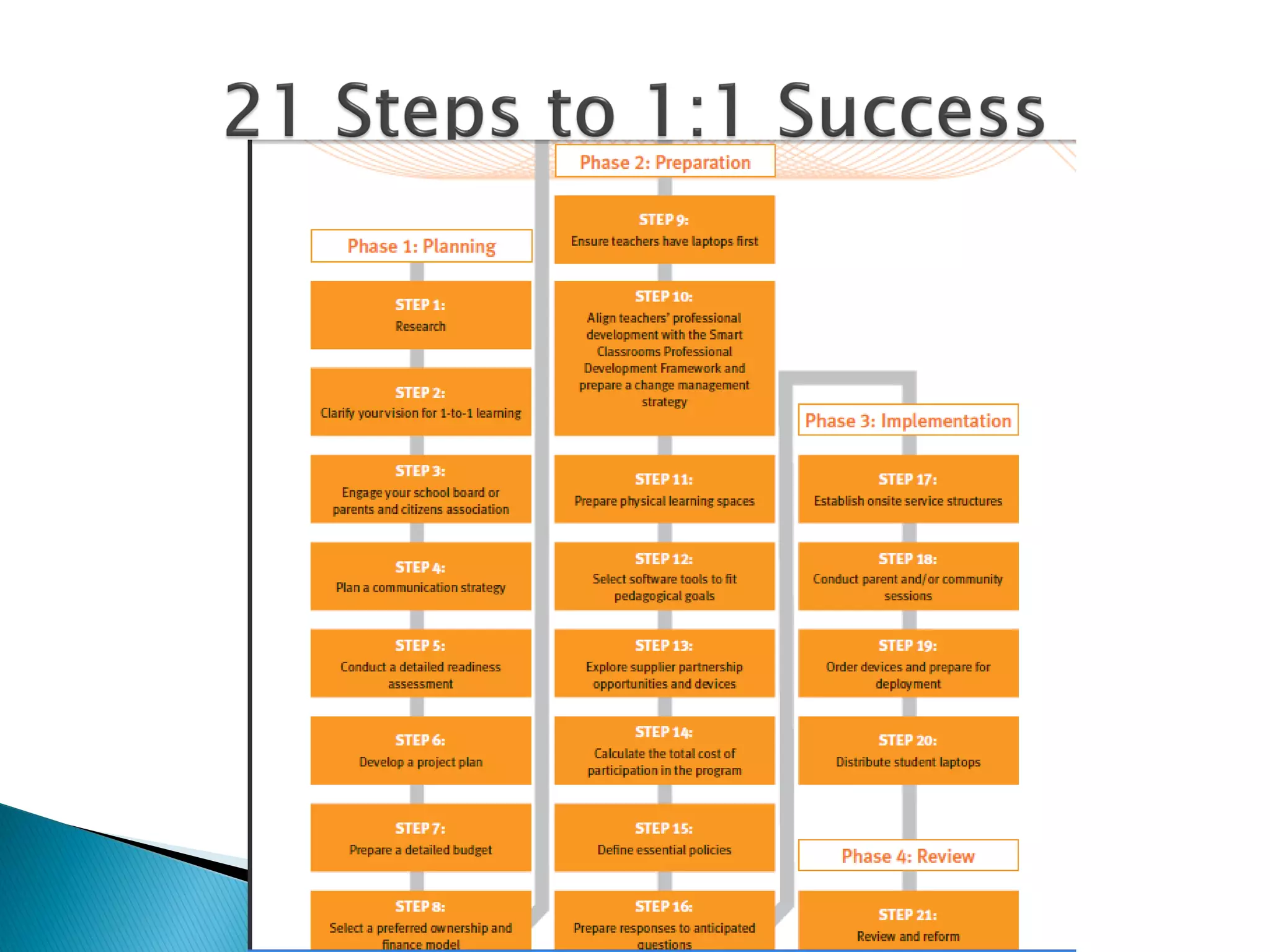
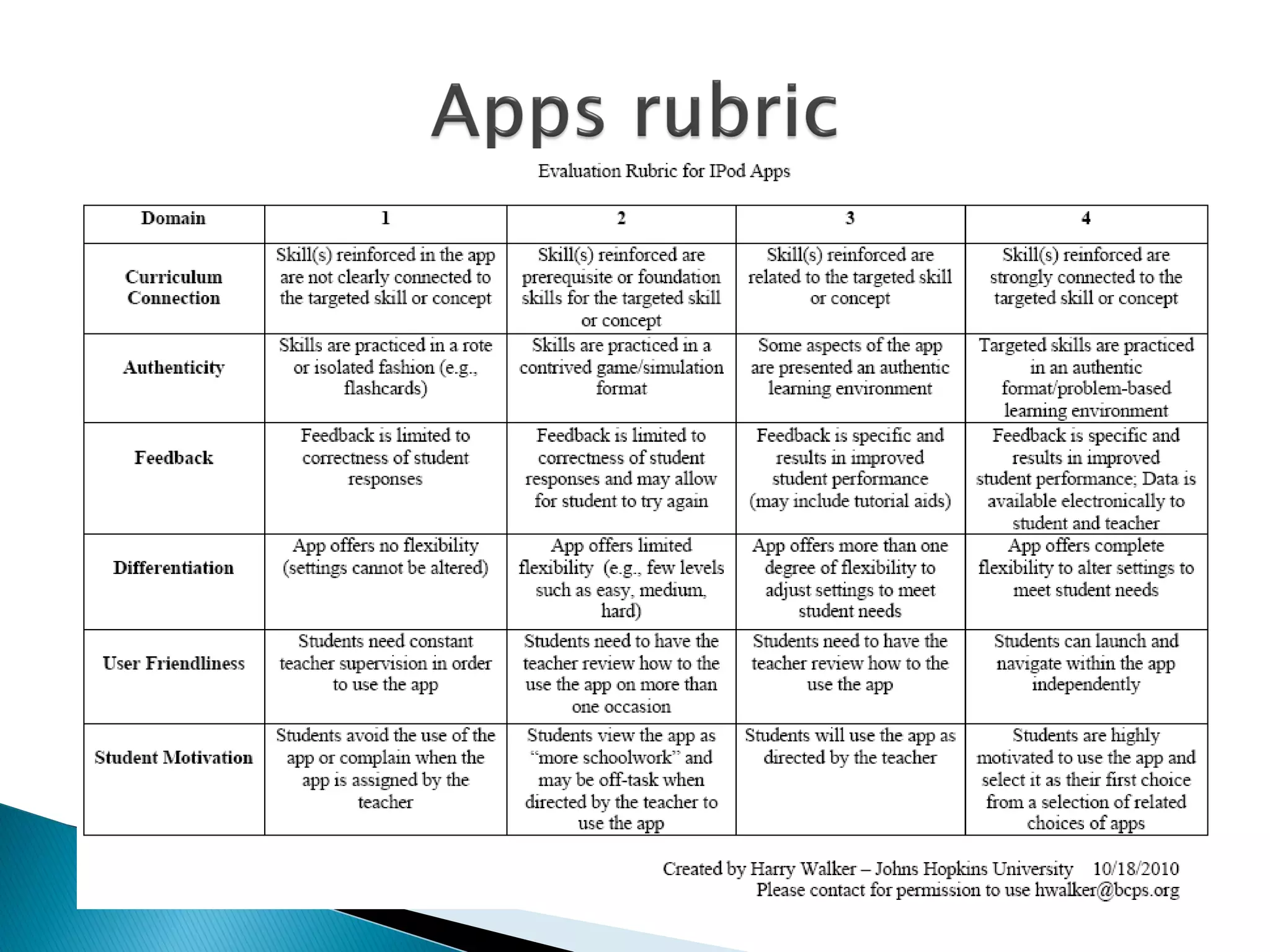
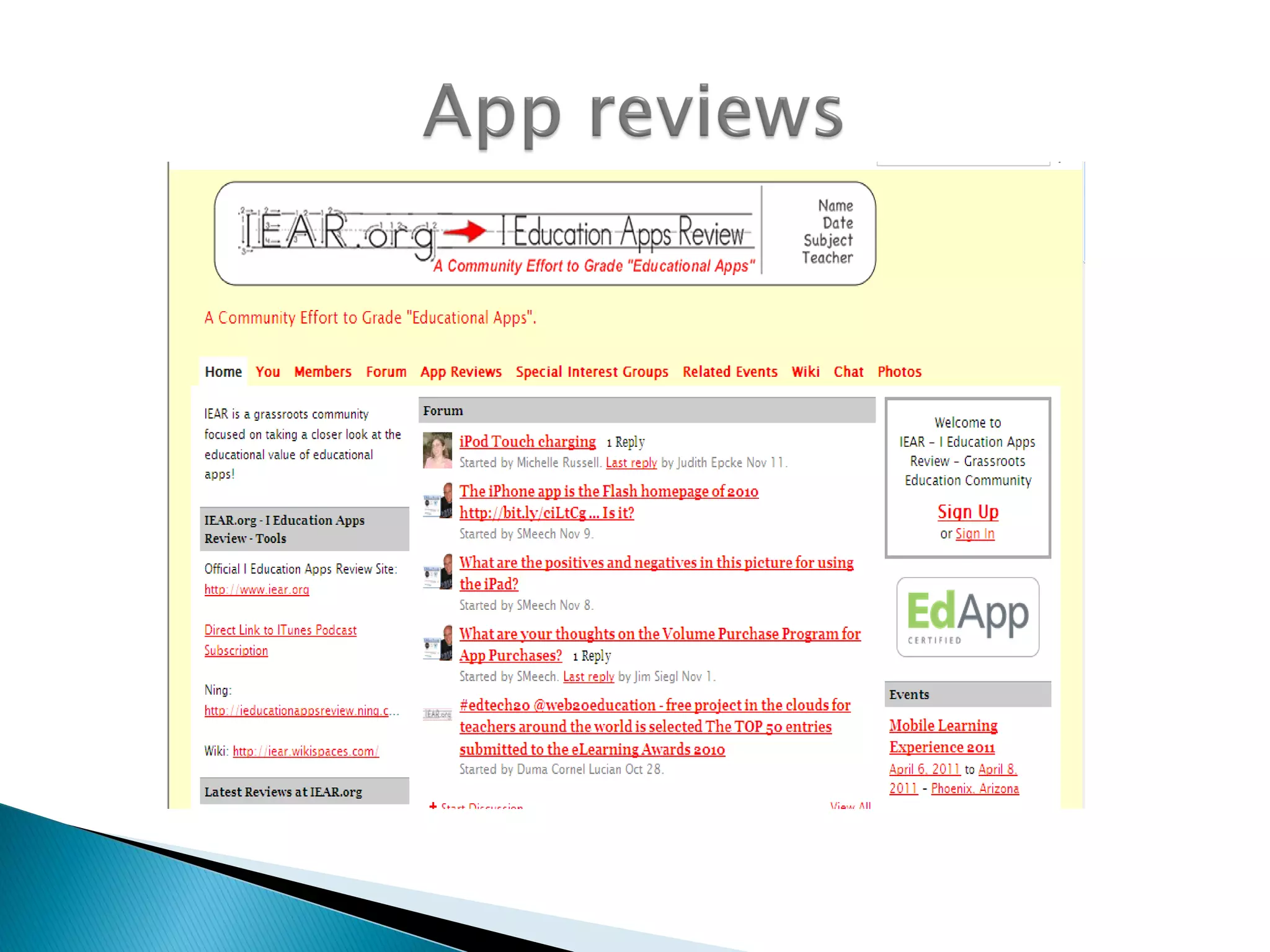
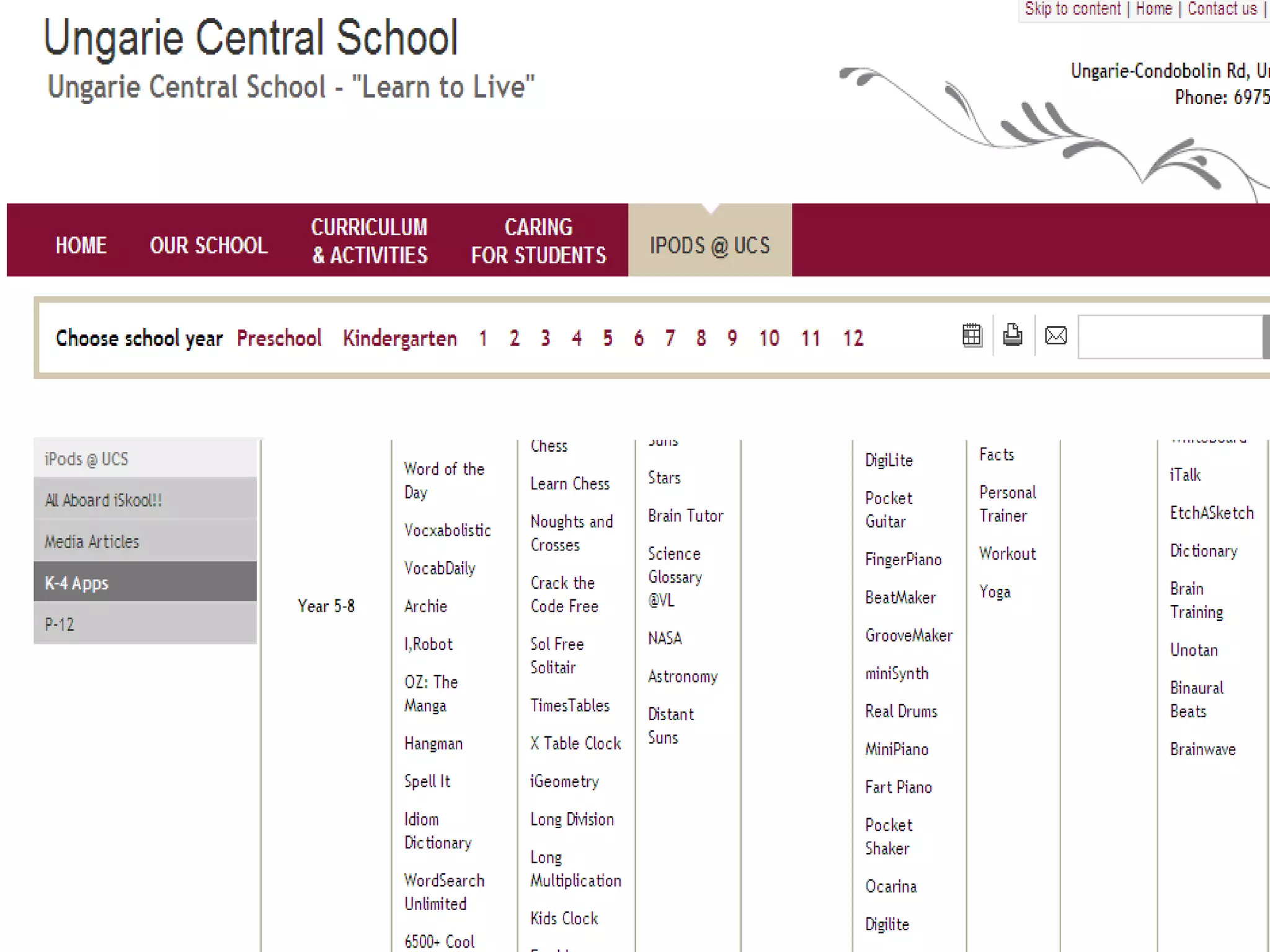
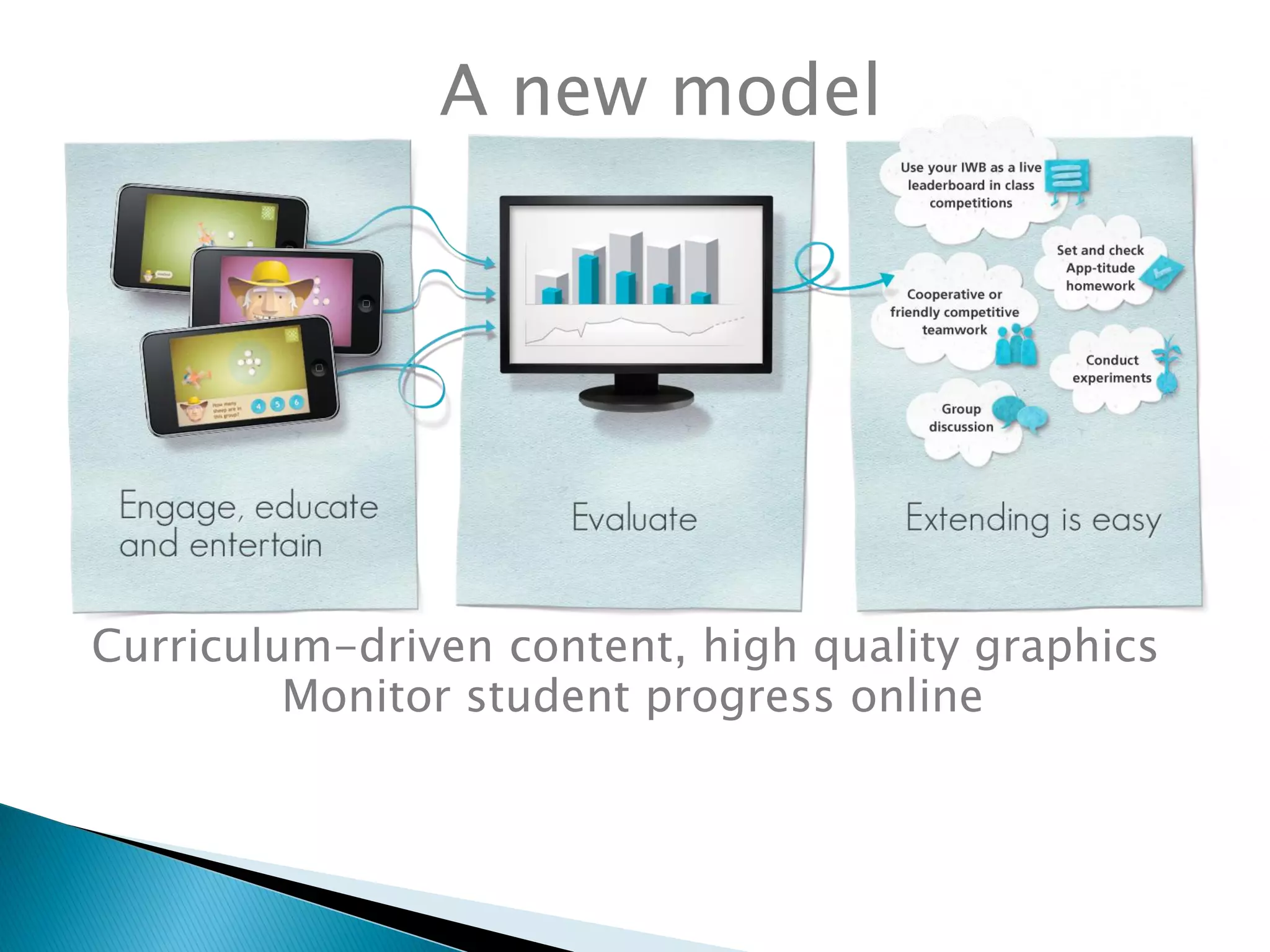
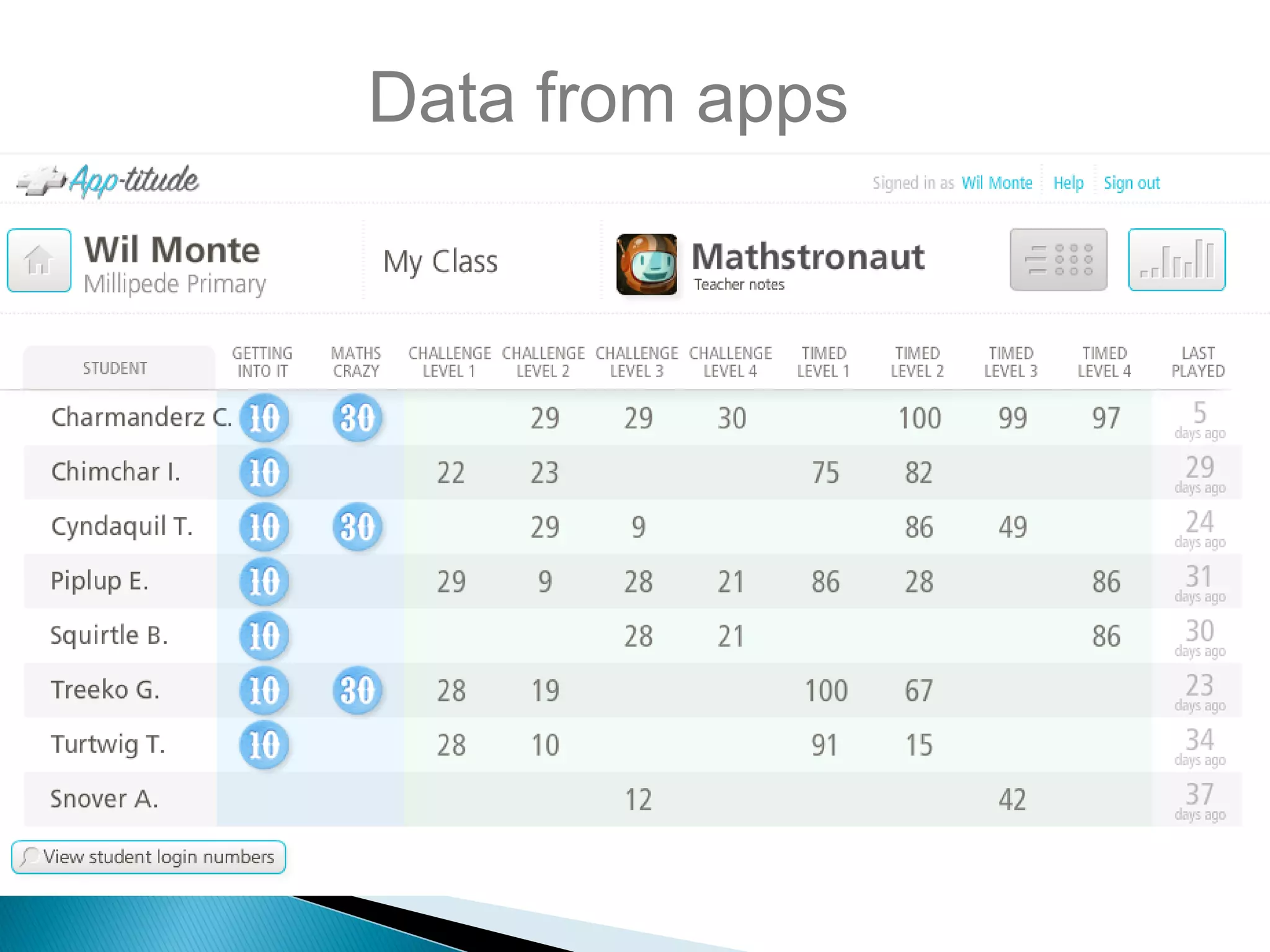
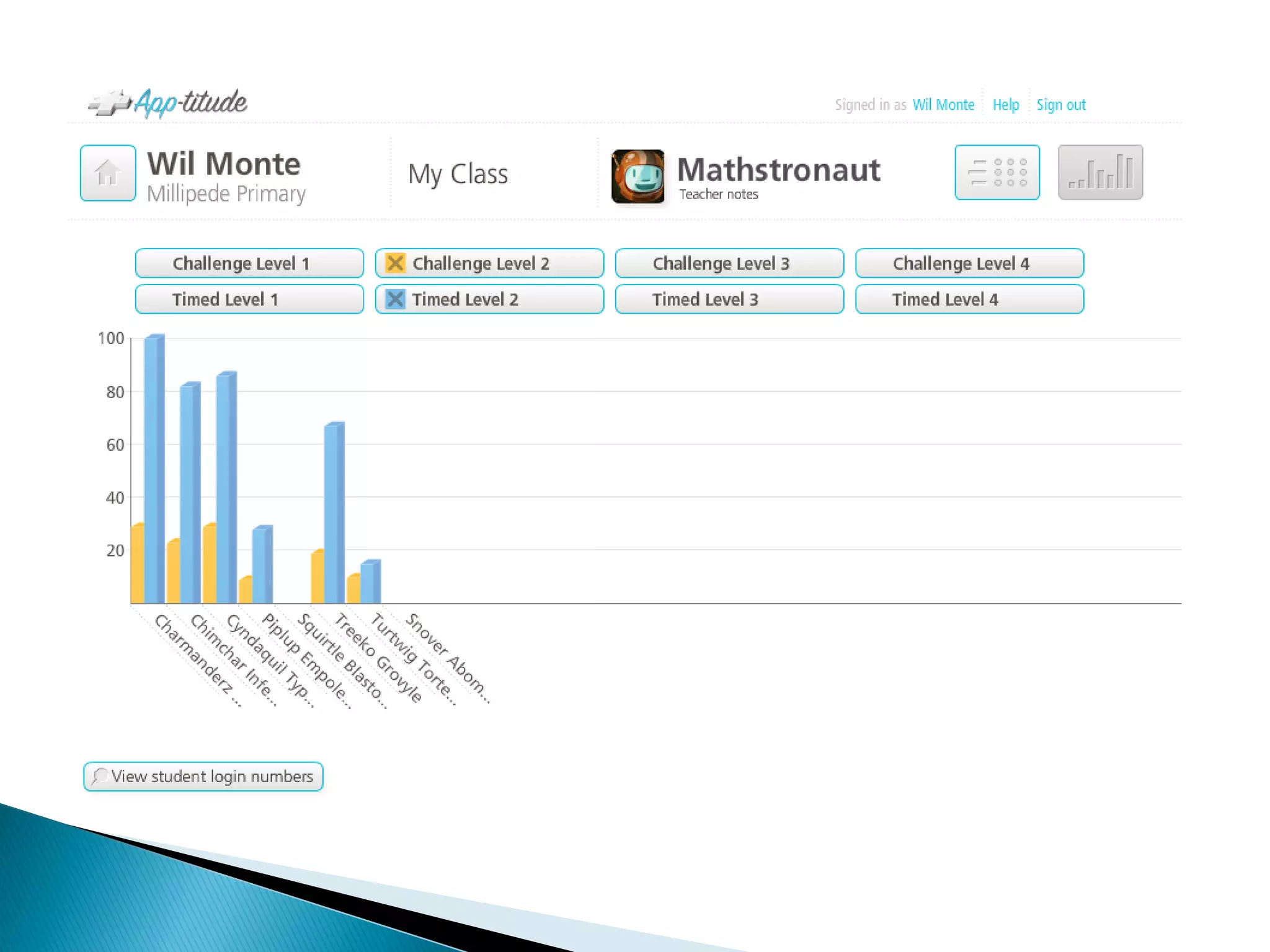
The document discusses mobile learning and educational apps. It provides research on the benefits of mobile learning, such as increased student engagement, motivation, and literacy. Mobile devices can enhance learning in core subjects and support collaboration. The document also shares examples of mobile learning projects and reviews of educational apps. It emphasizes that curriculum should drive the use of technology and provides tips for developing an effective implementation strategy for mobile devices in schools.