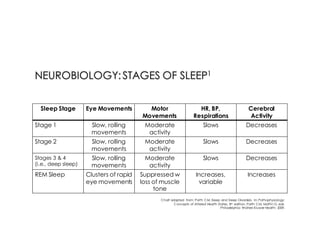
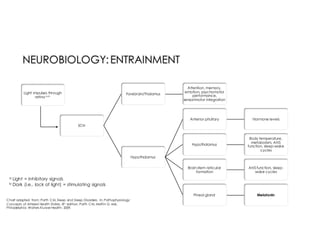
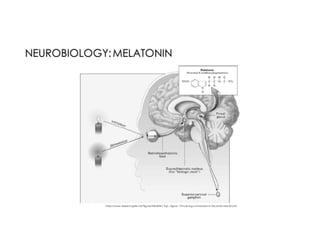
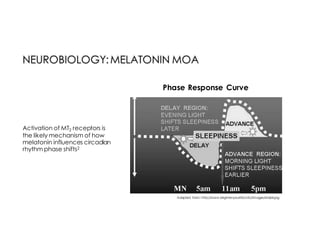
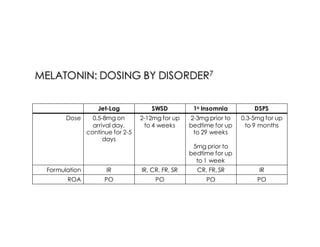
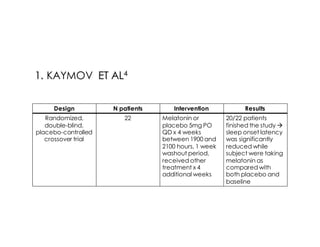
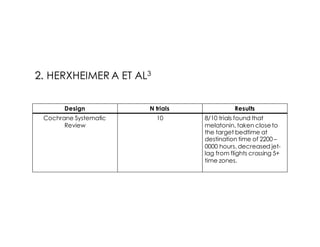
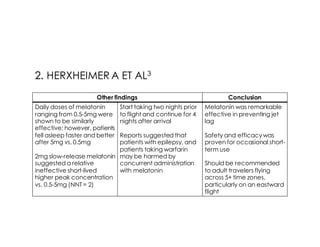
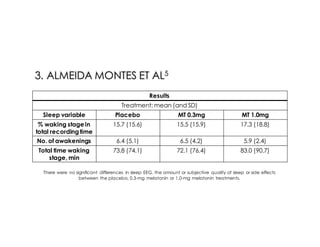
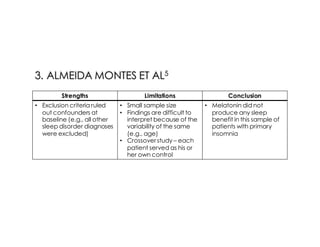
This document discusses melatonin's role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. It describes how melatonin is produced in the pineal gland and responds to light exposure, activating receptors involved in sleep regulation and circadian phase shifting. Studies show that oral melatonin supplementation can effectively treat jet lag when taken around bedtime at the destination for 2-5 days after long-haul flights. Melatonin doses from 0.5-5mg are similarly effective for this use and have a good safety profile when used short-term. However, melatonin did not demonstrate sleep benefits versus placebo in patients with primary insomnia.