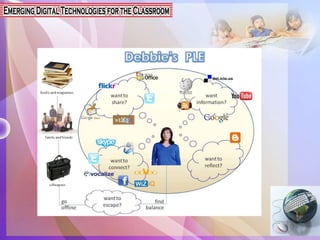
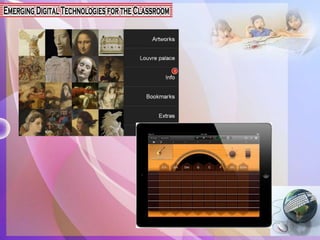
This document discusses emerging technologies that have the potential to transform learning, including mobile apps, tablet computing, game-based learning, personal learning environments, and natural user interfaces. It describes how these technologies engage students and better meet the needs of different learners. While technologies can be useful tools, quality instruction is still important. The document outlines several advantages of integrating technology, such as improved performance and productivity, but also notes disadvantages like potential loss of focus or not all students having access.