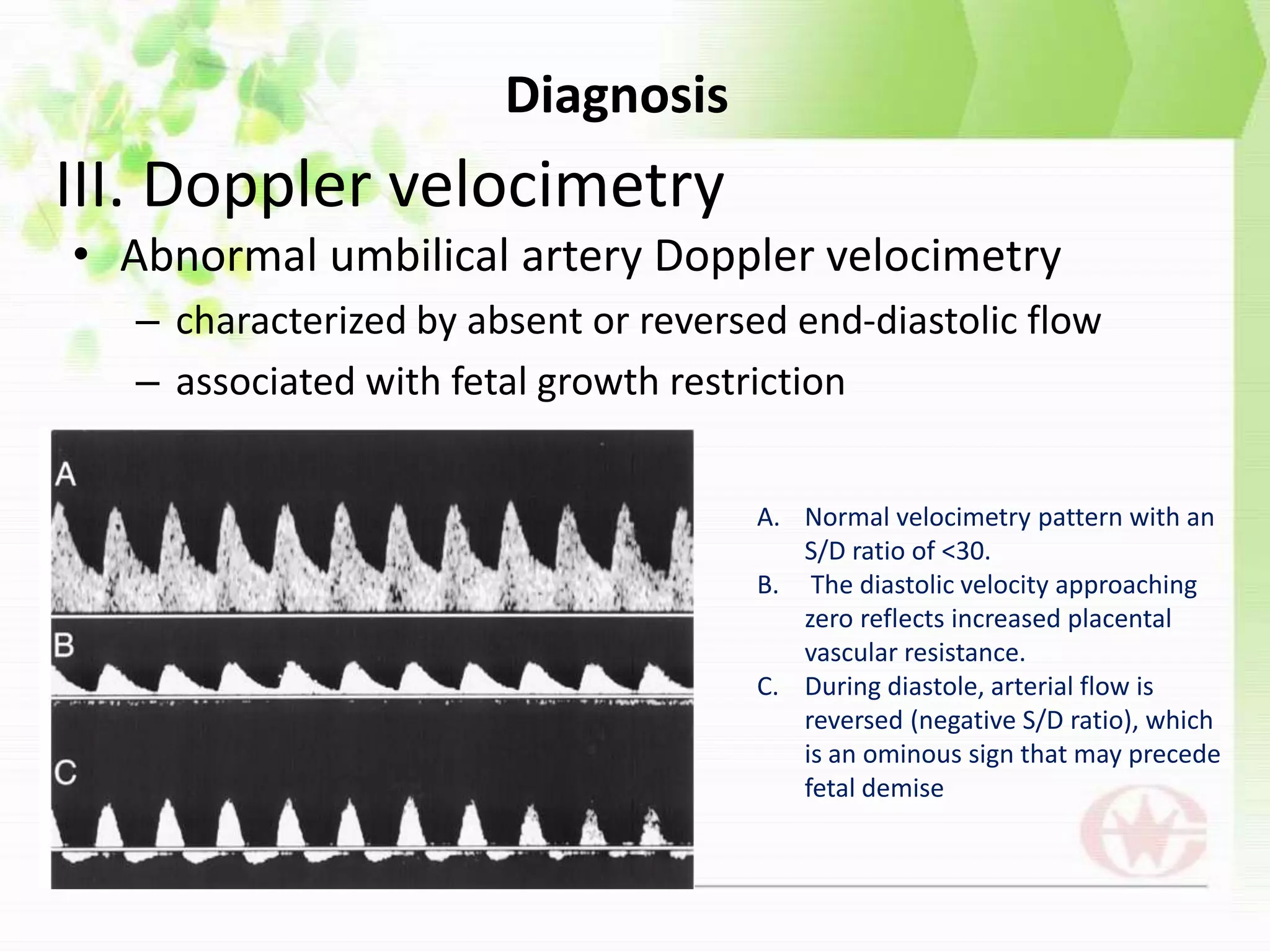
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) can be classified as symmetrical or asymmetrical based on ultrasound measurements of head and abdominal circumference. Symmetrical IUGR results in proportional growth restriction from early pregnancy insults while asymmetrical IUGR shows brain sparing and a decreased abdominal circumference from late pregnancy placental insufficiency. IUGR is diagnosed through clinical assessment, ultrasound measurements of fetal size below the 10th percentile, and abnormal Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery. Management depends on gestational age, with delivery near term for growth restriction and observation with fetal surveillance for earlier restriction unless severe complications arise. Long term risks for infants with IUGR include metabolic and neurological sequel