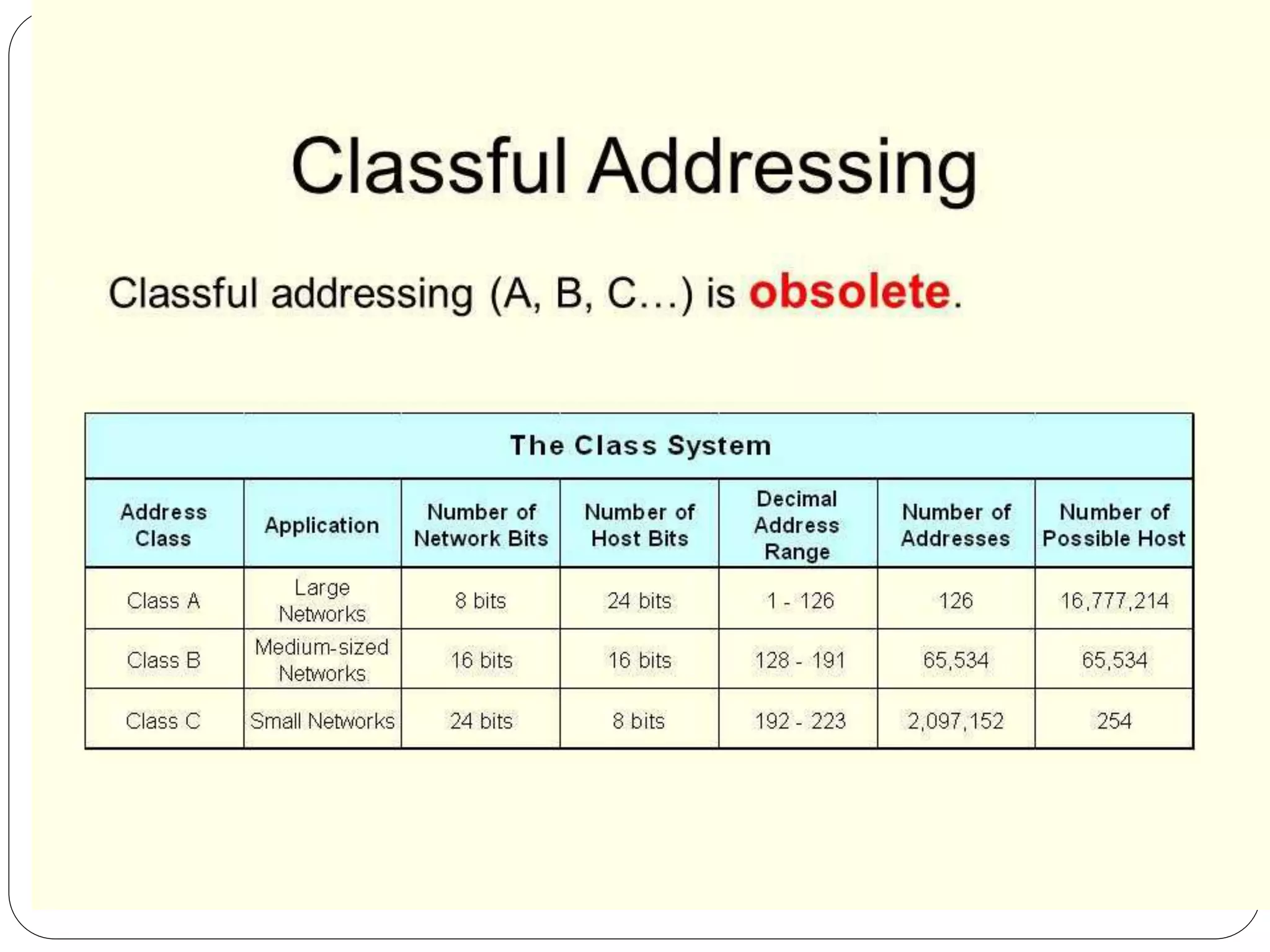
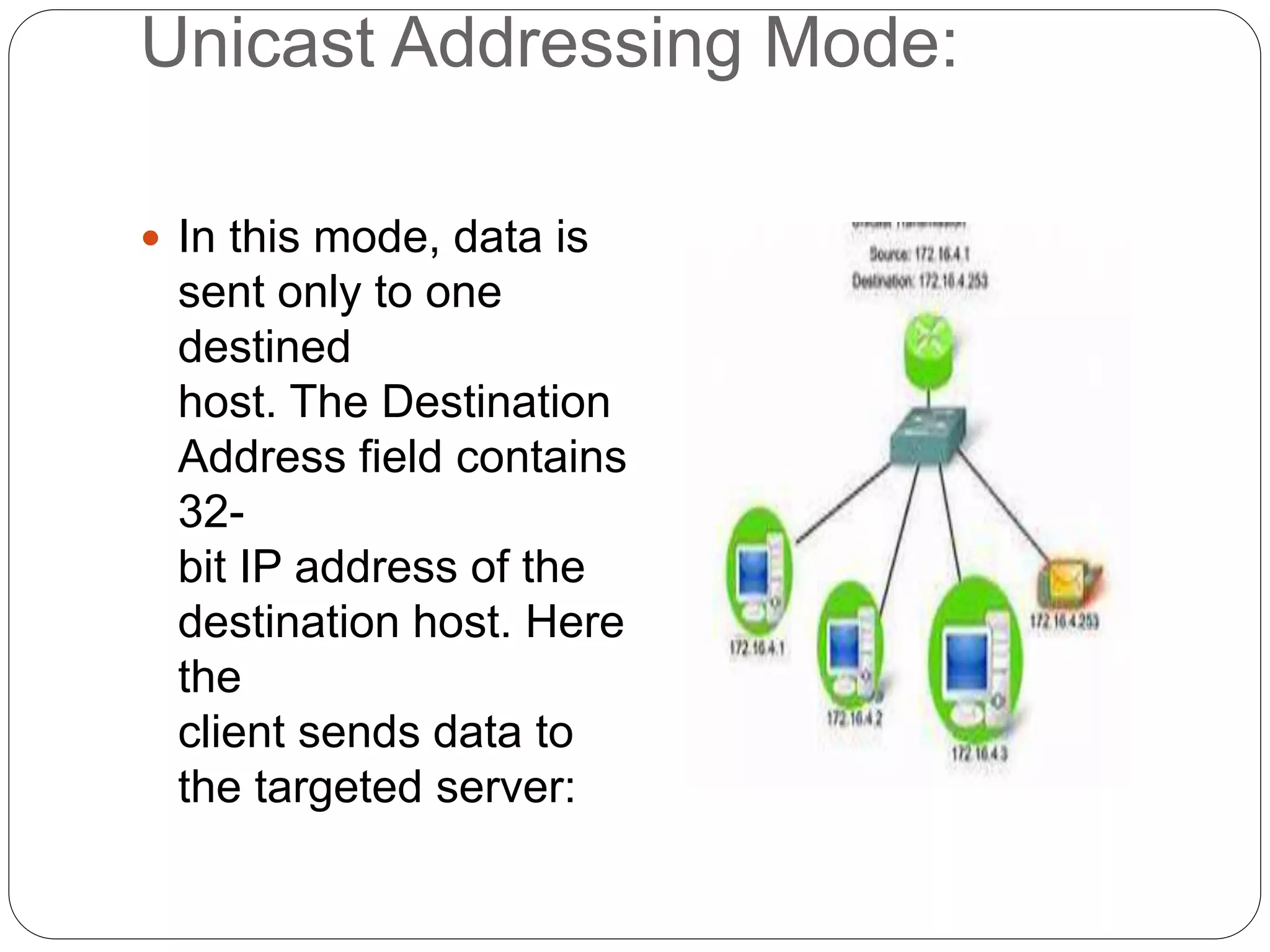
This document discusses IPv4 addressing and the key components of an IPv4 address. It explains that an IPv4 address is a 32-bit address that uniquely identifies a device connected to the internet. It also describes how an IPv4 address is comprised of four octets separated by periods, with each octet representing an 8-bit number between 0-255. The document further discusses binary and decimal conversion of IP addresses and how subnet masks are used to identify networks and allow communication between hosts on the same network. It concludes by summarizing the different addressing modes of unicast, broadcast and multicast.