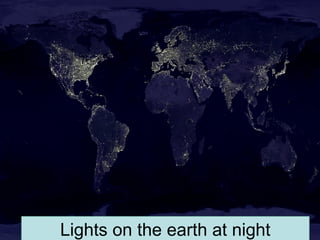
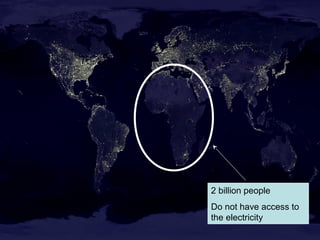
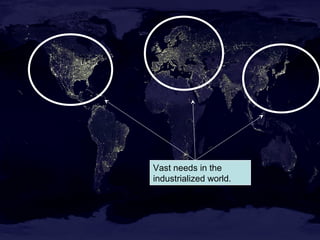
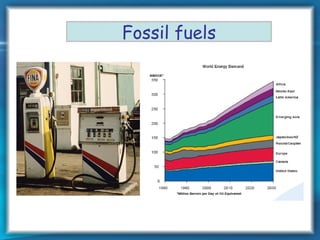
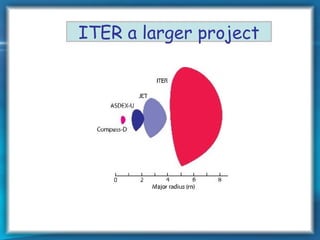
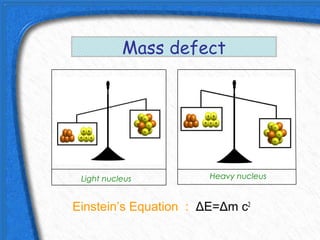
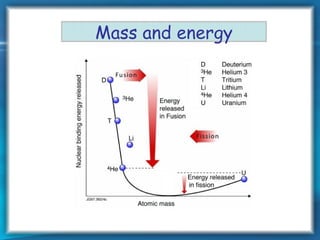
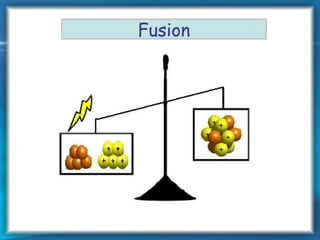
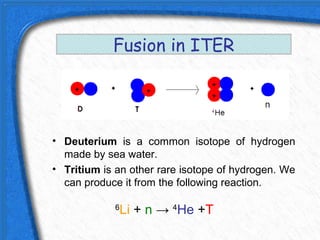
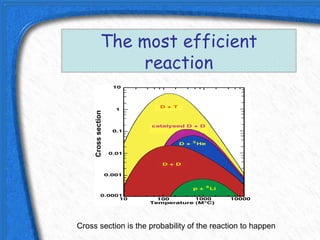
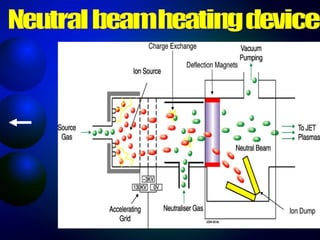
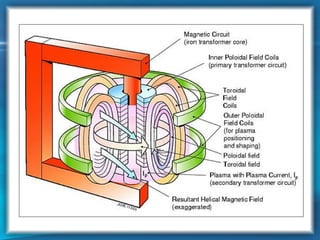
This document discusses nuclear fusion as a source of energy. It provides an overview of fusion, including what it is, the conditions needed to achieve it, and its safety advantages over other energy sources. ITER is introduced as a large-scale international project working to develop fusion as an energy source. Key points covered include how deuterium and tritium are used as fuel, the extremely high temperatures required to fuse atomic nuclei, and how magnetic confinement is used to control the plasma within the reactor.