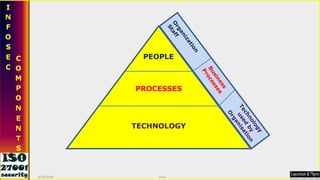
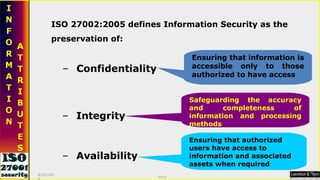
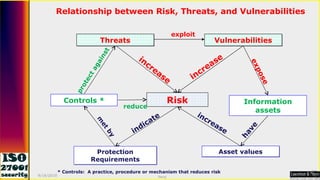
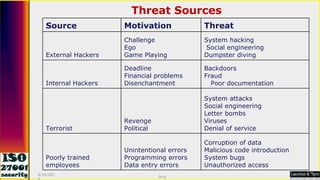
This document serves as a comprehensive guide on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) based on ISO/IEC 27001:2005. It emphasizes the importance of properly protecting information as a vital organizational asset and outlines key components such as risk management, security strategies involving people, processes, and technology, and the necessity of compliance with international standards. Additionally, it discusses the roles of various stakeholders in information security, classifications of information assets, and the overarching aim of maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.




































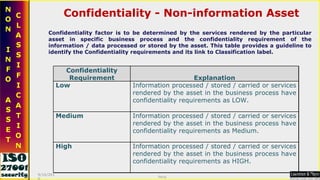
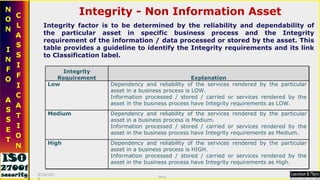
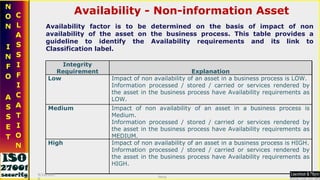
![Non-information Assets [Physical] Information is processed with the help of technology. The assets, which are helpful in creating, processing, output generation and storage. Such assets need to be identified and valued for the purpose of their criticality in business process. Asset valuation of non information / physical Assets like software, Hardware, Services is carried out based on different criteria applicable to the specific group of physical assets involved in organization’s business processes. 9/16/2010 Saroj](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ismsawarenesstraining-111019004916-phpapp02/85/Isms-awareness-training-49-320.jpg)

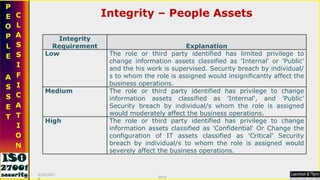
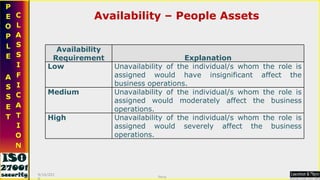





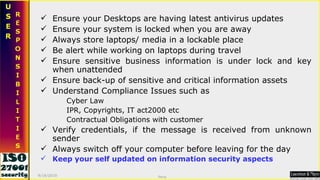

![Thanks [email_address] 9/16/2010 Saroj](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ismsawarenesstraining-111019004916-phpapp02/85/Isms-awareness-training-64-320.jpg)