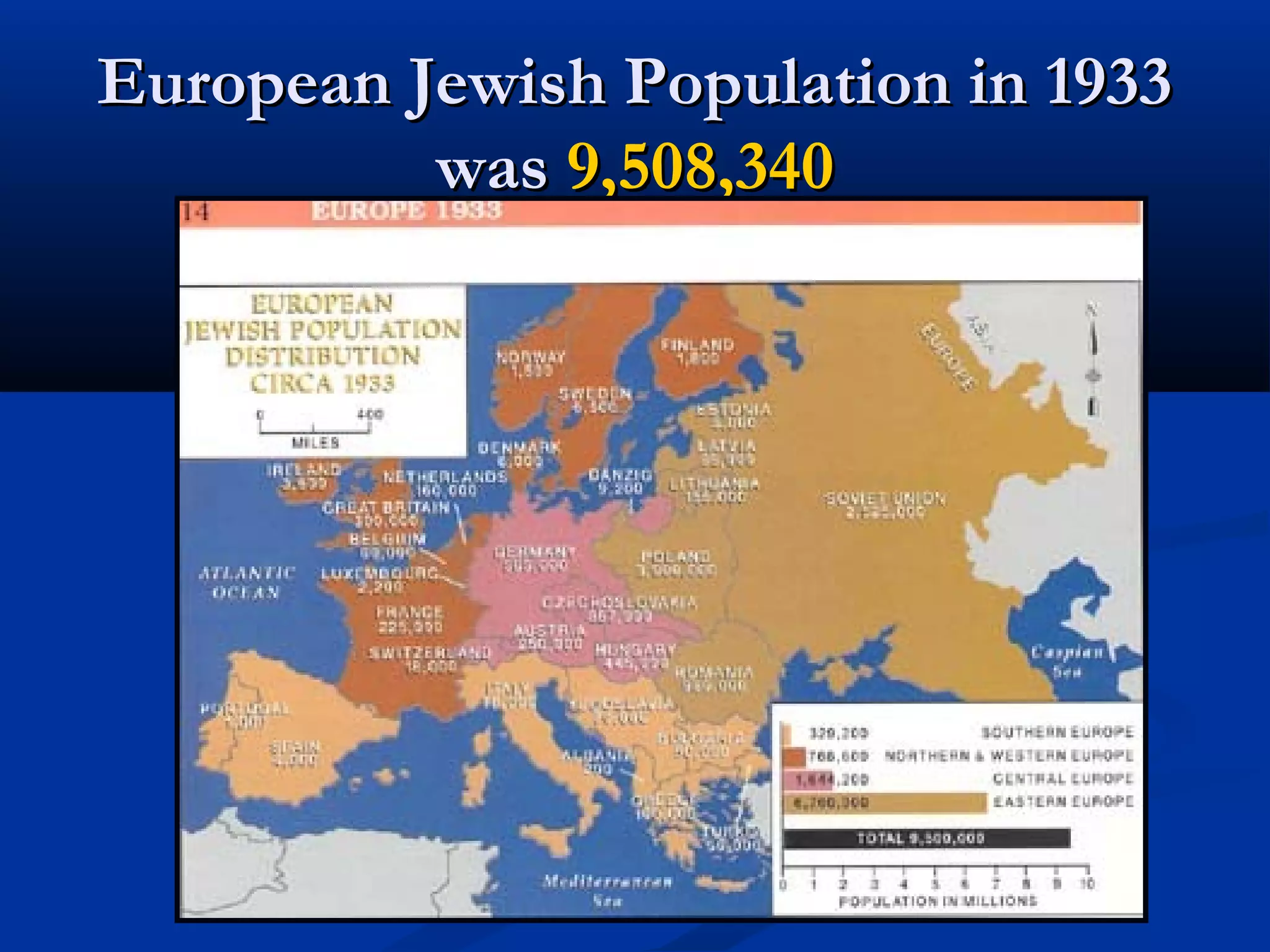
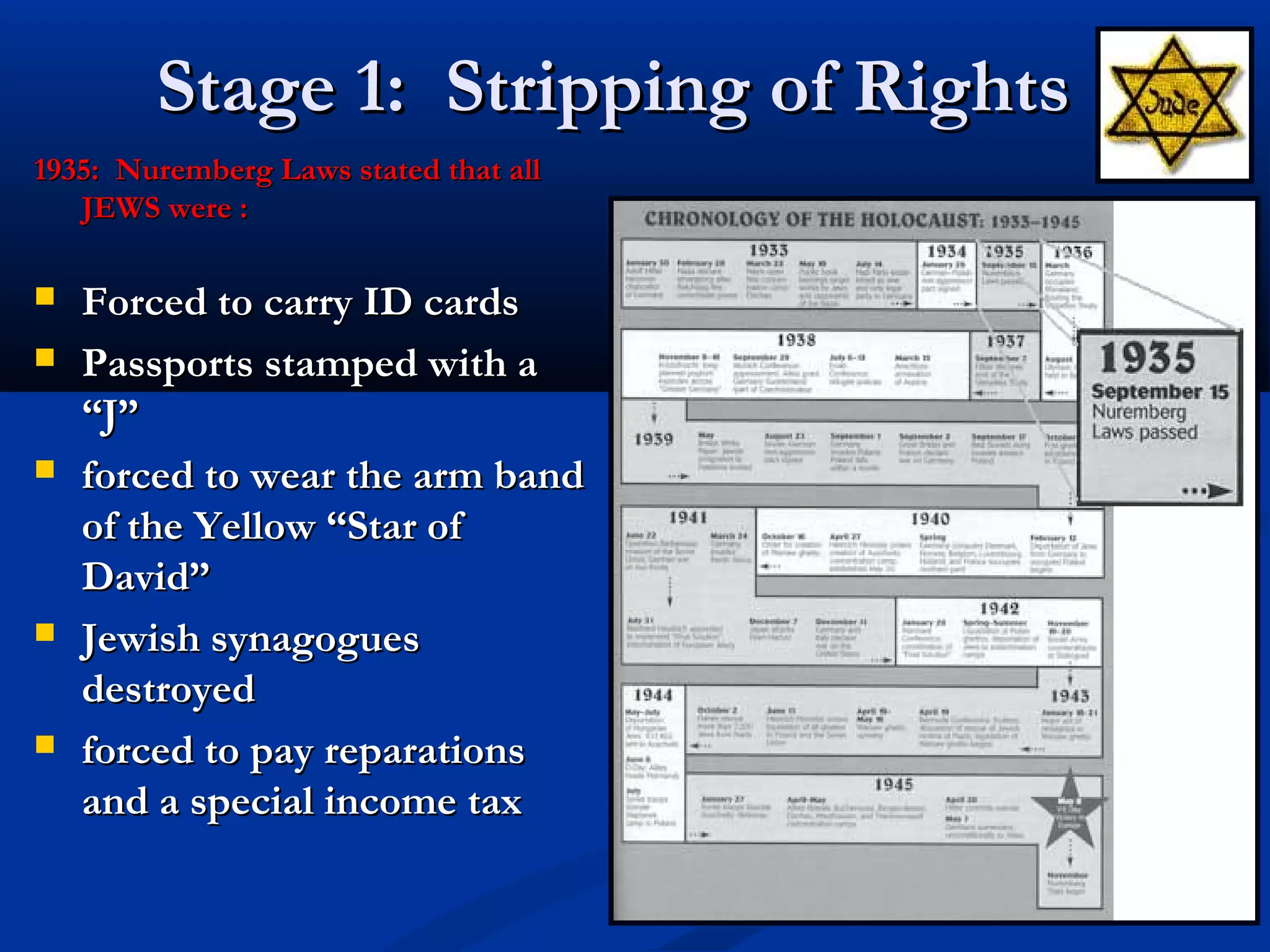
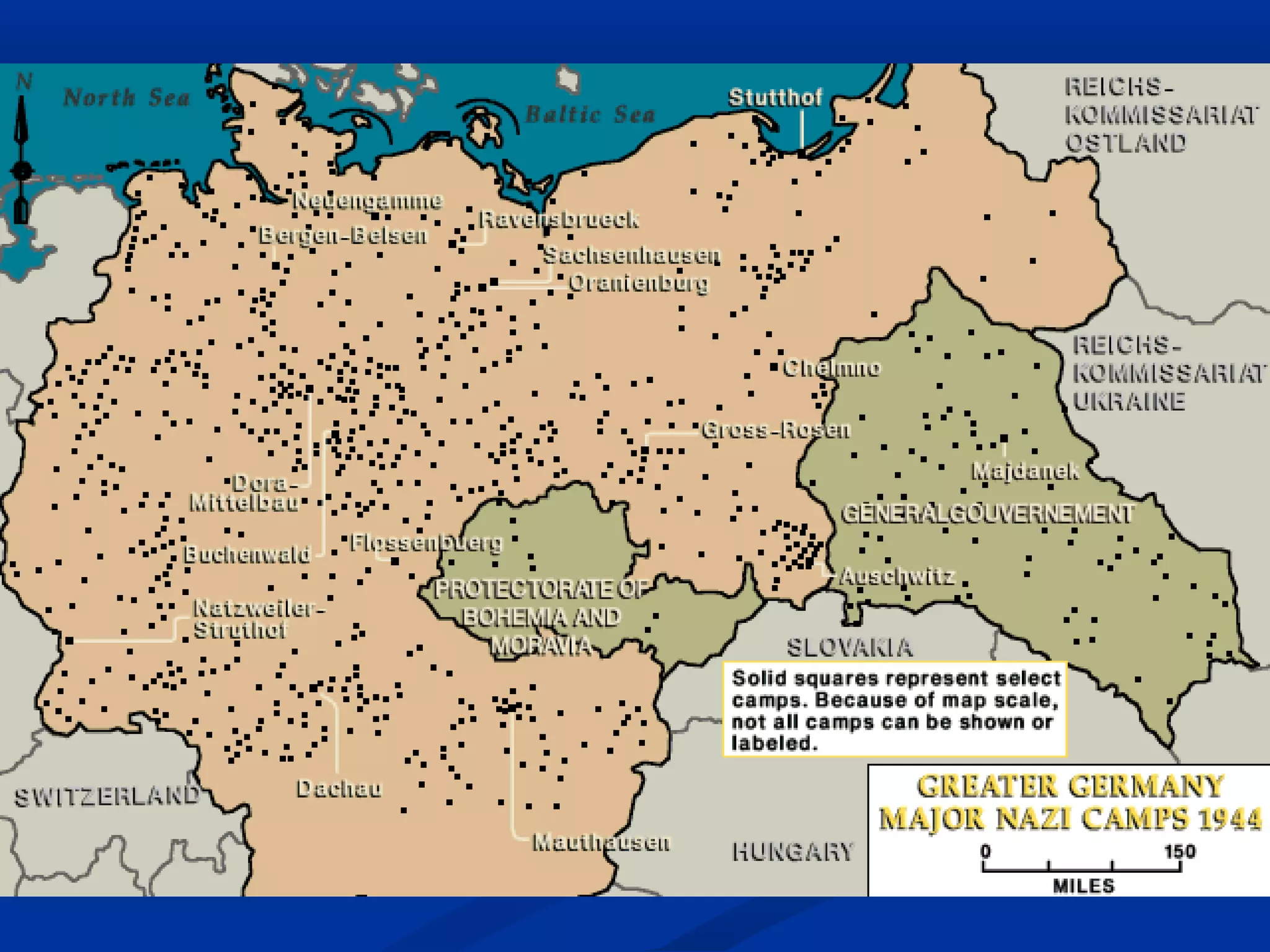
The Holocaust resulted in the genocide of approximately 11 million people, including 6 million Jews, between 1933 and 1945 under the Nazi regime in Germany. Jews faced escalating oppression through stripping of rights, segregation in ghettos, imprisonment in concentration camps involving slave labor and inhumane conditions, and extermination in death camps using gas chambers and crematoriums. By systematically isolating, persecuting and murdering Jews and other targeted groups, the Nazis pursued the "Final Solution" aiming to annihilate the Jewish population of Europe.