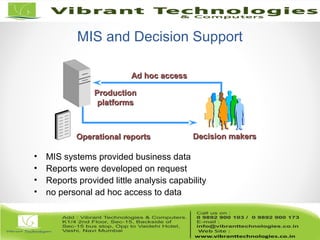
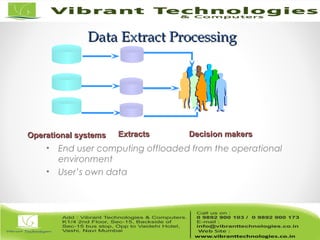
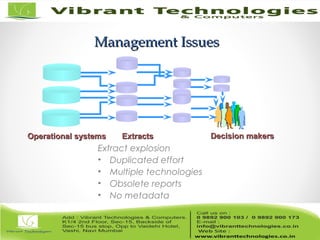
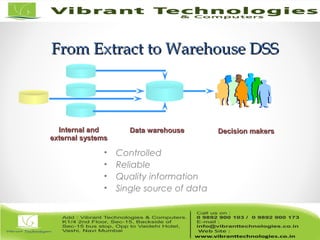
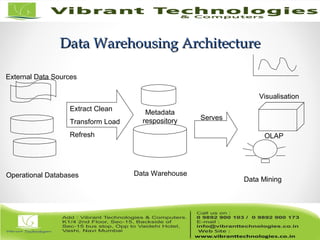
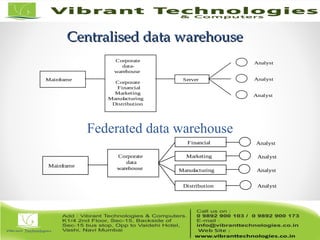
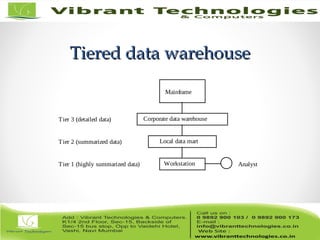
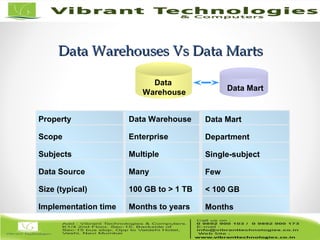
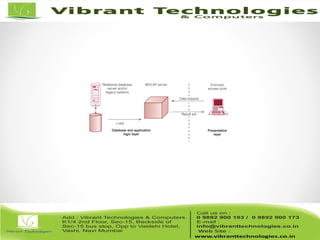
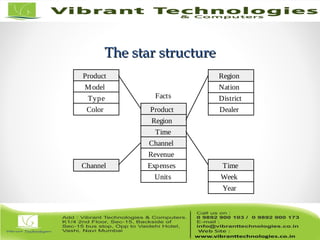
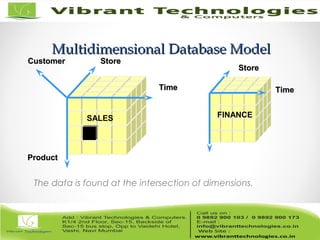
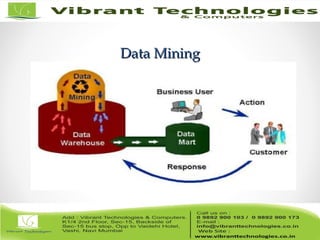
The document discusses the evolution of data warehousing from traditional database management systems (DBMS) to decision support systems (DSS), emphasizing the need for analytical capabilities and consolidation of data across business units. It highlights characteristics of online transaction processing (OLTP) systems versus decision support functions, addressing issues related to data extraction and quality. Additionally, it outlines various data warehousing architectures, tools for end-user access, and data mining functions that enhance decision-making capabilities.