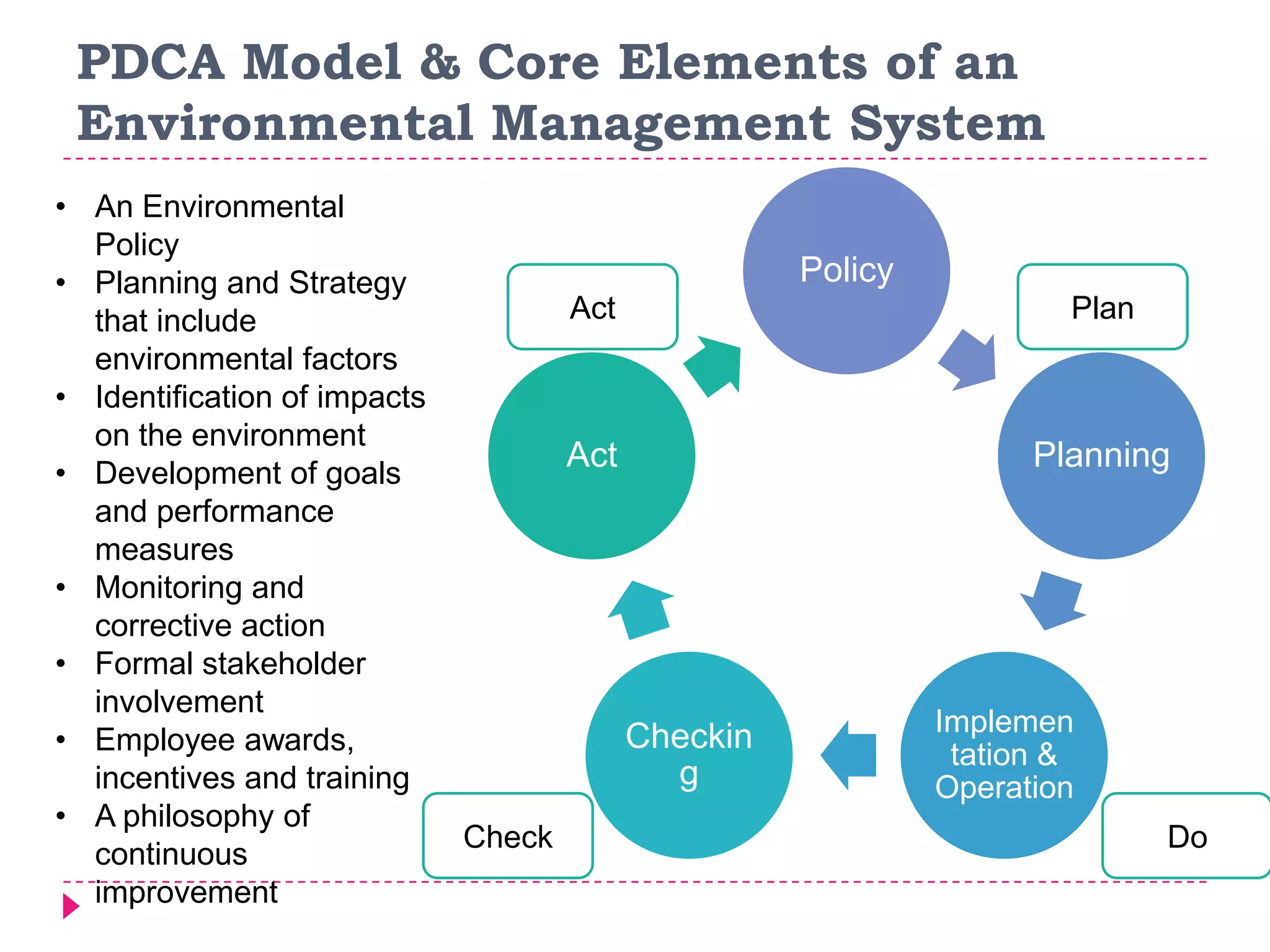
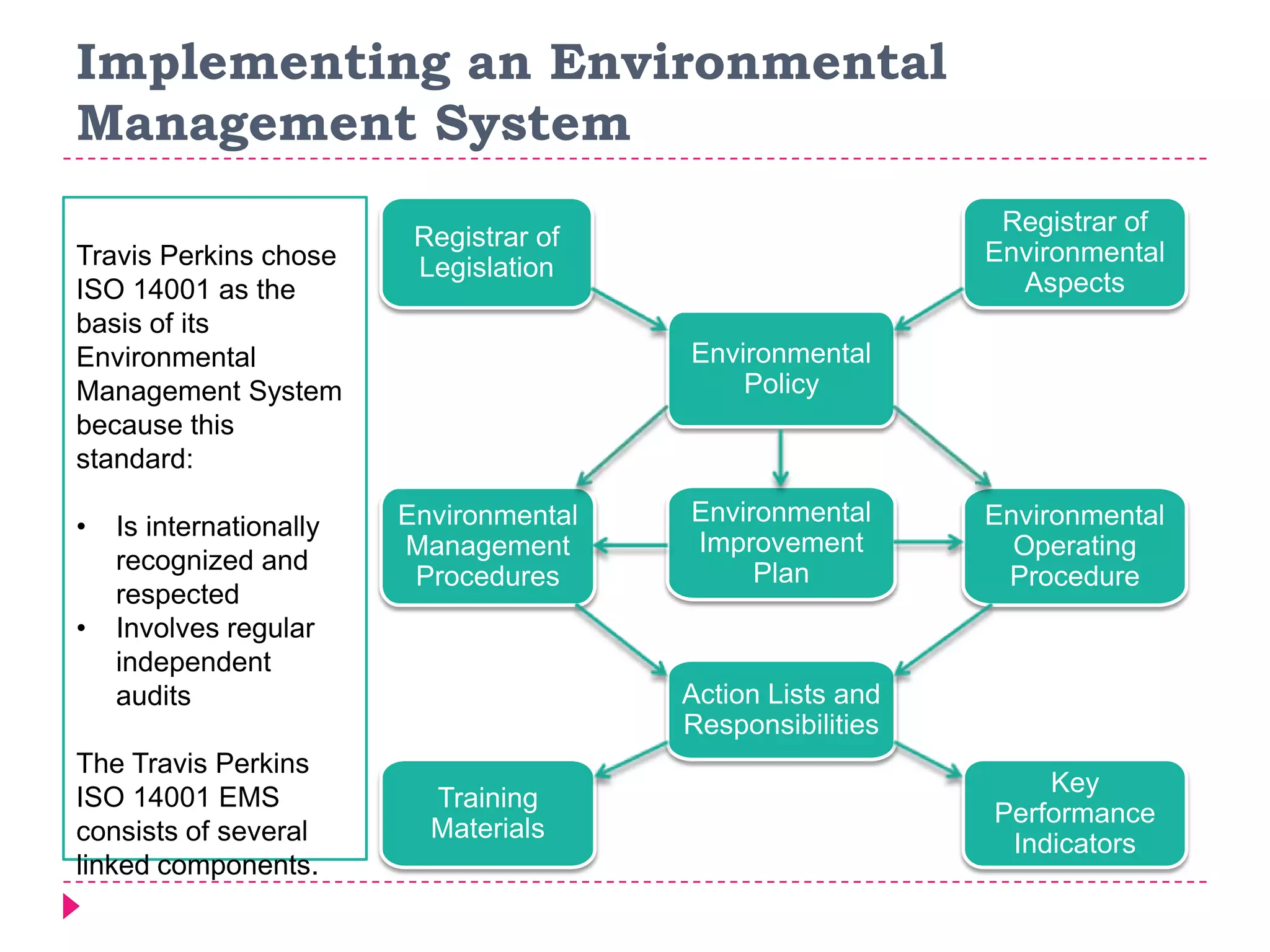
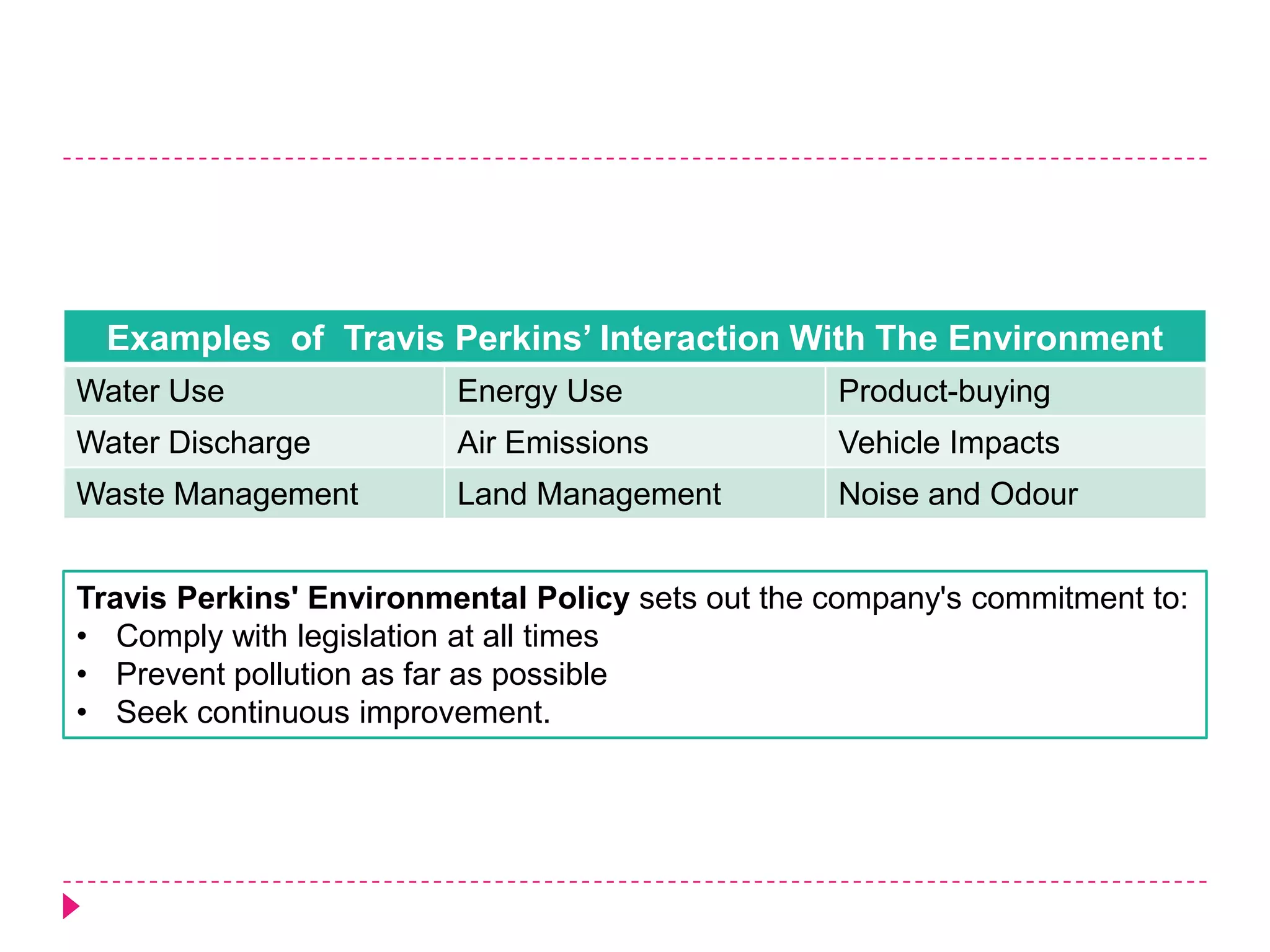
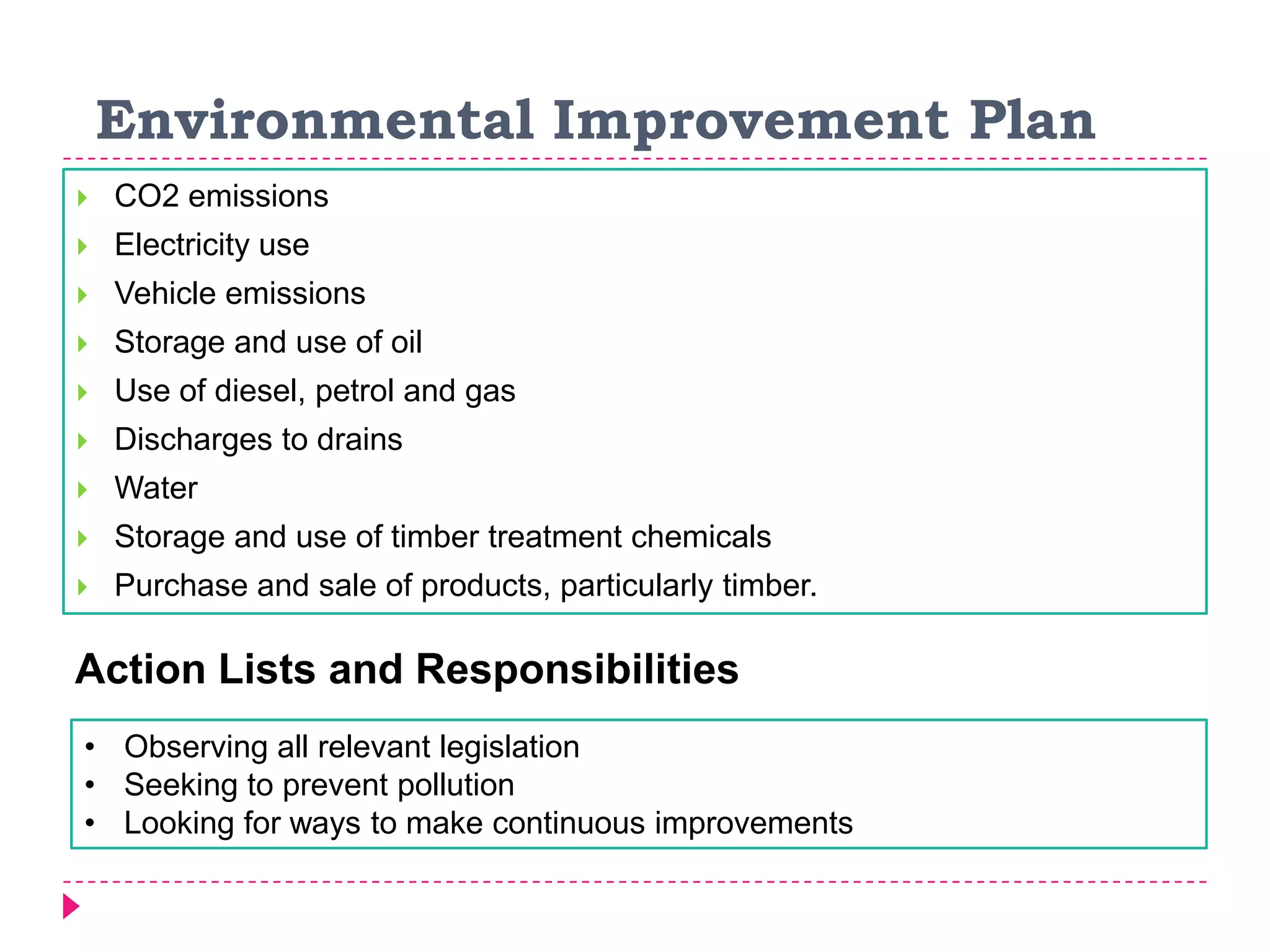
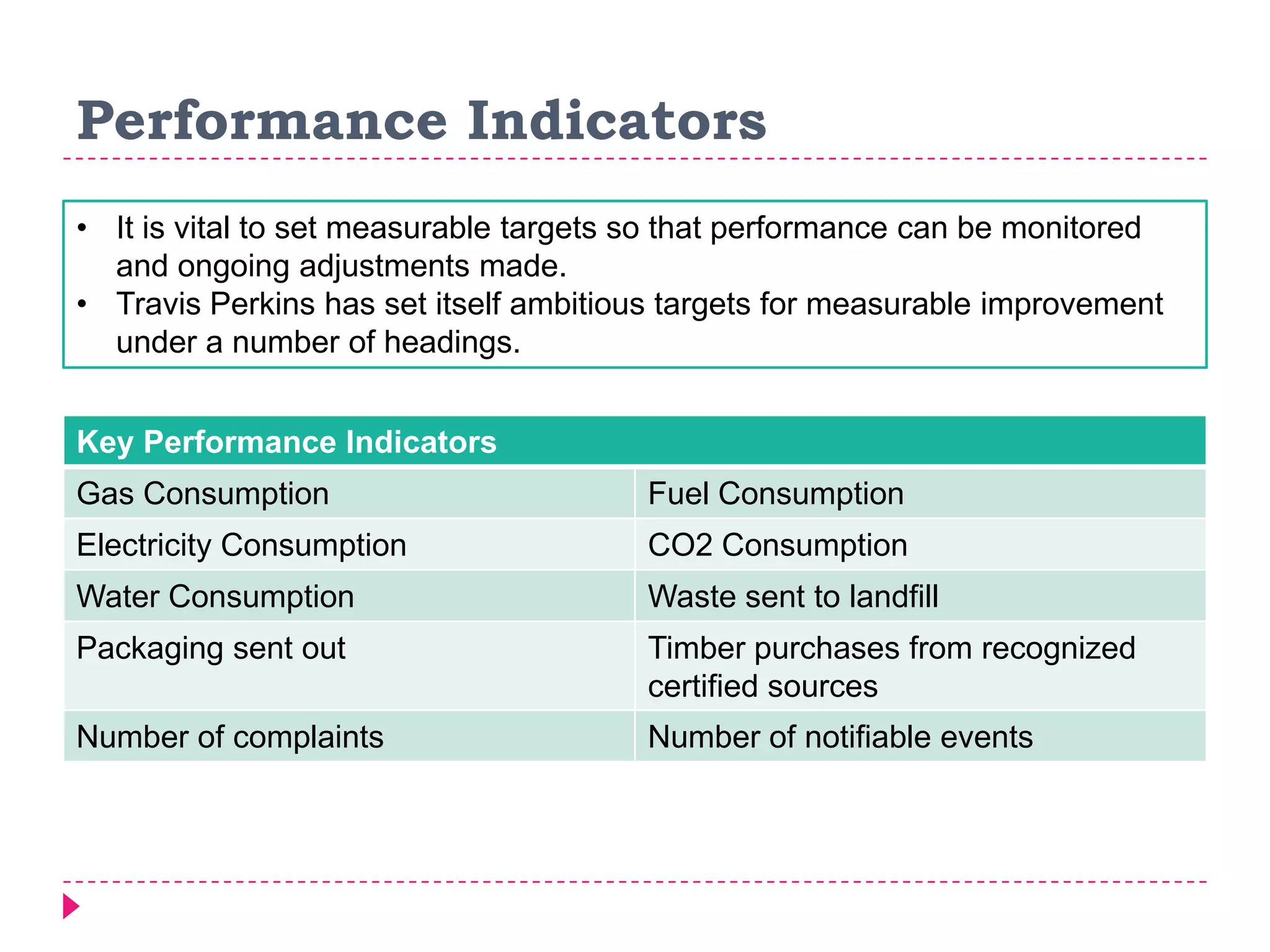
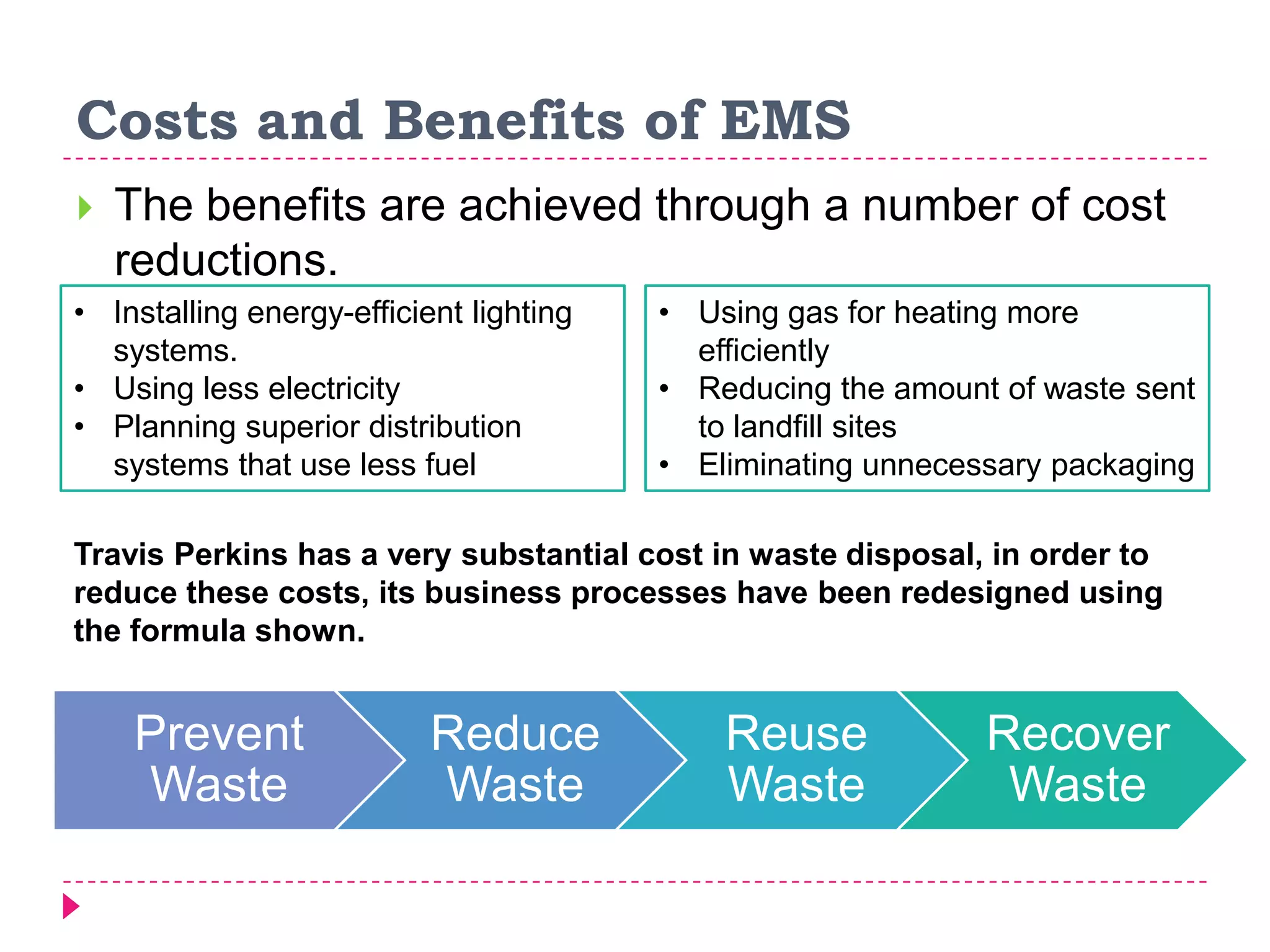
An environmental management system (EMS) is a set of processes and methods that help align corporate strategies with environmental protection. An EMS identifies environmental impacts and establishes rules to help an organization minimize harm. Travis Perkins, a building materials supplier, implemented an EMS based on ISO 14001 standards to reduce costs, comply with regulations, and improve its environmental performance and reputation. Key elements of Travis Perkins' EMS include setting targets in its environmental policy and improvement plan, assigning responsibilities, and tracking performance indicators to monitor progress.