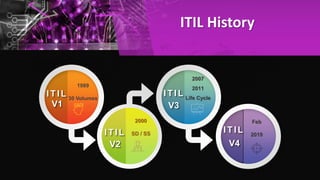
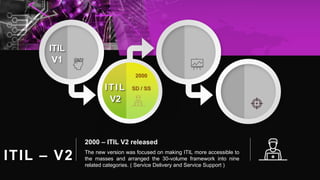
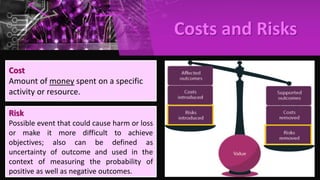
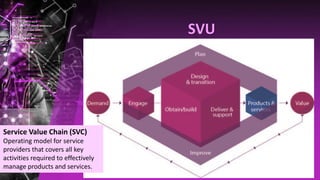
The document outlines the history and evolution of ITIL from version 1 to version 4, highlighting the transition from a 30-volume framework to a more accessible and streamlined version. It details the key concepts of IT service management (ITSM), benefits of ITIL, service value system, and various ITIL practices. Additionally, it discusses ITIL certification schema and how it supports aligning IT with business needs.