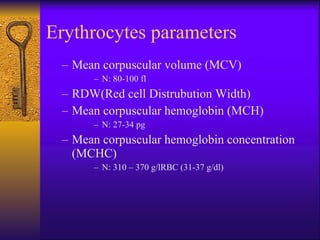
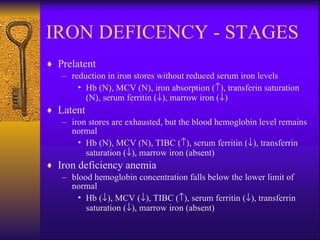
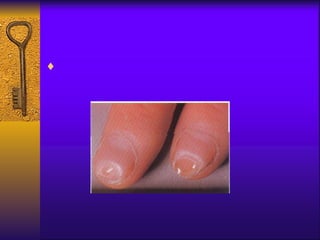
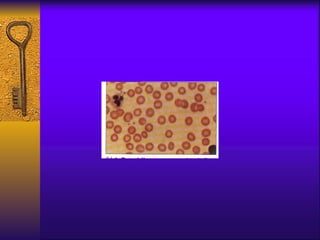
The document discusses iron deficiency anemia, including its definition, symptoms, causes, stages, diagnostic tests, and treatment options. Key points include:
- Iron deficiency anemia is defined as a reduction in hemoglobin concentration below the reference value.
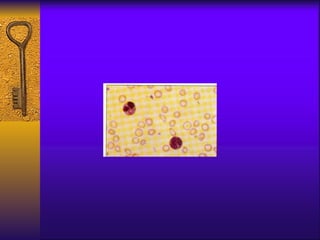
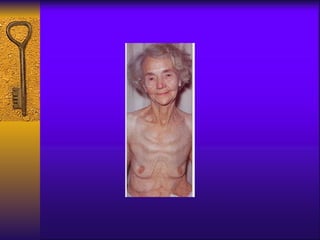
- Symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, and headaches. Specific symptoms like glossitis or koilonychia may also occur.
- Causes include chronic bleeding, decreased iron intake, and increased iron requirements during growth or pregnancy.
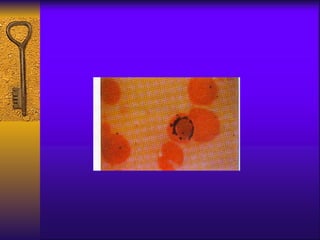
- Diagnosis involves blood tests measuring iron levels, iron binding capacity, ferritin, and a bone marrow smear.
- Treatment options include oral or parenteral iron supplementation to restore iron stores over 6-9