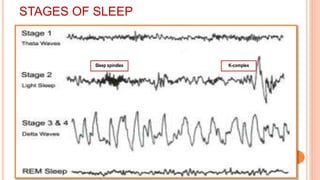
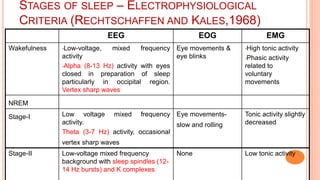
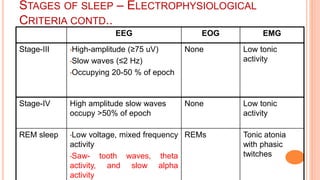
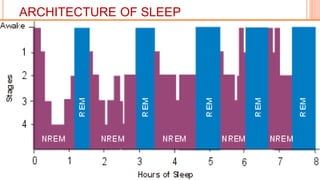
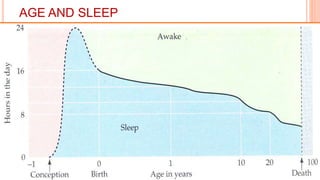
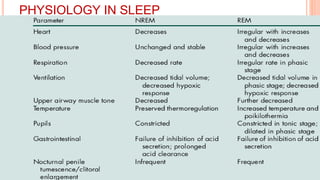
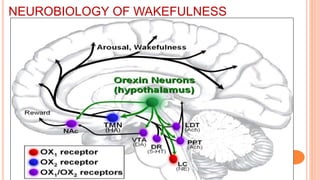
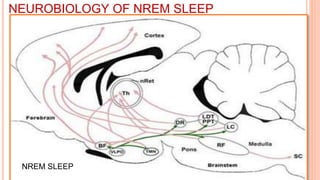
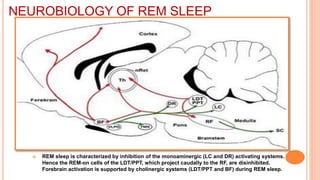
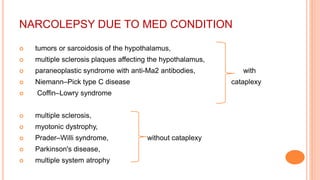
This document provides an overview of sleep, including its definition, stages, neurobiology, and relevance to psychiatry. It describes the two main types of sleep - REM and NREM sleep - and the different stages of NREM sleep. The neurobiology of sleep and wakefulness involves separate but interacting systems in the brainstem, hypothalamus, and basal forebrain. Key structures and neurotransmitters that promote wakefulness include the ascending reticular activating system, locus ceruleus, tuberomamillary nucleus, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus, and hypocretin. Age and circadian rhythms also influence sleep patterns.