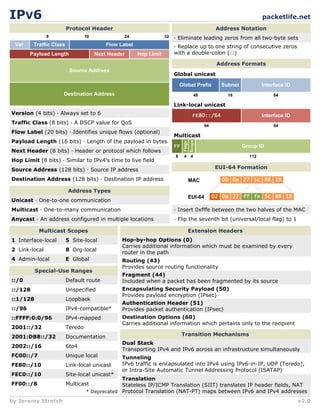
The document provides information on IPv6 including address notation, address formats, extension headers, address types, multicast scopes, special-use ranges, header options, and transition mechanisms between IPv4 and IPv6. Address notation describes eliminating leading zeros and replacing consecutive zeros with "::". Address formats include global unicast, link-local unicast, and multicast addresses. Extension headers include traffic class, payload length, and source/destination addresses. Transition mechanisms allow dual stacking, tunneling, and translation between the two protocols.